Vertebral Column Flashcards
(17 cards)

Erector Spinae
Consists of 3 muscles, the iliocostalis, longissimus and spinalis. These muscle are extensors of the trunk. Since these are the deep muscles of the back, they are innervated by the dorsal rami of spinal nerves.


Note - the ligamentum flavum are composed of lots of elastic fibers (yellow color).




These veins drain the vertebrae and communicate with cervical, intercostal, lumbar and sacral veins. Cancer cells can move through these veins and because there are no valves, can settle in bone along the spinal column.


The epineurium is formed when the spinal nerve leaves the vertebral canal via the intervertebral foramen and 2 layers of the spinal meninges invaginate the nerve - arachnoid and dura - forming a “dural sleeve” which is the epineurium.


In the sacrum, the intervertebral foramen are replaced by the anterior and posterior sacral foramina. The ventral rami of sacral spinal nerves (mixed) exits through the anterior sacral foramina, while the posterior rami exit through the posterior sacral foramina. Rami are always mixed – motor and sensory -


The pia mater of the spinal cord has a pair of denticulate ligaments (one on each side of the spinal cord) with 21 attachments per side which attach it to the arachnoid and dura maters. Named for their tooth-like appearance, the denticulate ligaments are traditionally believed to provide stability for the spinal cord against motion within the vertebral column.

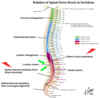
The spinal cord (sacral cord segments) typically ends at the caudal portion the second lumbar vertebra. The pia continues as the internal medullary filum and fuses with the arachnoid and dura at approximately the second segment of the sacrum. The fused dura, arachnoid and pia continue as the external medullary filum to attach to the coccyx. The sacral segments of the spinal cord are referred to as the conus medullaris. After the spinal cord ends, the subarachnoid space with its CSF is called the lumbar cistern. It is occupied by the lumbar and sacral spinal nerves. This cluster of nerves is referred to as the cauda equina (horse’s tail).
The vertebral column develops faster than the spinal cord causing a slanted exit of nerves from the spinal column.



The spinal cord (sacral cord segments) typically ends at the caudal portion the second lumbar vertebra.








The intervertebral disc consists of fibrocartilage. The outermost covering of the disc consists of dense connective tissue and is called the annulus (anulus) fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus is a jelly-like substance forming the core of the disc, and in ruptured discs is the material extruded when herniation occurs.


Note the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments – run the entire length of the spine.

Where do herniated discs usually occur?
When herniation of the fourth intervertebral disc occurs, pressure is placed on the L5 spinal nerve, producing pain. The pain radiates into the back and down the lower extremity and onto the dorsum of the foot. Refer to dermatome distribution.
Disc is always below vertebrae. Herniated disc will not affect its compliment nerve but the one(s) below it.


Lumbar puncture occurs between L4 and L5 or L3 and L4. Needed is inserted into the lumbar cistern which is the subarachnoid space containing CSF.



