WEEK 6: Crystalline Lens Flashcards
(24 cards)
Describe the location of the lens
Located in the posterior chamber of the eye, behind the Iris and in front of the vitreous chamber
What is the function of the crystalline lens?
- Provide 1/4 of the refractive power of the eye - accommodation (change the refractive power of the eye to see up close) 15 - 20D. Helps focus light onto the retina - filter of ultravioilet light and light with a wavelength of between 300 - 400 nm -wall between the anterior and posterior chamber, and make a seperated anterior and posterior structures of the eye. -
Implications of lens dysfunctions
- struggling with accommodation - Presbyopia -
Describe the structure and different layers of the lens
- Lens Capsule - Anterior epithelium - Lens Fibres Cortex, Adult nucleus, Foetal nucleus and embryonic nucleus
Explain epithelial cell differentiation and the process of lens fibre formation
Epithelial cell proliferation occurs in the germinative zone. Cells are cubiodal. Then they move to the transitional zone were they are on their way to becoming lens fibres, then they move pass the equator to elongate and become secondary lens fibre cells. Below the equator cells become columnar in shape and elongate anteriorly and posteriorly. Cells become arranged in meridional rows.
Where are primary cell fibres formed?
Embryogenesis
Understand the structures involved in accommodation
Ciliary muscles Radial fibres Zonules Crystalline lens Circular fibres
Understand and describe the process of accommodation
The ciliary muscles contract Circular fibres contract - moving the ciliary body forward and inward Releases tension on zonules lens become more spherical - increase in dioptric power which allows for clear near vision
What type of cataract is this?

Sclerosis Cataract - hardening and yellowing/browning (brunescene)
What type of cataract is this?

Cortical: usually wedge shaped opacities. Can also have visible striations (loss of structure) in cortex
What type of cataract is this?

Nuclear Sclerosis: hardening, clouding and yellowing (brunescene)
What type of cataract is this?
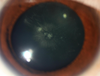
Sub-capsular: usually posterior
The crystalline lens provides:
about 1/2 the refractive power of the eye
about 3/4 of the refractive power of the eye
all the refractive power of the eye
about 1/4 the refractive power of the eye
about 1/4 the refractive power of the eye
Which of the following terms does NOT describe the human crystalline lens?
anterior surface follows an elliptical curve
biconvex
vascularised
transparent
vascularised
The youngest fibres in the human crystalline lens are located at:
the equator
the anterior pole
the embryonic nucelus
the fetal nucleus
the embryonic nucelus
The diameter of the crystalline lens does not change from birth to adulthood. true or false
false
A lens bow is located in the [A] of the human crystalline lens
crystalline lens cortex
cortex
lens cortex
The anterior Y suture is an erect Y.
True
False
False
The fibres in the crystalline lens behave as a:
gland
neuron
muscle
syncytium
syncytium
The refractive index of the crystalline lens ranges from:
- 21-1.40
- 41-1.60
- 38-1.41
- 8-1.0
1.38-1.41
What is the main purpose of catalase and glutathione peroxidase in the crystalline lens?
to counteract oxidative damage to the crystalline lens from circulating hydrogen peroxide in the aqueous humor
to provide rigidity to the crystalline lens fibre cell membranes
to facilitate relaxation of accommodation
to promote uptake of glucose by the crystalline lens for lens metabolism
to counteract oxidative damage to the crystalline lens from circulating hydrogen peroxide in the aqueous humor
Crystalline lens zonule are also known as:
suspensory ligaments
circular fibres
outer lens capsule
bundles
suspensory ligaments
When the lens is accommodating, the ____ of the ciliary muscle contract. When the lens is not accommodating, the ______ of the ciliary muscle contract.
circular fibres
radial fibres
Which type of cataract is normally associated with yellowing of the oldest fibres in the lens?
nuclear sclerosis


