Week 3: Dermatology Flashcards
(58 cards)
What are the eight characteristics that the FNP should describe of every skin lesion?
Number
Size
Color
Shape
Texture
Primary lesion
Location (specific landmarks)
Configuration (describing patterns)
What are examples of primary lesions?
Erosions Ulcers Nodules Ecchymosis Petechiae Palpable purpura
Flat lesion
can’t palpate with eyes closed
Macule
flat and < 1 cm
Patch
flat and > 1 cm
Raised lesion
palpate with eyes closed
Papule
raised, < 1 cm, not fluid filled
Plaque
raised, > 1cm, not fluid filled
What are some terms used to refer to the shape of a lesion?
Circular
Oval
Annular: ring-like with central clearing
Nummular: coin like, no central clearing
Polygonal
What are some terms used to refer to the texture of a lesion?
Smooth Fleshy Verrucous / warty Scaly Fine and dry (Tinea pedis) Hard and keratotic (Actinic keratoses) Greasy (Seborrheic dermatitis)
What characteristics would you expect of actinic keratoses? What conditions mimic actinic keratoses?
Hard and keratotic
- mimics superficial xerosis or seborrheic dermatitis

What characteristics would you expect of basal cell carcinoma (BCC)? What conditions mimic BCC?
pinky patch that doesn’t heal, possible focal scaling
mimics actinic keratosis and SCC in situ

What exam findings are concerning for malignant melanoma?
A - assymmetry
B - irregular border, esp notching
C- color, esp colors black, blue and red
D- diameter >6mm
E- evolving
E - elevated
F- firm
Growing
What are the characteristics of a spider angioma?
Fiery red, very small to 2cm
Central body, sometimes raised, surrounded by erythema and radiating legs
Pressure on body causes blanching of the spider
Face, neck, arms, upper trunk
Almost never below waist
normal/common on face and chest
Also seen in pregnancy and liver disease

What are the characteristics of a spider vein?
Blueish
Size variable; small to several inches
Shape: variable, spider, linear, irregular, cascading
pulsatility and effect: absent; pressure over center DOESN’T blanch but diffuse pressure blanches the veins

What are the characteristics of a cherry angioma?
Bright ruby read, purplish with age
1-3mm
Shape: round, flat, sometimes raised, may be surrounded by pale halo
Pulsatility and effect of pressure:
Absent, partial blanching, esp if pressure applied with edge of pinpoint
Location: trunk, extremities
Sig: none, increases in size and #’s w/ aging
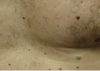
What are some examples of sun damage? How do they present?
Solar lentigo: bilateral symmetric brown macules located on sun exposed skin, face, shoulders, arms, hands
Solar elastosis: Yellowish white macules or papule in sun exposed areas, foreheads
Actinic purpura: ecchymoses only on dorsal forearms and hands but NOT extending above “shirt sleeve” line on upper arm
Poikiloderma: red patches in sun damaged areas, esp V neck, with fine telangiectasis and both hyper and hypopigmentation
Wrinkles: increased sun damage and tanning lead to deeper wrinkles at earlier age
Cutis rhomboidalis nuchae: deeper wrinkles on posterior neck that “criss cross)

What are some abnormal nail findings?
- paronychia: staph aures/strep; superficial infection of lateral nail folds; red swollen, tender
- clubbing: vasodilation w/ inc blood flow, hypoxia, CHD, interstitial lung disease, lung cancer, IBD, malignancies
- Habit tic deformity: depression on central nail; “christmas tree” ; repetitive trauma from rubbing index finger over thumb
- melanonychia: increased pigmentation in nail matrix; streaks; normal ethnic variation
- onycholysis: painless separation of opaque nail bed from pink nail bed; trauma, psoriasis, fungal infection, allergic reactions to nail cosmetics
- onychomycosis: nail thickening and debris; from tinea pedis, fungal
- terry nails: white nail plate with ground glass; liver disease, cirrhosis, HF, diabetes
- transverse linear depressions (beau lines): temp disruption of proximal nail growth from systemic illness; severe illness, trauma, raynaud’s disease
- pitting: punctuate depressions of nail plate by defective layering of superficial nail plate; psoriasis

Skin findings of someone with chronic renal disease?
pallor
xerosis
uremic frost (crystallized urea)
pruritus
half & half nails
calciphylaxis (Ca accumulates in small blood vessels of fat and skin tissues)
blood clots, painful skin ulcers, infxns
skin findings of somone with crohn’s disease?
- Erythema nodosum
- Pyoderma gangrenosum
- Enterocutaneous fistulas
- Aphthous ulcers
skin findings of somone with Cushing disease?
Striae
Atrophy
Purpura
Ecchymoses
Telangiectasis
Acne
Moon facies
Buffalo hump
Hypertrichosis
skin findings of someone with diabetes
Pruritus
Diabetic dermopathy
Acanthosis nigricans
Candidiasis
Neuropathic ulcers
Necrobiosis lipoidica
Eruptive xanthomas
skin findings of Dyslipidemias
Xanthomas (tendon, eruptive, tuberous; Lesions on skin with cholesterol and fat)
Xanthelasma






















