10. Pelvis and Gluteal Region Flashcards
Identify the following lower limb regions.

Blue: Anterior Thigh
Yellow: Medial Thigh
Green: Knee/Popliteal Fossa
Orange: Leg
Pink: Foot (dorsal and plantar)

What are the bones of the pelvis?
Hip bone, sacrum, coccyx
What do the bones of the pelvis form?
the pelvic inlet=pelvic brim (hip bone, sacrum, coccyx)
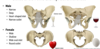
Identify the following parts of the pelvis and hip.

Blue: Hip bone
Green: Sacrum
Orange: Coccyx
Purple: Femur
anterior view circle: pelvic intlet
posterior view circle: pelvic outlet
What does the false pelvis hold?

False pelvis is above the inlet (true pelvis is in between inlet and outlet)
False pelvis holds the intestines.
What articulation is found when the two parts of the hip bones meet anteriorly?
Pubic symphysis
What are the three parts of the hip bones. Identify them.

Red: ischium
blue: pubis (thinner, smaller aspect)
rest: ilium
Identify all parts of the illium of the hip bone on the posterior aspect.


Identify all parts of the illium of the hip bone on the posterior aspect.


What does the acetbulum hold?
the acetabulum holds the head of the femur
What articulates with the auricular surface?
the auricular surface is where the sacrum articulates with the ilium
What does the arcuate line become?
The arcuate line becomes the pectineal line
Identify the various part of the ischium of the hip bone.


Identify all the parts of the pubis of the hip bone. (of the anterior view only)

the orange part that represents the hole is the obturator foramen

Identify all the posterior parts of the pubis of the hip bone.


What inserts onto our pubic tubercle?
rectus abdominis and inguinal ligaments
When is the pelvis properly aligned?
When the ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine) is lined up with the pubis tubercle (you have anterior and posterior tilt that allows you to bear weight on your femur)
What is the ischiopubis ramus formed of?
the ramus of the ischium and the inferior pubis ramus
What does the arrow point at?

sacral promontory
What are the four joints found in the pelvis?
lumbosacral joint
sacroiliac joint
sacrococcygeal joint
pubic symphisis
What joint is this? Which ligaments reinforce this joint?

JOINT: lumbosacral joint
Blue: anterior longitudinal ligament
green: iliolumbar ligament
What joint is this? Which ligaments reinforce this joint?

JOINT: sacroiliac joint (sacrum and ilium meet at the auricular surface)
orange: anterior sacroiliac ligament
purple: posterior sacroiliac ligament
pink: interosseus sacroiliac ligament (between 2 bones)

Identify the structure in pink and green.

pink: inguinal ligament (goes from ASIS to pubis tubercle): it is the tendon extension of the external oblique
green: obturator membrane
Identify the orange and purple ligaments. Where do they insert?

purple: sacrotuberous ligament (inserts onto ischial tuberosity)
orange: sacrospinous ligament (inserts onto ischial spine)