10. Metabolism and enzymes Flashcards
Anabolic and catabolic reactions in the cell are controlled in the presence of specific what?
Enzymes.
There are thousands of chemical reactions occurring constantly within all living cells. Together, these are a cell’s what?
Metabolism.
This varies from cell to cell, but it is important to remember that these are not random reactions; each one occurs specifically, at a certain location, speed, and time, to allow the cell to get the energy it needs to function and survive.
A chain of reactions is called a pathway, and each step of a pathway is controlled by a what?
Enzyme.
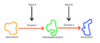
The first type of reaction is what?
Catabolic.
These are reactions that break down large molecules into smaller, simpler molecules.
An everyday example of a catabolic reaction is when starch breaks down into what?
Glucose. This is catabolic reaction.
In catabolic reactions, large molecules are broken down into smaller molecules.
When these reactions occur, a net amount of energy is released. This is called a what reaction?
Exergonic reaction (think ex = exit = out).
The other main type of reaction is called an anabolic reaction. This is where what?
Smaller molecules are brought together to build larger molecules.
An example of an anabolic reaction is what?
An example of this is forming proteins. Small amino acid molecules are bonded together to form larger proteins.
It takes energy to build these bonds, and these are called what reactions?
Endergonic reactions, as they absorb energy. A net amount of energy is then stored in these bonds, so the product has more energy than the reactants.
Energy is carried between reactions by what?
ATP molecules (adenosine triphosphate).
In any reaction, what type of energy required for the reaction to occur?
Activation energy.
What do enzymes do to the activation energy level required?
Enzymes lower the activation energy so that the reactions can happen much faster. They provide an alternative pathway, where the substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme.

Enzymes are large what type of molecule?
Globular protein molecules.
The long amino acid chains fold into a specific 3D shapes. This is described as what type of protein structure?
Tertiary.
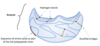
Enzymes are very specific. They will catalyse one or two very specific reactions.
This is because enzymes have an active site that is specific for the molecules in that reaction. The substance that the enzyme acts upon is called the what?
Substrate.
Biochemical processes are controlled and regulated by a series of specific enzymes. For example the reactions in glycolysis, which is the first reactions in respiration, requires a series of how many steps, each with its own specific enzyme?
Nine steps.
There are two main models of enzyme specificity.
The first is what?
The Lock and Key Model.
The enzyme has an active site which specifically fits the substrate, like a key fitting a lock. If the substrate doesn’t fit in the active site, then the reaction will not occur.

The second model of enzyme specificity is what, which is when the substrate interacts with the active site and alters its shape?
Induced Fit.
These changes ‘mould’ the active site to the substrate, and make the bonds between the substrate and the enzyme even stronger.
Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up the rate of reactions in living things.
They are made of what?
Proteins.
The amino acids continue to add to the growing polypeptide chain. The order of amino acids is determined by the code in a molecule called what?
Messenger RNA (mRNA).
The order of amino acids is called the primary structure of the protein.

The polypeptide chain then folds to form secondary structures which are held together by hydrogen bonds. The two main secondary structures are the what?
α−helix and the β−pleated sheet.
Fibrous proteins such as collagen and keratin only have primary and secondary structures. Enzymes are globular proteins and have tertiary structure.
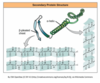
The secondary structure may then be folded to form a 3D shape, known as a globular protein. This is held together by various bonds including hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds and Van der Waals forces. This gives the protein a very specific shape, and this is very important for how enzymes function. In some proteins, several polypeptide chains may link together to form a protein.
This is known as what structure?
Quaternary structure.

