W3 SS values and ANOVA Flashcards
(18 cards)
What is the d value and what is it’s formula?
Measures the size of the effect.
Cohen’s d is an effect size used to indicate the standardised difference between two means.
d = 1 means a difference of 1 SD (on average)
Or
d = t sqrt(1/n₁ + 1/n₂)

If there is dependancy What is the d value formula?
The mean if the differences is then divided by the sqrt of sum(current diff - diff’s mean)^2 / N-1

What does R² mean and tell us?
The amount of variance in the outcome (Y) explained by the model. a.k.a the coefficient of determination
What values do we need to calculate the R²?
- Total Sum of Squares: SST
- Residual Sum of Squares: SSR
- Model Sum of Squares: SSM
What is the Total sum of squares, and how do we calculate it?
It’s the difference between what we observed and the mean of our observations.
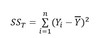
What is the Residual (Error) sum of squares, and it’s formula?
The difference between the observed data and the our predictions
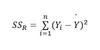
What is the Model sum of squares and what’s it’s formula?
The difference between the mean of our observations and our predictions…
The improvement in prediction by going from the mean to the line of best fit.
SST-SSR
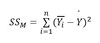
What is the formula for R²?
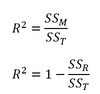
What values does the one-factor (between subject) ANOVA give us?
ANOVA gives us an F-value and a p-value.
- F value can be converted to t-value, if two levels
What does the F value tell us?
- The higher the value of what I can explain, the higher the value of F, for a given value of what I cannot explain
- The higher the value of what I cannot explain, the lower the value of F, for a given value of what I can explain
- If I know as much as I don’t know, F = 1
- Interpretation is easy, e.g., F = 3 => model can explain 3x more than it cannot explain

What is the Grand Mean
- The mean of the means
- The mean for all observations, across groups

What is the Total Variation and what’s the formula?
It’s represented by the sum of the squares of the differences of each mean with the grand mean.
Includes the between group variation and the within group variation.
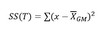
What is the whole idea behind analysis of variance?
The whole idea behind the analysis of variance is to compare the ratio of between group variance to within group variance.
The variation due to the interaction between the samples is denoted SS(B) for Sum of Squares Between groups.
How do you calculate SSB?
(Sum of Squares Between groups)
- For each subject, compute the difference between its group mean and the grand mean. The grand mean is the mean of all N scores (just sum all scores and divide by the total sample size N)
- Square all these differences
- Sum the squared differences
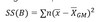
How do you calculate SSW? What is it?
(Sum of Squares Within groups)
- For each subject, compute the difference between its score and its group mean. You thus have to compute each of the group means, and compute the difference between each of the scores and the group mean to which that score belongs
- Square all these differences
- Sum the squared differences

What is the MSB and how do you calculate it?
It’s the variance due to the interaction between the samples.
MS(B) is calculated from the sample means (compared to MSE, which is calculated from sample variances). To find MS(B), divide the between group variation (SSbetween) divided by between group degrees of freedom (k-1).
Degrees of freedom equal the number of values in a data set minus 1

Why should we look at the adjusted R-squared value when we conduct a multiple regression?
Adjusted R-squared is a more conservative estimate of R-squared that takes into account the fact that we have added multiple predictors to our model.
What is the MS(W), Mean Square Within groups, and how do you calculate it?
“df” is the total degrees of freedom. To calculate this, subtract the number of groups from the overall number of individuals.
Since each sample has degrees of freedom equal to one less than their sample sizes, and there are k samples, the total df is k less than the total sample size: df = N - k



