Week 3 Flashcards
Hypothalamus and Pituitary (49 cards)
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
-Works to regulate homeostasis -It is the relay station between the nervous and endocrine system -Controls the sex drive and sexual behaviours -Controls emotions and behaviour patterns -Controls the sleep-awake cycle
What hormones are produced by the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus will synthesise and produce hormones for the posterior pituitary which are ADH (also known as Vasopressin) and Oxytocin. For the anterior pituitary it will produce the tropic hormones TRH, CRH, GnRH, and GHRH
What are the actions of ADH?
It has two main functions. -It causes water re-absorption in the nephrons in the kidney. -Can cause smooth muscle contraction and vasoconstriction which raises the blood pressure
What are the actions of oxytocin?
-It will stimulate milk ejection by contracting the myoepithelial cells in the mammary gland -Can cause the uterus to contract during child birth -Can cause sexual arousal and produce nurturing feelings
Describe negative feedback.
This is where the end product of a process will reduce the stimuli for the same process. Effectively reducing the production of the end product
Describe positive feedback
This is where the end product of a process will increase the stimuli for the same process.
What is another names for the anterior and posterior pituitary?
Anterior - adrenohypophysis Posterior - neurohypophysis
What are the two types of neurons that mediate the endocrine function in the hypothalamus?
Magnocellular Parvocellular
What are the two magnocellular neurons?
The paraventricular and the supraoptic
What is the location of the pituitary?
It is inferior to the hypothalamus and lies in a depression in the base of the skull called the sella turica
What is the embryonic origin of the anterior and posterior pituitary and relate to their function.
Posterior pituitary: From the hypothalamus or more specifically the 3rd ventricle of the cerebrum. As it is from neural origin it is a neural endocrine gland. Anterior pituitary: from cells of the roof of the embryonic oral cavity, more specifically Rathke’s pouch. It is from a vascularised place and thus is an endocrine organ.
Where do the neurons of the anterior pituitary release their hormones?
They release them into the median eminence
What are the two classes of hypothalamus regulatory hormones?
-Releasing hormones which will stimulate the secretion of one or more hormones -Inhibiting hormones which prevent the synthesis and secretion of hormones
What is the name of the blood supply in the anterior pituitary?
The hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal vessels
Describe the blood supply to the anterior pituitary
The superior hypophyseal artery which supplies the primary capillary plexus. This then leads into the long hypophyseal portal veins to the secondary capillary plexus before the hormones are released into a vein
What is the term used to describe the hormones that are released into the median eminence?
Hypophyseotropic hormones
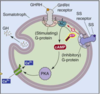
What is the action of TRH?
Stimulates secretion of TSH by thyrotropes
What is the action of GnRH?
Stimulates the secretion of FSH and LH by gonadotropes
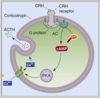
What is the action of CRH?
Stimulates secretion of ACTH by corticotropes
What is the action of GHRH?
Stimulates the secretion of GH by somatotropes
What is the action of GHIH? (also known as somatostatin)
Inhibits the secretion of growth hormones by somatotropes
What is the action of PIH?
Inhibits the synthesis and secretion of prolactin by lactotropes
What types of hormones is CRH? (protein, peptide, catecholamine, etc.)
Peptide
What type of hormones is TRH? (protein, peptide, catecholamine, etc.)
Peptide