Protein structure can be observed using techniques such as X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, however these methods are expensive and take considerable time. More commonly, protein structure is predicted based on the amino acid sequence, using what?
Computer modelling.
There are many things that can affect the activity of enzymes. Many of these are to do with the environment of the substrate and enzyme.
Two of these are what?
Temperature and pH.
Enzymes have an optimal temperature - this means at this temperature they will work at their fastest.
But, as a general rule, as enzymes get hotter, they work faster. This also works in reverse, as they get colder, they work slower.
However, enzymes also stop working when it gets too hot. This is called what?
Denaturing.
Because of how enzymes work, what 2 things can we do to food to make it last longer or safer to eat?
We can store our food in cold places to make it last longer. That’s why storing food in the fridge or freezer can make food safe to eat even if the food was bought some time ago.
Because excessive heat denatures proteins, we can make food safe from bad or dangerous proteins and enzymes by cooking our food before we eat it!
What happens when enzymes get too hot?
However, above the optimum temperature, the kinetic energy becomes too high, and the bonds that hold the 3D shape of the enzyme begin to break.
The enzyme starts to change shape, which means the active site is disrupted and the enzyme activity quickly starts to drop. This change of shape of the enzyme is called denaturation. This is irreversable.
Enzymes in the human body usually have an optimum temperature of what?
37oC.
The optimal pH (the pH where the enzyme works best) is different for different types of enzymes. Enzymes inside our bodies usually have an optimal pH of between what?
6−8, because that is the approximate pH of our bodies.
What happens if the pH gets too high or too low?
As the pH mores away from the optimal pH, either becoming more acidic (lower pH) or more basic (higher pH), the bonds start to become distrupted and the shape of the enzyme changes.
The enzyme is denatured.
Some enzymes need to be activated by other molecules or ions called what?
Cofactors.
These extra factors come in two classes; inorganic cofactors or coenzymes.
Inorganic cofactors are generally inorganic ions, whereas coenzymes are small, non-protein molecules, often used to carry substances to and from reactions. Coenzymes are particularly important in terms of what?
Metabolic pathways.
Inorganic cofactors are often metal ions such as what, which are needed for the enzyme to function?
Fe3+.
Coenzymes are organic molecules such as what?
NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
This is involved in electron transfer during several redox reactions in cells. Again the coenzyme is required to allow the enzyme to function.
The rate of reaction of enzymes can also be changed by what?
Inhibitors.
What are the 2 types of inhibitors?
Competitive and non-competitive inhibitors.
Competitive inhibitors also bind to the active site of the enzyme, instead of the substrate. A competitive inhibitor cannot be bound to the enzyme at the same time as the substrate (one or the other).
Non-competitive inhibitors bind elsewhere on the enzyme, at an allosteric site (a site that is not the active site). Binding here can still alter the shape of the enzyme, and hence its activity.
Enzymes are classified into six groups, based on the type of reaction they catalyse. What are they?

Amylases are a group of hydrolase enzymes which catalyse the breakdown of carbohydrates. In humans they are made in the salivary glands and the pancreas.
Salivary amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch into which disaccharide?
Maltose.
If you put some starchy food in your mouth, such as bread, and don’t swallow, you will notice that the food starts to taste sweeter. This is because the enzyme in your saliva is breaking down the starch molecules into sweet sugars.
You can test for the presence of starch with what?
Iodine solution.
This is a yellow-brown liquid, which turns a blue-black colour with starch.
Catalase is an oxidoreductase enzyme, which breaks down toxic hydrogen peroxide into what?
Water and oxygen.
The enzyme catalase is found in lysosomes, which are organelles. They are particularly common in which cells, which are important in breaking down toxins?
Liver.
Therefore samples of liver tissue can be used as a source of catalase. For example, you could cut liver up into different sized pieces and add to the same volume of hydrogen peroxide, then measure the rate of oxygen production. This would show how surface area affects the reaction. You could also test the effect of temperature or pH by varying the conditions of the reaction. Yeast is also a source of catalase.
Proteases are a group of hydrolase enzymes, which break down the peptide bonds in proteins, eventually forming what?
Amino acids.
An example is pepsin, which is a protease found in the stomach. It is produced as an inactive precursor called pepsinogen, which is activated by stomach acid to form the active enzyme, pepsin.
Pepsin is important in digestion, helping digest protein in your diet.
Lactase is also a hydrolase enzyme. It is used to digest which disaccharide?
Lactose sugar in milks into the monosaccharides glucose and galactose. It is used commercially to produce lactose free dairy products, such as lactose free milk.
Lactose → Glucose + Galactose


