Superficial Back Flashcards
(23 cards)
Vertebrae

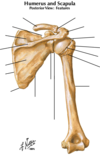
Humerus and Scapula

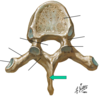
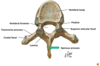
How many vertebrae in each of the 5 vertebral column?
Cervical - 7
Thoraxic - 12
Lumbar - 5
Sacral - 1 (5 fused)
Coccyx (3-4 fused)

Trapezius
Origin : back of the skull, nuchal ligament, and spinous processes of C7 to T12 vertebrae.
Insertion : lateral third of clavicle, acromion and spine of the scapula.
Innervation : accessory nerve
Blood Supply : superficial branch of the transverse cervical artery
Action : elevation, retraction, and depression of the scapulae. The upper and lower parts working together, elevate the glenoid cavity superiorly.

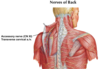

Recent evidence suggests that the accessory nerve lacks a cranial root and has no connection to the vagus nerve.


Rhomboid Major and Minor
Origin : spinous processes of C7 to T5
Insertion : medial border of the scapula
Innervation : dorsal scapular nerve.
Action : retract the scapula and rotate it to depress the glenoid cavity.
Note: In reflecting, attempt to identify the dorsal scapular nerve, the nerve supply to the rhomboid muscles and the levator scapulae


Levator scapulae
Origin : transverse processes of C1 – C4 vertebrae
Insertion : upper portion of the medial border of the scapula
Innervation : dorsal scapular nerve
Action : serves to elevate the scapula


Latissimus dorsi
Origin : spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae below T6, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and lower 3 or 4 ribs.
Insertion : intertubercular groove of the humerus.
Innervation : thoracodorsal nerve
Action : extends, adducts and medially rotates the upper extremity
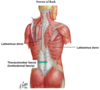



Serratus anterior
Origin : lateral border of ribs 1-8
Insertion : medial border of the scapula
Innervation : long thoracic nerve
Action : protracts the scapula and holds it against the body wall. Also, it facilitates rotation of the scapula.
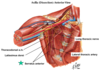


Cause?

Injury to the long thoracic nerve results in “winged scapula”.
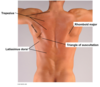
Triangle of auscultation

Triangle of auscultation formed by the trapezius, rhomboid major and latissimus dorsi.

Deltoid
Origin : lateral third of the clavicle, the acromion, and the spine of scapula
Insertion : deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
Innervtion : axillary nerve
Because of its origin, the functions vary depending upon the part that is functioning. From a clinical viewpoint, its function as an abductor of the upper extremity is most significant.


Axillary nerve to deltoid enters posterior deep surface


The subacromial bursa (subdeltoid bursa) is located deep to the deltoid and acromion
Calcification of the supraspinatus tendon leads to inflammation of the bursa, causing pain on abduction of the upper extremity (painful arc syndrome).

Supraspinatus and Infraspinatus
Origin : respective fossae of the scapula
Insertion : greater tubercle of the humerus.
Innervation : suprascapular nerve
Blood supply : suprascapular artery, a branch of the thyrocervical trunk that originates from the subclavian artery
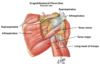
Muscles of the rotator cuff
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis

Teres minor
Origin : lateral border of the scapula
Insertion : greater tubercle of the humerus
Innervation : axillary nerve
Action : along with the infraspinatus, it laterally rotates the upper extremity
Teres major
Origin - inferior angle of the scapula
Insertion : medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus
Innervation : lower subscapular nerve
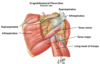
The quadrilateral or quadrangular space.
Formed by three muscles and the medial border of the humerus.
The axillary nerve and the posterior circumflex vessels (artery and vein) forming the neurovascular bundle pass through this space to reach their destination.

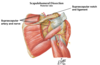
The suprascapular nerve passes below the ligament, while the suprascapular artery and vein pass above.

Omohyoid muscle
consists of two bellies, a superior and an inferior. The superior belly is attached to the hyoid bone, while the inferior belly attaches to the superior border of the scapula immediately medial to the suprascapular notch.



