Week 1 - Introduction Flashcards
(50 cards)
Body Regions - Anterior

1 - Head
2 - Neck
3 - Thorax
4 - Abdomen
5 - Pelvis
Limb Regions - Anterior

1 - Shoulder
2 - Arm (brachium)
3 - Cubital Fossa
4 - Forearm (antebrachium)
5 - Wrist
6 - Hand
7 - Groin
Body Regions - Posterior

6 - Back
7 - Gluteal Region
Limb Regions - Posterior

8 - Hip
9 - Thigh
10 - Popliteal fossa
11 - Leg (crus)
12 - Ankle
13 - Foot
Supine
Prone
Lying face Up
Lying face Down
Superficial
Deep
Closer to body surface
Farther from surface
Superior
Inferior
Closer to head
Closer to Feet
Proximal
Distal
Closer to heart
Farther from heart
Medial
Lateral
Closer to midline
Farther from midline
Sagittal Plane
divides body into left/right sections
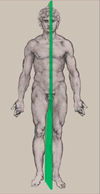
Coronal Plane
divides body into anterior/posterior sections

Axial Plane
divides body into superior/inferior sections; by convention, viewed from inferiorly (used in CT/MRI)

Leg Connective Tissue

1 - Dermis (inner skin layer)
2 - Subcutaneous fat
3 - Bone
4 - Deep fascia
5 - Tendons
6 - Adventitia (outer layer of blood vessels)
7 - connective tissue surrounding nervous
Leg Muscle Groups

1 - Deep fascia
2 - Fascial Septa
3 - Periosteum
4 - Tendons
Axial Bones - Anterior

1 - Skull
2 - Mandible
3 - Teeth
4 - Sternum
5 - Ribs (12)
Axial Bones - Posterior

6 - Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7)
7 - Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12)
8 - Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L5)
9 - Sacrum
10 - Coccyx
Appendicular Bones - Posterior

8 - Ilium
9 - Pubis
10 - Ischium
11 - Femur
12 - Tibia
13 - Fibula
14 - Tarsals
15 - Metatarsals, Phalanges
Appendicular Bones - Anterior

1 - Clavicle
2 - Scapula
3 - Humerus
4 - Radius
5 - Ulna
6 - Carpals
7 - Metacarpals, Phalanges
Axial Joints - Anterior

1 - Temporomandibular
2 - Laryngeal
3 - Chondrosternal
4- Costochondral
Axial Joints - Posterior

6 - Atlanto-occipital
7 - Costovertebral, Costotransverse
8 - Lumbosacral
Appendicular Joints - Anterior

1 - Pubic symphysis
2 - Sternoclavicular
3 - Acromioclavicular
4 - Glenohumeral
5 - Elbow
6 - Radioulnar
7 - Radiocarpal
Appendicular Joints - Posterior

8 - Sacroiliac
9 - Hip
10 - Knee
11 - Talocrural
12 - Pubic symphysis (cartilaginous)
Dorsiflexion
Dorsal/superior surface moves closer to anterior surface of leg

Plantarflexion
plantar (volar, inferior) surface moves closer to posterior surface of leg



















