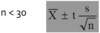Week 4 - Confidence Intervals Flashcards
(47 cards)
Most common CIs?
90%, 95% or 99%
(0% to 100% are possible, though not usually desirable)
Hypothesis testing involves generating an ____________ about the ___________ ____________.
hypothesis, population parameter
Confidence Interval (CI) estimate…
Range or interval of values for parameters with a level of confidence attached (95% confidence that the interval contains the parameter)
Why are confidence ‘intervals’ also called ‘confidence interval estimates’?
Because the method used to calculate confidence intervals is an estimation.
Why Confidence Interval Estimate vs. Point Estimate?
Generally, point estimates are not accurate enough to provide information about the parameter, or the variability within the parameter.
Estimation uses sample data to generate ________ in the population.
Parameters
Do the properties of CLT hold if the population is normally distributed and the population is > 30?
Yes
95% confidence interval means that
We are 95 % confident that interval contains mew
When Student’s t Distribution?
- Distribution not normal
- n < 30
What type of sample is used in confidence interval calculations?
Random sample is preferred.
Measurements of sample population are called _________.
Parameters.
What is Statistical Inference?
Process of reaching a conclusion about a population based on information from a sample of that population
What is mu1 - mu2?
Difference in means
In CI >= 30 formula, what are:
X bar,
Z,
s, and
n?
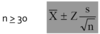
X bar = Point Estimate
Z = value from Z table
s = standard deviation
n = sample size
What is Sp?
Pooled Estimate of Common Standard Deviation
What is mud?
Mean difference
How do you calculate confidence interval?
CI = point estimate +- margin of error
Point Estimate = X bar
Margin of Error = (Z*(s/(square root of ‘n’)))
therefore,
CI = X bar +- (Z*(s/(square root of ‘n’)))
*Z or t value, based on sample size*
When do you use the CI estimation for mud?
- When you have a continuous outcome, and
- When you have two matched/paired samples,
- Unit of analysis is a pair
When do you use the CI estimation for mu?
- When you have a continuous outcome, and
- When you have a single sample, and
- When you want to estimate for the population mean for that sample.
Do the properties of CLT hold true if sample is < 30 and normally distributed?
Yes.
What is formula for CI for mud?
Xbard = Σ(x1 - x2)/n
In confidence interval estimates, _____________ gives the range of values above and below the ___________.
margin of error
point estimate
Can you use t distribution for large n?
Yes, because when n is large, t is approximately equal to standard normal distribution (Z).
The words ______ and ______ clues that we’re calculating Mean Difference.
before, after
pre, post