Vasculitis Flashcards

palpable purpura

leukocytic vasculitis
what to do if you suspect a vasculitis
- determine extent of disease - what organs does it effect
- BIOPSY - or angiogram, but biopsy is better
Four types of small vessel vasculitis
- Henoch-Schoenlen Purpura
- Wegener’s granulomatosis
- microscopic polyarteritis/polyangiitis
- Churg-strauss syndrome
skin clues to vasculitis
- palpable purpura
- ulcers - esp in stellate shape
- nodules
- ischemic digits
- livido reticularis, or reticulated purpura

reticulated purpura: a clue to deep vascular involvement

leukocytoplastic vasculitits
Henoch-Schoenlein Purpura - sx
small vessel vasculitis w/
- dependent skin rash - palpable purpura
- abdominal pain/bloody diarrhea due to vasculitis of bowel lining
- glomerulonephritis - sometimes
- arthralgias
+ fever and malaise
in a child
usually self-limited
biopsy findings for Henoch-Scholein purpura
neutrophilic, leukocytoclastic process w/ IgA
Wegner’s granulomatosis/ Granulomatosis polyangiitis
small vessel vasculitis
classic traid: granulomatous inflammation of upper airway, lower airway (lung + trachea), and kidney (focal segmental glomerulonephritis)
systemic sx: epistaxis, SOB, evidence of GN
assoc w/ cANCA in 90% (antibodies to serine proteinase 3)
Microscopic polyarteritis/polyangiitis
small vessel vasculitis
Wegner’s-like presentation: involves skin, kidney, lungs (diffuse alveolar hemorrhage syndrome)
pANCA (specificity for MPO)
Churg-Strauss syndrome
small vessel vasculitis
similar to Wegener’s in pt w/ hx of asthma or atrophy
sx: pulmonary infiltrates, cardiac and neuro features w/ blood eosinophilia
polyarteritis nodosa
medium vessel vasculitis - neutrophilic
almost always secondary to Hep B
sx: ANEURYSMS, gut ischemia, renal artery involvement + hypertension, large ulcers, mononeuritis, systemic sx (weight loss, fever)
Kawasaki’s disease
medium vessel vasculitis
febrile illness in children under age 6
sx: inflammation of oral mucous membrane, lymphadenopahty, rash, irritability
complication: coronary arteritis – want to prevent this
Takayasu’s aortitis
large vessel vasculutis
inflammation of aorta and its branches
initial phase: fever, malaise, weight loss, ischemic sx
later: progressive vascular occlusion, lose pulses
epi: more common in asian women
giant cell arteritis
large vessel vasculitis
most common vasculitis in adults > 55
affects extravranial elastic arteries –> headache, facial pain, visual loss from ischemic optic neuropathy
also can present w/ polymyalgia rheumatica or wasting systemic febrile disease

biopsy in polyarteritis nodosa - shows inflammed vessel and aneurysm
elastic lamina destroyed

polyarteritis nodosa
common causes of secondary vasculitis
- other connective tissue disease
- infections: hep B and C, parvovirus, herpes zoster, SBE
- drug induced: cocaine
- malignancy
- cardiac myxoma
- cryoglobulins
eye inflammation, sinusitis, lung lesions, hemoproteinuria, gangrene of fingers
dx? lab tests?
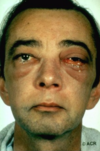
dx: Wegner’s/ Granulomatois Polyangiitis
test: cANCA
ANCA tests
pattern: cycoplasmic vs. perinuclear
most common antigens: cANCA = serine proteinase 3; pANCA = myeloperoxidase (MPO)
ANCA with discordanent antibodies (ex. cANCA w/ MPO)
happens w/ cocaine!
difference b/t vasculitis and vasculopathy
vascultitis: INFLAMMATION of vessel wall
vasculopathy: processes that cause vessel obstruction or narrowing that is non-inflammatory
* examples: cholesterol emboli, amyloid, vasospasn, SBE, more….

calciphylaxis - one cause of vasculopathy
Bechet’s vasculitis
involves veins and arteries
sx: painful oral and genital ulcers, thrombophlebitis, retinal vasculitis, anterior eye disease, encephalitis, rash
Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis
cold precipitating antibodies –> small vessel vasculitis
includes GN
assoc w/ Hep C
Buerger’s disease
thromboangiitis obliterans
destructive arterial and venous disease of hand and feet –> digit loss
may be a vasculopathy rather than vasculitis
strong association w/ smoking


