Week 2 OMK Objectives Flashcards
(41 cards)
List the three types of fuel found in the diet
Carbohydrates, proteins and fats
Identify healthy common sources of individual macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fiber)
Carbs: fruit, grains, legumes, veggies
Proteins: legumes, meat (chix, beef, pork)
Fats: nuts, fruit, dairy
Fiber: fruit, leafy greens, grains
Using the US Dietary Guidelines and MyPlate, select the general characteristics of a healthy diet, including the recommended contribution of various food groups and foods to be consumed in limited amounts
healthy diet includes fruit, vegetables, protein and grains and dairy. vegetables and grains should each take up over ¼ of the plate, and fruit and protein should each take up less than ¼ of your plate.
What are the recommended portion sizes for children, men and women for fruit, vegitibles, grains, protein, dairy, and oils?
Fruit: Children need ~2-3 cups, Women and Men need ~2 cups
Veggies: Children need ~1.5 cups, Women and Men need ~2-3 cups
Grains: Children need ~3-4 oz, Women and Men need ~3-4 cups
Protein: Children need ~5-6 oz, Women and Men need ~5-6 oz
Dairy: Children need ~3 cups, Women and Men need ~3 cups
Oils: Children need ~5 tsp, Women and Men need ~5-7 tsp
Describe MyPlate, explain how it could be used as a nutrition assessment tool, and give functional definitions of portion size in each category of the plate
MyPlate is an online resource that is aimed to promote American health and reduce overweight and obese persons by educating people about healthy food options. It emphasizes fruit, grains, vegetables, dairy foods, and proteins. It provides tools and resources to help people to develop healthy diets and track their individual diets and physical exercise.
Define Define Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
The average daily dietary intake level that is sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97-98%) the individuals in a life stage and gender group.
Define Adequate Intake (AI)
If sufficient scientific evidence is not available to calculate an EAR or RDA an AL is set. It is estimates of nutrient intake by a group of apparently healthy people that are assumed to be adequate.
Define Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)
The highest average daily nutrient intake level that is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects to almost all individuals in the general population.
Define Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
The average daily nutrient intake level estimated to meet the requirement of one half of the healthy individuals in a particular life stage and gender group.
what are the recommended Dietary Guidelines for Carbohydrates, fat, and protein

List the kcal/g for each of the macronutrients

Outline the relationship between food intake and energy output
The production of heat in the body increases as much as 30% above resting level during digestion and adsorption of food. Over 24 hrs, this may amount to 5-10% of total energy expenditure.
Differentiate between moderate and vigorous activity

Explain how varying levels of physical activity influence an individual’s nutritional requirements.
A sedentary person requires about 30-50% more calories than their RMR, however a highly active individual may require 100% more calories above their RMR.
Discuss the oxidation or synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins and fat in the red blood cell, adipose tissue, liver, brain and muscle during the fed state and after an overnight fast
RBC: The erythrocyte performs anaerobic glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway for energy at all times (no mitochondria).
Adipose: In the fed state, insulin controls the absorption of glucose from various sources into adipose tissue. Triacylglycerides are synthesized and stored as fuel reserves. In the fasting state, triacylglycerols are degraded by hydrolysis, providing glycerol and fatty acids to the liver.
Liver: During the fed state, the liver stores glycogen, replenished proteins, and synthesizes triacylglycerols (fat), stored as Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL). In the fasting state, the liver degrades glycogen and performs gluconeogenesis. Oxidation of fatty acids supplies energy for gluconeogenesis, and acetylCoA for ketone body synthesis.
Brain: In the fed state, the brain uses glucose exclusively as a fuel source. In the fasting state, the brain can use either glucose or ketone bodies as fuel.
Muscle: In the fed state, muscle uses glucose as fuel, and increases protein synthesis to perform repairs. In the fasting state, the muscle can use fatty acids or ketone bodies from the liver as fuel. Protein in the muscle is degraded, and the resulting amino acids are used by the liver for gluconeogenesis.
Predict the ratio of glucagon/insulin in the fasting and fed states
Fasting: Glucagon ↑: Insulin ↓
Fed: Glucagon ↓: Insulin ↑
During the fed state, the high levels of insulin that are released act to promote storage of metabolic fuel, while the high levels of glucagon in the fasting state lead to promotion of breakdown of fuel stores which leads to, among other things, increase in blood sugar.
Describe the general structure and function of G protein-coupled membrane receptors and identify the general characteristics of second messenger systems associated these receptors
G protein coupled membrane receptor systems are tripartite:
1) A cell surface receptor
2) A G protein on the cytoplasmic face of the phosplipid membrane
3) An effector element (typically an enzyme or ion channel).
The surface receptor binds a ligand. This binding activates the G protein (often by replacing GDP with GTP), and the active G protein alters the activity of the effector element. This effector element changes the concentration of a second messenger within the cell. G protein coupled receptor systems often function to enact signal amplification, as the G protein can remain active for much longer than the time the ligand is bound to a receptor. The receptor itself (GPCR) is usually a seven-pass transmembrane protein (i.e. loops through the PM seven times).
Note: Glucagon activates a GPCR to perform its functions such as breakdown of liver glycogen, stimulation of gluconeogenesis, and stimulation of lipolysis (and then ketone body synthesis).
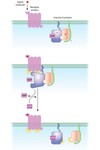
Illustrate the general functions of receptor tyrosine kinases and receptor-associated tyrosine kinases
Receptor tyrosine kinases regulate various processes in the cell. A signal molecule binds to the receptor, which causes dimerization of receptor molecules. The dimer’s cytoplasmic domains have tyrosine kinases, which phosphorylate one another and become “active.” These active domains phosphorylate the tyrosine residues on various signaling proteins in the cell. This means a single RTK can modulate several different biochemical processes.
Note: Insulin is a signal molecule that activates a single class of RTK to cause “increased uptake of glucose and amino acids and to regulate metabolism of glycogen and triglycerides in the cell.”
Describe the function, dietary sources, requirement, assessment, deficiency and toxicity for the water soluble vitamin thiamin.
Thiamin (aka B1)
Function: Required for carbohydrate metabolism; Prevents beri-beri disease
Sources: Whole and enriched grains, pork, wheat germ
Requirement: Adult Males: 1.2 mg/day; Females 1 mg/day
Assessment: Erythrocyte Transketolase Assay or High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) measurement of blood Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
Deficiency: Beri-beri (leg edema, heart failure, mental dementia, GI problems, muscle wasting) or Wernicke-Korsakoff (brain damage, disorientation)
Toxicity: Essentially nontoxic
Describe the function, dietary sources, requirement, assessment, deficiency and toxicity for the water soluble vitamin niacin
Niacin
FUNCTION: Important in metabolizing proteins as coenzyme
SOURCE: Liver, meats, whole & enriched grains, nuts and legumes; tryptophan is a precursor
REQUIREMENT: M: 16 mg/day, F: 14 mg/day
ASSESSMENT: Urinary secretion of N1-methylnicotinamide
DEFICIENCY: Pellagrea (dementia, diarrhea, dermatitis, death)
TOXICITY: Large amounts may lead to flushing; “Higher doses of niacin (3000 mg/day) reduce LDL cholesterol 15 to 20% but may cause jaundice, abdominal discomfort, blurred vision, worsening of hyperglycemia, and precipitation of preexisting gout.” (Merck)
Describe the function, dietary sources, requirement, assessment, deficiency and toxicity for the water soluble vitamin **riboflavin **
Riboflavin
FUNCTION: Helps conversion of carbs, fats, proteins into energy
SOURCE: Milk (& milk products), organ meats, eggs, leafy green veg, whole & enriched grains
REQUIREMENT: M: 1.3 mg/day; F: 1 mg/day
ASSESSMENT: Urinary excretion; erythrocyte riboflavin; Glutathione reductase activity
DEFICIENCY: Cheliosis (inflammation and fissuring at corners of the mouth, scaling of lip skin) or stomatitis (general inflammation of the mouth, incl gums, tongue, lips, palate); Magenta-colored tongue
TOXICITY: Essentially nontoxic
Describe the function, dietary sources, requirement, assessment, deficiency and toxicity for the water soluble vitamin pantothenic acid
Pantothenic acid
FUNCTION: Part of coenzyme A, which is essential for metabolism of carbs and fatty acids, and synthesis of sterols
SOURCE: Organ meats, beef, egg yolks
REQUIREMENT: M&F: 5 mg/day
ASSESSMENT: Blood levels
DEFICIENCY: Rare
TOXICITY: Essentially nontoxic
Describe the function, dietary sources, requirement, assessment, deficiency and toxicity for the water soluble vitamin biotin
Biotin
FUNCTION: Important in metabolism of carbohydrates & fats
SOURCE: Organ meats, eggs, milk, fish, nuts
REQUIREMENT: M&F: 25 mg/day
ASSESSMENT: Reduced urinary excretion of biotin; increased urinary excretion of 3-hydroxisovaleric acid
DEFICIENCY: Alopecia, bowel inflammation
TOXICITY: Essentially nontoxic
Identify the factors that should be considered when determining a person’s caloric needs
Basal Metabolic rate: The energy needed by the body for basic functions
Dietary-induced Thermogenesis The energy the body needs to digest food, transport and absorb nutrients.
The thermic effect of activity: Most variable—based on physical activity of individual. Sedentary people thermic effect of activity could only total 15 percent of daily total energy expenditure; while athletes percentages may exceed 80%.


