Wk 11: Comparing Multiple Groups Flashcards
(28 cards)
What is a parmetric test?
T test is based on estimating parameters from the sample (e.g. sample mean).
What is a non-parametric test?
compares the ranks of values instead of the values themselves.
- Comparing ranks can be a more robust approach, just like the median is less affected by outliers than the mean.
- Ordinal data (e.g. survey results) should use nonparametric tests.
What is the Mann-Whitney U Test?
nonparametric version of the independent-samples T test

What does the Mann-Whitney U Test test?
whether two distributions are the same.
What is the null hypothesis in the Mann-Whitney U Test?
No difference between the means of two groups.
What are the assumptions in the Mann-Whitney U Test?
The two distributions have the same shape and scale. But it does not assume the two distribution to have the same location.
What can affect the Mann-Whitney U Test? What can be done?
Outliers affect the means. Can remove outliers and run Mann-Whitney U test again.
What is the intepretation of the Mann-Whitney U Test?
- sig.
- p>0.05
- p<0.05)?

- Sig. is P value.
- P >0.05 is insignificant, which supports null hypothesis.
- P <0.05 is significant, which supports “effect” hypothesis.
What is ANOVA?
uses F-tests to test the equality of means.
What are 4 “steps” in ANOVA?
- First, measure the total variability in the response.
- Second, look at the variability within each group.
- If the within-groups variability is less than the total variability, then it suggests that knowing which group a person belonged to has given some information about them.
- This reduction in variability is called the between-groups variability.
What does ANOVA stand for?
Analysis of Variance
What are 3 assumptions in ANOVA?
- Independent groups: Check study design
- Normal variability between groups: Check data, especially important for small samples.
- Equal variance between groups: Check Levene’s test, boxplots
What are _____ in F tests?
- null hypothesis
- F statistic
- P-value
- Null hypothesis: All groups have the same mean.
- F statistic measures how different the groups are, relative to their variability.
- P-value is the probability of getting an F statistic as observed if the null hypothesis is true..
What is R2?
- Total variability is the sum of squared standard deviation under the proposed model vs. under default explanation
- R2 tells you the percentage of variability that is due to the proposed model.

What is the interpretation of ANOVA?

- First, look at test of homogeneity of variance to check whether the two groups have equal variance.
- If P >0.05, then it supports null hypothesis (equal variance), so you can use ANOVA
- If P <0.05, the it does not support null hypothesis (unequal variance), so you need to use Welch’s ANOVA rather than normal ANOVA.
- Or you can transform the data using log to get equal variance.
- Second, look at ANOVA.
- Sum of squares is total variability.
- df is degrees of freedom (n-1).
- Mean square = sum of squares / df
- F distribution is the ratio of sample variance (mean square between groups / mean square within group)
- P >0.05 suggests insignificant difference between groups means.
What do you first look at in interpretation of ANOVA?
First, look at test of homogeneity of variance to check whether the two groups have equal variance.
- If P >0.05, then it supports null hypothesis (equal variance), so you can use ANOVA
- If P <0.05, the it does not support null hypothesis (unequal variance), so you need to use Welch’s ANOVA rather than normal ANOVA.
- Or you can transform the data using log to get equal variance.
What do you look at second in interpretation of ANOVA?
Second, look at ANOVA.
- Sum of squares is total variability.
- df is degrees of freedom (n-1).
- Mean square = sum of squares / df
- F distribution is the ratio of sample variance (mean square between groups / mean square within group)
- P >0.05 suggests insignificant difference between groups means
What are 2 things that this show (bars)?
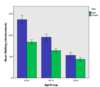
- Difference between bars (1st set of bars) suggests significant variability
- Similar bars (3rd set of bars) suggests no significant variability
What do these box plots show compared to bars?
Side by side boxplots show the variability even better.
What are 3 steps in the interpretation of the Wlech’s ANOVA?

- First, look at test of homogeneity of variance to check whether the two groups have equal variance.
- P <0.001 is very strong evidence of unequal variance, so you use Welch’s ANOVA
- Skip the ANOVA table because you cannot use it.
- Second, look at Welch’s ANOVA.
- P <0.001 is very strong evidence of difference in means between the groups.
What is normal variability? Why is it important? Small vs large sample?
- Checking normal variability is especially important for small samples.
- If the populations are non-normal, then the type 1 error rate might be inflated, where you will incorrectly reject the null hypothesis more frequently than you should.
- Address this by making threshold for evidence lower or increasing sample size.
- In larger samples, skews do not matter as much because it will approach normally distribution (central limit theorem).
What is a residual?
A residual is a prediction error, or in other words, the difference between the observed response and the response predicted by our model (e.g. mean response).
- e.g. One participant had a score of 9. The mean score is 5. So the residual is 9-5 = 4.
What are 2 reasons for using residuals?
- check assumptions
- estimate within-group variability
What does black line and blue bubbles mean?

- Black line = mean
- Blue bubbles = residual