Vaccinations and Vaccine Preventable Diseases Flashcards
Original Method of Vaccination
variolation
Introduced Variolation to Colonies
Reverent Cotton Mather
Discovered cowpox vaccine to protect against smallpox
Edward Jenner
Passive vs. Active Immunity
- Passive (no B or T-cell short term immunity)
- infant covered by maternal or IV administered immunoglobulin
- IVIg, Hep B, tenanus, rabies
- Active
- naturally occurring d/t contact w/ disease (variable response and long term effect)
- vaccine induced
Vaccine Types
- live attenuated (weakened) viruses
- inactive/killed viruses
- recombinants
- reassortments
- immunologic bacterial components
- toxoids
Live Attenuated Virus Vaccines
- measles, mumps, rubella
- varicella
- nasal influenza
Inactivated/Killed Virus Vaccines
- polio
- Hep A
- injected influenza
Recombinant Vaccines
use a piece of the germ that stimulates immune response
- Hep B - HBsAg protein inserted into yeast
- HPV - particles synthesized from recombinant HPV proteins
- shingles - varicella glycoprotein with adjuvant
Reassortment Vaccines
5 rotavirus strains re-assorted to express multiple serotypes
- live virus
- given orally
Immunologic Bacterial Components
parts of baceria given to prevent reaction
- pertussis
- H. influenza B
- Strep pneumonia
- meningococcal
Toxoids
create immunity to toxin produced, not the germ
- diptheria
- tetanus
Vaccines not common in U.S.
- cholera
- smallpox
- BCG (for TB)
- typhoid fever
- yellow fever
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Measles (RNA virus)
- S/s: Koplik spots, rash, fever, cough, coryza (inflammation w/ mucous in nasal mucosa), conjuntivitis
- Comp:
- otitis media, pneumonia, croup (steeple sign), diarrhea
- acute encephalitis
- fatality
- subactue sclerosing panencepalitis (SSPE)
- behavioral and intellectual decline, no tx
- Dx: clinical, IgM/IgG serology
- Tx: supportive care
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Mumps (RNA virus)
- S/s:
- parotitis (swelling of parotid, sometimes other salivary)
- painful w/ ingestion of sour substance
- Complications:
- orchitis if after puberty
- arthritis, thyroiditis, mastitis, cerebellar ataxia, encephalitis, hearing loss
- Dx: clinical, lgM/IgG serology
- DDx: parotitis other causes
- Influenza A, EBV, parainfluenza, bactria
- DDx: parotitis other causes
- Tx: supportive
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx
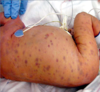
Rubella (RNA virus)
- S/s:
- generalized maculopapular rash
- postauricular and occipital lymphadenopathy
- polyarthralgia/arthiritis in teens and adults
- Complications:
- congenital most serious- first trimester
- microcephaly, deafness, congenital heart dz, cataracts
- lifelong sequelae requiring tx
- congenital most serious- first trimester
- Dx: serology IgM/IgG
- Tx: supportive (this is a mild illness)
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Varicella (Herpes virus)
- S/s: pruritic vesicular rash, fever, gen. systemic illness
- Complications:
- bacterial infection in lesions, pneumonia, cerebellar ataxia, encephalitis, thrombocytopenia
- severe if immunocompromised
- milder after vaccination
- Dx: clinical, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test of vesicle fluid, IgM/IgG serology
- Tx: supportive, VZIG (neonate, immuno.), Acyclovir interrupts viral replication
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Shingles (Varicella zoster)
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Diphtheria (Corynebacterium diphtheria)
- S/s:
- membranous pharyngitis, cervical adenpathy, low fever
- Complications:
- life-threatening respiratory obstruction
- Dx:
- culture on special agar medium sent to CDC
- Tx
- Equine antitoxin (must test for horse serum sensitivity)
- Erythromycin or PCN alternatively
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx
Tetanus (Clostridium tetani)
toxin of soil/intestinal bacteria or passed from mom causes illness
- S/s: trismus, severe generalized muscle spasms
- Complications
- DDx:
- must exclude strychnine, hypocalcemia, conversion disorder
- Tx:
- human tetanus immunoglobulin
- metronidazole and PCN also given
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Pertussis (Bordatella pertussis)
- S/s: URI prodrome progressing to spasmotic coughing
- Complications:
- pneumonia, apnea, subdural/subconjunctival bleeding, death
- Dx: PCR nasal/posterior pharynx swab
- Tx:
- Oral Azithromycin (reduces sx only in catarrhal stage)
- convalescent stage can be weeks to months
- vaccine only effective 3-5 years
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Hemophilus influenza Type B (Hib bacteria)
(untypable not covered by immunization - less severe)
- S/s:
- site dependent: epiglottitis, meningitis (MCC age < 3), conjunctivitis, otitis media
- Dx: culture from infected body fluid
- Tx:
- 2nd/3rd gen Cephalosporin
- presumtive tx is multiple abx pending cultures
- epiglotitis requires emergent airway procedure
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Streptococcal pneumonia (S. pneumo, Staph pneumo)
Prevnar vaccine covers 23 strains fo S. pneumo
- S/s: common cause of pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, conjunctivitis
- Complications:
- septicemia, meningitis (esp. very young/old)
- Dx: culture of infected site (blood or CSF)
- Tx:
- usually presumptive - multiple abx
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx

Neisseria meiningitidis
- S/s: abrupt onset of fever, myalgias, malaise, variable rash
- Complications:
- meningococcemia and meningitis (MCC in children)
- fulminant dz - limb ischemia, coagulopathy, shock, coma
- Dx: bacterial culture of blood/CSF
- Tx (meningococcal dz):
- tx symptoms of shock / stay ahead of coagulopathy
- broad spectrum abx pending culture
- PCN G 300,000 U/kg daily
- Rifampin, Ceftriaxone for prophylaxis of exposed
Dz, S/s, Complications, Dx, Tx
destruction of nerve cells in spinal cord

Polio virus
last US case 1979; still in Nigeria, Afghanistan, Pakistan
- S/s:
- muscle wasting- flaccid paralysis w/ loss of reflexes in affected limb
- bulbar dz may lead to respiratory paralysis
- sore throat, malaise, fever, HA
- Tx: supportive



