Vitals Flashcards
What to measure for vitals (6):
- temperature - heart rate - blood pressure - respiratory rate - oxygen saturation - pain
vital signs provide quantitative measures of the status of the ___________ system and reflect the function of ________.
- cardiovascular/pulmonary - internal organs
Vitals can be used to establish (5):
- baseline measurement - prognosis - appropriate level of exercise - treatment effectiveness - need for further work up or referral
5 factors that affect vitals:
- level or amount of physical activity - environmental temperature - age - emotional status - physiological status
Observation: Things to watch for:
- facial expression - general appearance - any signs of distress
Body Temperature sites: ____, _____, _____, _____, ____ equipment: ______, _____ normal:
Body Temperature sites: oral, rectal, axillary, temporal, ear equipment: electronic (oral, temporal, ear), mercury normal: body - 96.8-99.3, rectal - 97.8-100.3
What can affect temperature? (8)
- time of day - age - environment - activity - emotions - site taken - infection - menstrual cycle - using different methods for measurement
Temperature deviations (3):
- fever >98.6 - pyrexic > 100.0 - hyperpyrexic > 106.0
______ creates palpable pressure in arteries
diastole
normal ranges: - adult - newborn - child
adult: 60-100 bpm newborn: 100-150 bpm child: 70-130 bpm
HR deviations (5):
regular, irregular, thready, tachy, bradycardia
HR locations (5):
- radial - brachial - femoral - carotid - temporal
- pulse decreases with activity - pulse doesn’t increase with activity - pulse rate doesn’t plateau - pulse doesn’t decline with decrease in activity - pulse declines with activity increasing - pulse rate increase is not proportional to activity - irregular pulse
Abnormal pulse responses and action
measures oxygen saturation in the blood
pulse oximetry
What can affect oxygen saturation?
altitude and temperature
low circulation oxygen levels
hypoxemia
low oxygen in the tissues despite adequate perfusion
hypoxia
reflection of cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, hemodynamic factors
blood pressure
BP: systole
left ventricle contraction
BP: Diastole
relaxation/filling left ventricle-resistance in aorta during ventricular relaxation
BP cautions: (3)
- avoid contraction of UE muscles during measurement - appropriate size - repeating measurement too soon
the average pressure that occurs during a single cardiac cycle (diastole and systole)
Mean Arterial Pressure MAP
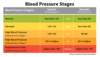
there are _#_ stages of HTN
4
prehypertension =
120-139/80-9
Stages of HTN: stage I stage II stage III stage IV
stage I: 140-159/90-99 stage II: 160-179/100-109 stage III: 180-209/110-119 stage IV: >210/>120
respiratory rate adult: infant: deviations:
adult: 12-18 resp/min infant: 30-50 resp/min deviations: rate, rhythm, depth, character, dyspnea, orthopnea, apnea
Resp rate assessment sites:
- thorax - abdomen