Week 3 The endocrine system I Flashcards
(25 cards)
What is the Endocrine System?
Complex organisms (both invert. & vertebrate spp.) require chemicals to communicate between cells
What are the chemicals which allow this communication & their properties?
neurotransmitters - signal between neurones
- very fast (milliseconds to seconds)
- transient (stop acting quickly)
- over relatively short distances (μm to mm)
hormones – signal between endocrine glands and target cells
- relatively slow (minutes to days)
- sustained
- over relatively long distances (cm to m)
Duration vs Speed in the Endocrine system:
Long distance regulatory system for “slow and sustained responses” (duration vs speed)
- Nervous system = speed
- Hormones = sustained action
Multiple ____ interact in the endocrine system
Multiple endocrine glands* interact in the endocrine system
What are the several distinct endocrine axes within the endocrine system?
- Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
- Hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis
- Hypothalamo-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis
- Growth hormone axis
What are the Endocrine Glands?
hormones - soley endocrine function

How are Endocrine Glands Classified?
-
Central (primary) endocrine glands
- Hypothalamus (secretes tropic hormones; regulates endocrine function of anterior pituitary gland)
- Pituitary gland (anterior and posterior lobes)
- Pineal gland (melatonin)
- Peripheral (secondary) endocrine glands e.g. gonads, adrenal, thyroid, pancreas etc.

What are the Functions of the Endocrine System?
- Regulate homeostasis (nutrient metabolism, electrolyte and water balance)
- Adaptation to stress
- Supports smooth, sequential growth & development
- Controls reproduction
- Regulates erythrocyte production
- Controls and integrates activities of circulatory, digestive and nervous systems
What is a Hormone?
“Long distance chemical mediator secreted by an endocrine gland into the blood, which transports it to its target cell” (Sherwood, 2016)
May be secreted from neurones - neurohormones / neuropeptides e.g. oxytocin & vasopressin
Distance of action is variable:
- Autocrine actions (ECF)
- Paracrine actions (ECF, blood or lymph)
- Endocrine actions (blood)
How are Hormones Classified?
Hydrophilic
- Peptide hormones (e.g. insulin or oxytocin)
- Biogenic amines
- Catecholamines (derived from Tyr e.g. adrenaline [epinephrine])
- Indoleamines (derived from Trp e.g. melatonin)
Hydrophobic
- Biogenic amines
- Thyroid hormones (iodinated tyr derivatives)
- Steroid hormones derived from cholesterol (e.g. cortisol, estradiol, progesterone and testosterone)
What are Peptide Hormones?
- Encoded by genes – transcribed and translated in endocrine cells
- Peptides can undergo post-translational modifications – form complex protein and glycoprotein hormones
- Packaged in vesicles – secreted by exocytosis

What are Catecholamines?
- Comprised of catechol group (C6H4(OH)2) (derived from Tyr) plus a side chain a.a.
- Adrenaline (epinephrine) secreted from adrenal medulla – mediates acute stress
- Neurotransmitters = noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and dopamine

What are Indoleamines?
- Comprised of indole group (C8H7N) (derived from Trp) plus a side chain a.a.
- Only hormone = melatonin (secreted by pineal gland – mediates circadian rhythm)
- Neurotransmitter = serotonin (secreted by neurones – maintain mood)

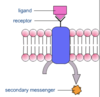
How do Hydrophilic Hormones Act?
Hydrophilic hormones (peptide hormones, catecholamines and indoleamines)
- Transmembrane receptor
- Commonly leads to generation of a second messenger
- Activates (protein) kinase enzymes
- Alters activity of existing proteins (conformational change)
- Rapid actions (minutes)
What are Thyroid Hormones?
- Biogenic amines – iodinated derivatives of Tyrosyl residues in thyroglobulin
- Thyroxine (tetraiodothyronine = T4) and triiodothyronine (= T3) secreted from thyroid gland
- Act via intracellular / nuclear receptor – increase BMR

What are Steroid Hormones & their families?
Derived from cholesterol (C27)
Two families:
-
Corticosteroids – synthesised in adrenal cortex
- Glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol) (C21)
- Mineralocorticoids (e.g. aldosterone) (C21)
- Adrenal Androgens (e.g. DHEA) (C19)
-
Gonadal steroids – synthesised in ovary, testis and placenta
- Progestogens (e.g. progesterone) (C21)
- Androgens (e.g. testosterone) (C19)
- Estrogens (e.g. estradiol) (C18)
How do Hydrophobic Hormones Act?
Hydrophobic hormones (thyroid & steroid hormones)
- Intracellular (nuclear) receptors
- Ligand-dependent transcription factors
- Regulate gene expression (activation / upregulation or repression by modifying histone acetylation)
- New proteins transcribed and translated in target cell
- Can be structural proteins or functional proteins (e.g. metabolic enzymes)
- Slow actions (hours/days)

Homeostasis relies on what negative feedback loops?
Homeostasis relies on negative feedback loops:
- Direct feedback loops (only true example = ANP)
- First order feedback loops (neural or neurohormonal)
- Second order feedback loops (neural & endocrine)
• Third order feedback loops (neural & endocrine)
In vertebrate taxa, most endocrine axes operate on second or third order feedback loops
How is Hormone Secretion Regulated (Direct and First-order feedback loops)?
Direct feedback loops–> can only be regulated at 1 control point
First-order feedback loops–> can only be regulated at 1 control point

How is Hormone Secretion Regulated (Second-order and Thrid-order feedback loops)?
Second-order feedback loops –> can only be regulated at 2 control point
Third-order feedback loops –> can only be regulated at 3 control point

What is the role of Role for Neuroendocrine Reflexes?
Rapid increase in hormone secretion due to neural reflex – accelerates endocrine loop
- E.g.1 ANS (sympathetic) control of catecholamine secretion from adrenal medulla for “fight or flight” response (norepinephrine and epinephrine increase heart rate, metabolic rate etc.)
- E.g.2 Fergusson reflex from vagina to hypothalamus to accelerate OT secretion at parturition (stimulates myometrial contractions)
- E.g.3 Suckling reflex from mammary gland to hypothalamus to accelerate OT secretion
What is the Role for Diurnal / Circadian Rhythms?
- Rhythmic variation in hormone secretion at different times of day / year
-
Entrained by external cues (e.g. photoperiod via melatonin)
- E.g. Circadian rhythym in plasma concentration of cortisol

What are Tropic Hormones?
- Affect synthesis and/or secretion of another (downstream) hormone
- Stimulate and maintain endocrine target tissue (can cause gland growth: “tropic” vs “trophic”)
-
Most (not all) hormones secreted by hypothalamus are tropic;
- e.g. TRH stimulates TSH synthesis and secretion
- All hormones secreted by anterior pituitary gland exert tropic actions on downstream glands; e.g. TSH stimulates thyroid gland; ACTH stimulates adrenal cortex; gonadotropins (LH & FSH) stimulate gonads

Negative feedback loops of Tropic Hormones:



