Week 2 Flashcards
How long can sperm survive in the female genital tract?
How long do ovum survive in the female genital tract?
5 days
17-24 hours
How does cervical position vary during fertility?
More fertile - cervix is high in the vagina, soft and open
Less fertile - cervix is low in vagina, firm and closed
In a ‘regular’ 28 day menstrual cycle, which days are considered to be the most fertile?
8-18
What are the 3 criteria for lactational amenorrhoea?
How effective is this as a contraceptive?
1) exclusively breast feeding
2) less than 6 months post natal
3) amenorrhoeic
98% effective (woman will still ovulate after delivery, hence why not 100%)
What is the mode of action of the combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP)?
Primarily inhibits ovulation through negative feedback on pituitary via oestrogen and progestogen
Also has an effect on cervical mucus and the endometrium
What kind of contraception is desogestrel?
How does it work?
Newer progesterone-only pill (POP)
Inhibits ovulation (NB - older POPs don’t inhibit ovulation!)
Also has effects on cervical mucus, fallopian tube transport and endometrial thickness
How long does the contraceptive implant last for?
What is its mechanism of action and how effective is it?
Up to 3 years
Main mode of action is inhibition of ovulation (and again, has effects on endometrium and cervical mucus)
Failure rate is 0.05% - very effective as it doesn’t rely on patient compliance
How long does the depo injection last for?
What is its mechanism of action and how effective is it?
Depo injection is repeated every 13 weeks, but lasts 14 weeks
Primarily inhibits ovulation
Failure rate is 0.2%
What are the 3 doses of IntraUterine System (IUS) currently available?
What is their mechanism of action and how effective are they?
Mirena - 52mg
Kyleena - 19.5mg
Jaydess - 13.5mg
Releases a small amount of hormone daily and mainly causes contraception through affecting implantation (renders the endometrium unfavourable)
High frequency pulses of GnRH result in release of ____
Low frequency pulses of GnRH result in the release of ____
High frequency pulses = LH release
Low frequency pulses = FSH release
What is the mode of action for the intrauterine device (IUD)
How long is it licensed for and what is the failure rate?
Primary mode of action is prevention of fertilisation - causes an inflammatory response in the endometrium and is toxic to both the sperm and the egg
Licensed for 5/10 years
What is the most effective form of contraception, based on % of women experiencing pregnancy in their first year of use?
Progesterone only implant (0.05%)
Before providing contraception, what examinations are done by the clinician?
Depends on the contraceptive being given
BP and BMI are recorded (a lot of options increase weight due to affecting appetite)
Check smear status if relevant
PV to check uterine size/position if required for IUD fit
What forms of contraception may be quick-started (started immediately and not waiting until next period) and which should not be?
Possible to Quick start
- Some CHCs
- POP
- Implant
- (Depo)
Avoid
- IUD (may cause miscarriage)
- Pills containing cyproterone acetate
When is emergency contraceptive required?
When contraception hasn’t been used/used correctly
Before new contraceptive method has had a chance to become effective
If more than one COC has been missed
If patch/ring has been off/out for more than 48 hours
If an implant has been fitted out with the first 5 days of cycle, and unprotected sexual intercourse has happened within the first 7 days of use
Up to 5 days after UPSI or within 5 days of predicted ovulation
What methods of emergency contraception are currently available?
Which is most effective?
Intrauterine
- copper IUD - TEN TIMES MORE EFFECTIVE than oral alternatives
Oral
- LNG-EC - up to 72 hours post UPSI (96 hours off license)
- UPA-EC - up to 120 hours post UPSI
Why can the copper IUD be used at emergency contraceptive up to 5 days post UPSI, or after 5 days after likely ovulation?
Because pregnancy doesn’t implant during the first 5 days post-fertilisation. Most happen at days 8-10, but earliest is 6
How does oral emergency contraceptive work?
LNG-EC - high dose progestogen (works before LH surge)
UPA-EC - anti-progestogen (works until after start of LH surge)
Both DELAY ovulation but neither are abortifactant and NEITHER work after ovulation

Under what circumstances should someone avoid UPA-EC?
If they are wishing to quick-start a hormonal contraceptive
They must delay their ongoing contraception for 5 days
If hormonal contraception has been used in the past 7 days
If the patient has acute severe asthma that is uncontrolled by oral steroids
Other than contraception, what are some of the other benefits of using hormonal contraception
Manage heavy menstrual bleeding
Managing painful periods
Managing irregular periods
Managing premenstrual symptoms
Endometriosis (oral contraptive helps to manage symptoms and prevent progression)
PCOS
Managing menstrual migraine
Acne, mood, hirsutism
Protection from certain cancers - endometrial, ovarian
Prevention of osteoporosis
What forms of combined hormonal contraceptive are there?
Combined oral contraceptive pill
Combined transdermal patch
Combined vaginal ring
What is the efficacy like for combined hormonal contraceptive?
How does weight affect this?
If perfect compliance - 0.3% failure rate
Typical compliance rate - 9% failure rate (people forget to take pill!)
The transdermal patch may have a possible decrease in efficacy in patients over 90kg
How should the combined oral contraceptive pill be taken?
Start in first 5 days of regular menstruation OR at any time in cycle when reasonably sure not pregnant, plus condoms for 7 days (“belt and braces”)
Take daily for 21 days followed by a 7 day break (during which there will be a period-like bleed) then start a new pack
By what mechanism might the combined hormonal contraceptive be thrombogenic?
Alteration in antithrombin III and Protein S, affecting the body’s natural coagulation defences
What are the main risks of taking the combined hormonal contraceptive?
Venous thrombosis - increased risk
Arterial thrombosis - increased risk
Adverse effect on some cancers due to hormonal action e.g. breast cancer, cervical cancer (both reduce back to baseline risk after 10 years of stopping CHC)
What risk factors propagate the risk for VTE in women taking the combined hormonal contraceptive?
Obesity
Smoking
Increased age
Known thrombophilia
Family history
Up to 6 weeks postnatal
Long haul flights/reduced mobility
APLS
When would the combined hormonal contraceptive be contraindicated?
In patients with a personal history or genetic family history (i.e. BRCA) of breast cancer
Which cancers is the combined hormonal contraceptive protective against? Which is it a risk factor for developing?
Protective - endometrial, ovarian
Risk - breast, cervical
…RCGP study showed a 12% reduction in all-cause mortality and no overall increase in cancer risk
What common skin condition is the combined hormonal contraceptive effective in treating?
Acne
How should Progestogen only methods of contraception be started/taken?
Day 1-5 of period
OR
Anytime if reasonably certain not pregnant plus condoms for 7 days (2 for POP). Again, belt and braces…
When can an IUS/copper IUD be inserted?
IUS - anytime in cycle if no unprotected sex (UPSI) in the past 3 weeks or since last menstrual period
Cu-IUD - as above, plus as emergency contraception
What 3 documents need to be completed in Scotland when performing an abortion?
- HSA1: two doctors are required to sign
- HSA2: to be completed by the doctor within 24 hours of an emergency abortion
- HSA4: must be completed by the doctor and sent to the Chief Medical Officer within 7 days of the abortion taking place
When performing an abortion in a woman under the age of 16, what framework is used to assess competence?
Gillick competence
(NB - Fraser guidelines are only concerned with contraception and focus on the desirability of parental involvement and the risks of unprotected sex in that area)
What are some of the important points to remember regarding a doctor’s right to conscientiously object?
Respect a patient’s point of views and avoid discrimination
Must not impose views on others but may explain their own views if invited
Ensure patient’s treatment is not delayed or denied
Treatment in the event of an emergency may not be denied
What are the gestational limits for termination of pregnancy, both in Tayside and the UK?
Tayside
- 18 weeks and 6 days
- Surgical termination up to 12 weeks
- Medical termination up to 18 weeks and 6 days
Legal limit for UK
- For social termination of pregnancy - 23 weeks and 6 days
- For foetal anomaly - any gestation
How is a medical Termination of Pregnancy performed?
How does this vary depending on length of gestation?
1) Oral Mifepristone 200mg (anti-progesterone)
2) 24-48 hours later - vaginal (or oral) prostaglandin e.g. misoprostol, gemeprost
If Early in pregnancy (e.g. <9 weeks) - option to complete part 2) at home
If Late/Mid-trimester - repeated doses of prostaglandin every 3 hours (maximum of 5 in 24 hours)
If this fails, move on to surgical evacuation
What are the 3 categories of time period in which an abortion may be performed?
Early (<9 weeks)
Late (9-12 weeks)
Mid-trimester (12-24 weeks)
How is a surgical termination of pregnancy performed?
What time period can each method be done?
Vacuum aspiration - 6-12 weeks (risk of failure if done sooner)
Dilatation and evacuation - 13-24 weeks (not available in Scotland)
When performing a surgical Termination of Pregnancy, what is given to ‘prime’ the cervix and minimise damage?
Vaginal prostaglandin is given
How is vacuum aspiration performed?
After vaginal prostaglandin is given, patient is taken in as a day case and put under GA. Routine USS is not required.
After the procedure is done, patient is fitted with a Long Acting Reversible Contraceptive (LARC) e.g. implant or IUD
Pregnancy test is done 2-3 weeks later to confirm if successful
What are some of the effects that HIV has on the immune system?
Sequestration of cells in lymphoid tissues >reduced circulating CD4+ cells
Reduced proliferation of CD4+ cells
Reduction in activation of CD8+ cells
Reduction in antibody class switching > reduced affinity of antibodies that are produced
Chronic immune activation
This all increases susceptibility to viral infections, fungal infections, mycobacterial infections and infection-induced cancers
What are the functions of CD4+ T helper cells?
Essential for the induction of the adaptive immune response. Done by…
- recognition of MHC2 APCs
- activation of B cells
- activation of cytotoxic T cells
- release of cytokines
What are the normal parameters for CD4+ T cells and at what point does the risk of opportunistic infections become noticeable?
Normal range - 500-1600 cells/mm3
Risk of opportunistic infections at <200 cells/mm3
At what points in HIV infection is rapid replication of virus seen?
After exposure, by when is infection established?
Very early (primary infection) and very late in infection (symptoms of AIDS)
Infection is established by day 3

What are the 3 phases of HIV infection, and what is the typical presentation at each phase?
Primary Infection (80% symptomatic, 2-4 weeks) - very high risk of transmission
- fever
- rash (maculopapular)
- myalgia
- pharyngitis
- headaches/asceptic meningitis
Asymptomatic Infection (can take years)
- ongoing viral replication and depletion of CD4+ count
- also ongoing immune activation
Symptoms of AIDS
- increase of opportunistic infections rises considerably
What are some of the opportunistic infections someone with HIV is at risk of?
BONUS: What are the treatments for these infections?
Pneumocystis pneumonia - high dose co-trimoxazole +/- steroid
Tuberculosis - 2 RIPE 4 RI
Cerebral toxoplasmosis - pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine and calcium folinate
CMV - ganciclovir
How does being underweight affect a woman’s fertility?
Reduced fertility
Underweight women are more than twice as likely to take more than a year to get pregnant
How does being overweight affect a woman’s fertility?
Reduced fertility
Have less chance of getting pregnant overall
More likely to take more than a year to get pregnant
Up to 3 times more likely to suffer oligo/anovulation
Impairs endometrial development and implantation
Associated with PCOS
What supplementation is recommended for all women trying to conceive?
How long should they be taking this for and at what dose?
400 micrograms Folic Acid pre-conception and throughout the first trimester
OR
5mg Folic Acid if the woman is obese, diabetic, on antiepileptics or there is a history of babies with neural tube defects
10 micrograms Vitamin D through pregnancy and continue afterwards if breastfeeding
(possibly Iron supplementation as well - shouldn’t be offered routinely as it doesn’t benefit the mother’s or baby’s health and may have unpleasant side effects)
What are the maternal and fetal risks of not taking Vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy?
Maternal risks - osteomalacia, pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, C section, bacterial vaginosis
Fetal risks - small for gestational age, neonatal hypocalcaemia, asthma/respiratory infection, rickets
Which groups of pregnant women are at the highest risk of iron deficiency?
How does iron deficiency affect pregnancy?
At risk - young first pregnancy, repeated pregnancies, multiple pregnancies
Iron deficiency increases the risk of stillbirth
Should Vitamin A supplementation be given in pregnancy?
What caution should be taken if so?
Should only be given in cystic fibrosis patients as they are lacking in Vitamin A
High doses of Vitamin A are teratogenic
Who is the Healthy Start Scheme (UK) available to and what does it contain?
Available to expecting mothers under 18 and those receiving benefits
Includes 70mg Vitamin C, 10 micrograms Vitamin D and 400 micrograms Folic Acid
What foods should be avoided in pregnancy and why?
Soft cheese, undercooked meat, cure meats, game, tuna, raw/partially cooked eggs, pate, liver and vitamin and fish oil supplements should all be avoided
They should be avoided because pregnant women are at greater risk of food-derived infections, mainly Listeria and Salmonella
How do the demands of lactation compare with pre-pregnancy demands (last two trimesters) in terms of calorie requirement?
Lactation calorie demands exceed prepregnancy demands by approx. 640 kcal/day
This is compared with 300 kcal/day during the last two trimesters of pregnancy
This deficit is usually covered by fat stores acquired during pregnancy, however if the woman was underweight she will then require more calories
What are the risks of obesity to the mother and the fetus?
Mother - diabetes, hypertension, thrombosis, infection
Fetus - macrosomia, NICU admission, still birth, neonatal death
What is the most common bacterial STD in the UK?
How is it transmitted and which age range shows the highest incidence?
Chlamydia
Transmission is vaginal, oral or anal
Highest incidence is in the 20-24 age range
What bacterial STD is associated with pelvic inflammatory disease in women?
What % of women develop this? What is the risk of PID?
Chlamydia is associated with PID in women
% of women w/ Chlamydia that develop PID is estimated at 9%
An episode of PID increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy ten-fold, and carries a tubal factor infertility of 15-20%
If symptoms of Chlamydia infection appear in a woman, how might she present clinically?
Post-coital or intermenstrual bleeding
Lower abdominal pain
Dyspareunia
Mucopurulent cervicitis
If symptoms of Chlamydia infection appear in a man, how might he present clinically?
Urethral discharge
Dysuria
Urethritis
Epididymo-orchitis
Proctitis
What are some of the complications of a Chlamydial infection?
PID (CT accounts for 50% of all cases)
Tubal damage in women - infertility and ectopic pregnancy
Chronic pelvic pain
Transmission to neonate if pregnant - 17% develop conjunctivitis, 20% develop pneumonia
Adult conjunctivitis
Reiter’s Syndrome (reactive arthritis, can’t see can’t pee can’t bend the knee), more common in men
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome (perihepatitis), occurs almost exclusively in women as a complication of PID
What is lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)? How does it present?
Serovars L1-L3 of Chlamydia trachomatis
Diagnosed mostly in MSM
Presents with rectal pain, discharge and bleeding, and there is a high risk of there being concurrent STIs (67% have HIV)
How is Chlamydia diagnosed and treated?
Females - NAAT (using a vulvovaginal swab)
Males - first void urine and add rectal swab if history of receptive anal sex
Treatment - Doxycycline 100mg BD for 1 week, PLUS Azithromycin 1G stat followed by 500mg daily for 2 days (NB - azithromycin no longer given, just doxy now due to the downstream effects of azithromycin)
Why was the treatment for Chlamydia trachomatis updated?
Updated to include Azithromycin due to the emerging STD Mycoplasma genitalium - exhibits high levels of macrolide resistance (JUST GIVE DOXYCYLINE! DON’T ANGER DR MOOKA!)
Associated with non-gonococcal urethritis and PID
Prevalence estimated at 1-2% of the ppn, asymptomatic carriage
Diagnosed with NAAT
What is the morphology of Gonorrhoea?
Gram negative, intracellular, diplococcus (looks like 2 kidney beans)
Describe the incubation period of Gonorrhoea
Are men or women more likely to transmit the infection?
Incubation of urethral infection in men is usually short (2-5 days)
Men are more likely to transmit the infection (50-90% risk of male to female vs 20% risk of female to male)
How might Gonorrhoea present clinically in males?
Asymptomatic in up to 10%
>80% present with urethral discharge
Dysuria
Pharyngeal/rectal infections, mostly asymptomatic
How might Gonorrhoea present clinically in females?
Asymptomatic (up to 50%)
Increased/altered vaginal discharge (40%)
Dysuria
Pelvic pain
Pharyngeal and rectal infections are also usually asymptomatic
Complications of Gonorrhoea infection is more likely in women than in men (3% vs 1%). What are some of the complications that could develop?
Bartholinitis
Tysonitis
Periurethral and rectal abscesses
Epididymitis
Urethral stricture
Endometritis
PID
Infertility
Ectopic pregnancy
Prostatitis
How is potential Gonorrhoea infection investigated?
NAATs (screening test) used in both symptomatic and asymptomatic cases with >96% sensitivity
Microscopy if symptomatic (urethral sensitivity 90-95%, endocervical 37-50%)
Culture if microscopy is +ve (more sensitive in male)
How is Gonorrhoea treated?
What has to be done following treatment?
First line is IM Ceftriaxone 500mg
Second line is Cefixime orally, 400mg (only done if IM Ceftriaxone is contraindicated or refused by patient)
Also have to do a test of cure following treatment
What is the incubation period and duration of a primary infection of genital herpes?
Incubation period - 3-6 days
Duration - 14-21 days
How might the primary infection of genital herpes present clinically?
Blistering and ulceration of the external genitalia
Pain
Dysuria
Vaginal or urethral discharge
Local lymphadenopathy
Fever and myalgia
What subtype of the herpes simplex virus is most likely to present with recurrent episodes?
What is it often mistaken for?
HSV-2 is more likely to present with recurrent episodes
Often overlooked/misdiagnosed as thrush
Recurrent episodes are usually unilateral, small blisters and ulcers, and minimal systemic symptoms. Episode typically resolves within 5-7 days
How is genital herpes diagnosed and managed?
Swab the base of the ulcer and send for HSV PCR
Give oral antivirals (Aciclovir 400mg TDS for 5-7 days)
Consider topical lidocaine 5% ointment if particularly painful
Can also recommend saline bathing and analgesia
Which subtype of HSV displays a greater degree of viral shedding?
When is this most common?
HSV-2 viral shedding is consistently higher
More frequent in the first year of infection and seen more in individuals with frequent recurrences
Which HPV subtypes are associated with the following presentations?
- anogenital warts
- palmar and plantar warts
- cellular dysplasia/intraepithelial neoplasia
Anogenital warts - HPV 6 and 11
Palmar and Plantar warts - HPV 1 and 2
Cellular dysplasia/intraepithelial neoplasia - HPV 16 and 18
What is the most common viral STI in the UK?
HPV - lifetime risk of acquiring infection is 80%
What is the incubation period of HPV?
How detectable is the infection?
3 weeks - 9 months (advise people that they may have had it for years before they go blaming their partners!)
Subclinical disease is common on all anogenital sites
If 80% of the ppn are exposed, approx. 10% of these will harbour detectable infection with only 1% developing anogenital warts
What are the potential outcomes of anogenital warts?
20-34% will resolve spontaneously
60% will clear following treatment
20% will persist despite treatment
Which subtypes of HPV are the cause of >90% of anogenital warts?
How are they treated?
HPV 6 and 11
Can use…
- Podophyllotoxin (topical and cytotoxic. Quick effect but not licensed for extra genital warts)
- Imiquimod (immune modifier and can be used on all anogenital warts. Better in IC/IS patients)
- Cryotherapy (cytolytic, can require repeated treatments)
- Electrocautery
- Vaccination
What bacterial species causes syphilis?
How might it be acquired?
Treponema pallidum
Transmitted through…
- sexual contact
- trans-placental/during birth
- blood transfusions
- non-sexual contact e.g. healthcare workers
What stages of syphilis infection are infectious and non-infectious?
What is the incubation period?
Infectious - primary, secondary, early latent
Non-infectious - late latent, tertiary
Incubation period is 9-90 days (mean of 21)
How does primary syphilis present?
Painless ulcer at the site of innoculation (chancre)
Site is usually genital (90%) but can also be extra-genital (10%)
Also presents with non-tender local lymphadenopathy
How does secondary syphilis present?
Skin - macular, follicular or pustular rash on the palms and soles)
Lesions of the mucous membranes
Generalised lymphadenopathy
Patchy alopecia
Condulomata lata - MOST HIGHLY INFECTIOUS LESION IN SYPHILIS, oozes a serum containing +++ treponemes
How is syphilis diagnosed?
Demonstration of treponema
- PCR
Serological testing - detecting antibody to pathogenic treponemes
- Non-treponemal
- VDRL (venereal disease research laboratory)
- RPR
- Treponemal
- TPPA (treponema pallidum particle agglutination)
- ELISA/EIA (screening test)
- INNO-LIA
- FTA abs
How is a) early syphilis and b) late syphilis treated?
a) Early - 2.4 MU Benzathine penicillin x1
b) Late - 2.4 MU Benzathine penicillin x3
What is Gillick competence?
What are the Fraser guidelines?
Gillick competence - concerned with determining a child’s capacity to consent
Fraser guidelines - refers specifically to consent for contraceptive treatment and sexual health matters
Which of the following are NOT STIs?
- Genital warts
- Vaginal thrush
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Herpes
Vaginal Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis are NOT STIs
What is the name of the space that lies inferior to the levator ani?
What is contained in this space in the woman?
The perineum
Contains the inferior part of the vagina, the perineal muscles, Bartholin’s glands, clitoris and labia
How can fluid collection in the pouch of Douglas be sampled?
Drained via a needle being passed through the posterior fornix of the vagina
What are the two main ligaments of the uterus?
Describe both briefly
Broad Ligament (wings)
- double layer of peritoneum
- extends between uterus and the lateral walls&floor of the pelvis
- helps to maintain the uterus in the correct midline position
- contains the uterine tubes and the proximal part of the round ligament
Round Ligament (tubes)
- embryological remnant
- attaches to the lateral aspect of the uterus
- passes through the deep inguinal ring to attach to the superficial tissue of the female perineum
- contained (proximally) within the broad ligament
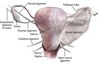
The round ligament is/is not a formation of the peritoneum.
What is this structure in the male?
Round ligament is NOT a formation of the peritoneum
The round ligament is a remnant of the gubernaculum and in the male is the spermatic cord)
What are the 3 surfaces/components of the broad ligament?
Mesometrium
Mesovarium (surrounding the ovary)
Mesosalpinx (surrounding the uterine tube)

Externally to internally, what are the 3 layers of the body of the uterus?
What part of the conception process occurs in the body of the uterus?
Perimetrium
Myometrium
Endometrium
Implantation occurs in the body of the uterus (anywhere else is an ectopic!)
What 3 layers of support are provided to the uterus to hold it in position?
What condition could result if any of these layers is damaged?
Numerous strong ligaments (e.g. the uterosacral ligaments)
Endopelvic fascia
Muscles of the pelvic floor (e.g. levator ani)
Weakness in any of these structures could result in uterine prolapse
Regarding the axes of the vagina, cervix and uterus, what is the most common position seen clinically?
Anteverted - cervix is tipped anteriorly relative to the axis of the vagina
Anteflexed - uterus is tipped anteriorly relative to the axis of the cervix
This results in the mass of the uterus lying over the bladder
What area must be sampled by the clinician during a cervical smear test?
The squamo-columnar junction (transition zone)
Brush is inserted into the external cervical os with firm pressure and then rotated
Where does fertilisation occur?
Where does implantation occur?
Fertilisation - ampulla of the fallopian tube
Implantation - body of the uterus
What is a bilateral salpingo-oophrectomy?
Removal of both uterine tubes and ovaries
How can you tell if there is an ectopic pregnancy within the fallopian tubes using a hysterosalpingogram (HSG)?
Normally, the radiopaque dye used in an HSG would spill out of the end of the uterine tube and into the peritoneal cavity, suggesting that the tube is patent
In an ectopic pregnancy contained within the fallopian tube, this dye would be blocked
What hormones are secreted by the ovaries in response to LH and FSH?
Oestrogen and progesterone
When performing a vaginal digital examination, what structures are felt for?
Ischial spines at 4 and 8 oclock laterally
Position of the uterus e.g. anteverted or retroverted
Adnexae (appendages) - uterine tubes and ovaries. Place examining fingers into lateral fornix, press deeply with the other hand into the iliac fossa of the same side. Can detect large masses or tenderness in these structures
What are the two triangles that make up the perineum? What make the points of these triangles?
Urogenital triangle
Anal triangle
Anteriorly, the pubic symphisis
Posteriorly, the coccyx
Laterally, the two ischial spines
What structures pass through the pelvic floor?
Distal parts of alimentary, renal and reproductive tracts from pelvis to perineum
Which nerve supplies the levator ani? What are its spinal roots?
Is this muscle skeletal or smooth?
Levator ani is a skeletal muscle (under voluntary control)
Supplied by the nerve to levator ani
Roots are S3, 4, 5
What are the 3 parts that make up the levator ani muscle?
Iliococcygeus
Pubococcygeus
Puborectalis
What nerve supplies the perineal muscles?
Where do all these muscles attach?
Supplied by the pudendal nerve
All attach at a bundle of collagenous and elastic tissue called the perineal body - important in pelvic floor strength and can be disrupted during labour
What structure can be cut to aid in delivery?
The perineal body - done more in the US, in the UK the musculature tends to be cut instead as collagenous material doesn’t heal as well, meaning pelvic floor weakness may develop

What structure in the female is the homologue to the bulbourethral gland in the male, and may potentially become enlarged due to infection?
Bartholin’s gland
What ribs does the female breast span?
2-6
Breast tissue lies on deep fascia covering which muscles?
Pectoralis minor and Serratus anterior
NB - breast tissue and muscle are NOT in direct contact
What is the name of the space that lies between the fascia and the breast?
What structures firmly attach the breast to the skin?
The retromammary space lies between the fascia and the breast
Firmly attached to skin via Cooper’s suspensory ligaments
How do the Level I, Level II and Level III axillary lymph nodes relate to pectoralis minor, respectively?
Level I - inferior and lateral to pec minor
Level II - deep to pec minor
Level III - superior and medial to pec minor

What is the blood supply to the female breast?
Arterial - Axillary and internal thoracic (internal mammary) arteries, both of which are branches of the subclavian artery
Venous - intercostal veins (means that cancers may pass to the thoracic spine)

From what point can amniocentesis be performed?
What test needs to be done for fetal screening prior to this?
Not before 16 weeks
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) can be performed this
When is a booking scan performed?
When is the next, more detailed scan performed?
Booking scan is booked at 12 weeks
Next more detailed scan is then at 20 weeks
When in a pregnancy can the following be detected via scan?
- cardiac anomalies
- microcephaly
- short limbs
- brain malformations
Cardiac - 12-20 weeks
Microcephaly - typically after 22 weeks
Short limbs - typically after 22 weeks
Brain malformations - between 18 and 21 weeks
Typically, all pregnant women are offered at least 2 US scans throughout their pregnancy. When are these performed?
What can also be screened for at the first scan?
1st scan (dating scan) - at 8 to 14 weeks
2nd scan (anomalies scan) - at 18 to 21 weeks
At the same time as the dating scan, a nuchal translucency (NT) scan can be included to screen for Down’s Syndrome
From what point can CVS testing be done in a pregnancy?
At 11.5+ weeks
From what point can amniocentesis testing be done in a pregnancy?
At 16+ weeks
How does free fetal DNA in maternal serum help with diagnosis of certain conditions e.g. Duchenne MD?
Patient pregnant 8 weeks w/ FHx of Duchenne MD
8 weeks sexing of fetus using free fetal DNA
If a girl, no need to worry
If a boy, proceed to more invasive testing


