User Setup & Login Process Flashcards
(37 cards)
Explain the concept of record ownership.
Every record in Salesforce must have an owner. Records can be owned by either users or queues. By default, the user that creates the record is the owner. Record owner is typically used to determine responsibilities (e.g. I manage the leads that I own), reporting (I am credited for the opportunities that I own), record security (discussed in Security Model – Free), and for a variety of other purposes.
Explain the difference between production and sandbox environments.
A sandbox is a copy of a production environment, commonly used for testing and development. Sandbox and production environments use different login URLs:
Production: https://login.salesforce.com
Sandbox: https://test.salesforce.com
What are the different types of Sandboxes?
TYPE COPIES METADATA COPIES DATA REFRESH LIMIT DATA LIMIT
- *Developer** Yes No Daily 200MB
- *Developer Pro** Yes No Daily 1GB
- *Partial Data** Yes Partial 5 Days 5GB
- *Full** Yes Yes 29 Days Same as Production (at time of copy)
Explain the importance of Salesforce user records.
An active user record is required to login to Salesforce. Records can only be assigned to an active user or a queue.
- 1 Person = 1 User = 1 User License
- Cannot be Deleted
- User name must be Unique (All Orgs)
- Record Assignment (Active User/Queue)
What determines what a user can perform?
Licensing (User & Feature) and Permissions

User Licesne Types
- Salesforce (Sales and Service Cloud)
- Salesforce Platform & Force.com (Custom Apps)
- Chattter (Chatter)
CRM Apps & Data
- Yes
- Limited/None
- Limited/None

Key User Settings
Licsensing - What security they can be granted (User License; Feature License)
Security - What the use can do (Role; Profile)
Localization - How information is displayed to the user (Locale; Language; Time Zone; Currency)
Explain the difference between deactivating and freezing a user account.
Freezing a user account will temporarily prevent a user from logging in (e.g. during a maintenance window, or if configuration prevents user deactivation), while deactivation of a user completely revokes access.
Things to consider when deactivating a user.
- Deactiving a user doesn’t delete records they own. The user still owns them until they are transfer to another user.
- Chatter profile still appears, but as inactive. He is removed from other’s profiles that were following him, and followers lists.
- You cannot deactive a user if they are default owners of leads or the sole recipient of a workflow email alert.
- A deactivated user doesn’t count against your organization’s available user licenses. However, deactivating a user doesn’t reduce the number of licenses for which your organization is billed; you must change your organization’s license count to change your billing.
*
Freezing User Accounts
- To prevent users from logging into your organization while you perform the steps to deactivate them, you can freeze user accounts.
- Freezing user accounts doesn’t make their user licenses available for use in your organization. You must deactivate user accounts to make their user licenses available.
Describe Queues
(Setup > Manage Users > Queues)
- Queues help your teams manage leads, orders, cases, service contracts, and custom objects.
- Once records are placed in a queue manually or through an automatic case or lead assignment rule, records remain there until they’re assigned to a user or taken by one of the queue members.
- Examples: Lead queues, Case queues, Knowledge article version queues, Service contract queues, Custom object queues.
Explain the difference between user and feature licenses.
- Every user must be assigned one (and only one) user license. This is their primary license.
- Users can also optionally be assigned one or more feature licenses. ___________________________
- Standard User Licenses
- Chatter User Licenses (External, Free and Only (plus))
- Communities (All external: Customer, Customer Plus & Partner)
- Service Cloud Portals
- Sites and Site.com (Guest or Site only users)
- Authenticated Website (used with Force.com sites)
Explain how licensing influences what actions a user can perform
- The combination of a user’s licenses and permissions determines what functionality they can access and what actions they can perform within Salesforce.
- For instance, to create a campaign within Salesforce, the user must have the Salesforce user license, the Marketing User feature license, and the permission to create campaign records (via profile or permission set). See Security Model – Free for details.
Explain the implications of user localization settings.
(Setup > Company Profile >Company Information)
- Locale: changes display of dates, times, numbers, names, and addresses.
- Language: determines which language translatable elements (UI, fields, etc.) are displayed in to the user.
- Time zone: determines the offset used to display time references in Salesforce (similar to changing the time zone on your computer).
- Currency locale: configured org-wide unless multiple currencies is enabled. Determines the formatting of currency fields, and used to determine currency conversion when multiple currencies is enabled.

Describe the translation capabilities of Salesforce
Salesforce has several tiers of language support; each supports translation to a different degree. Regardless of the language tier, custom elements (such as custom fields, objects, and picklist values) must be translated using the translation workbench.
Salesforce offers three levels of language support: fully supported languages, end-user languages, and platform-only languages. All languages are identified by a two-character language code (such as en) or a five-character locale code (such as en_AU).
Describe the capabilities of Salesforce to manage multiple currencies.
- By default, Salesforce supports one currency within an org.
- Multiple currencies can be enabled by feature request, and allows for static conversion rates between currencies. As of the Winter 15 release, the “Allow Support to Activate Multiple Currencies” checkbox is exposed under setup (Company Profile –> Company Information); however, you must still raise a case with Salesforce to enable the feature after checking this box in setup.
- Once multiple currencies is enabled, advanced currency management allows for dated exchange rates (e.g. use the exchange rate at the opportunity’s close date instead of a static rate).
Describe the different methods that can be used to authenticate to Salesforce.
- Website: The standard Salesforce user interface.
- API: Used for programmatic access, such as the data loader.
- Single Sign On (SSO): Not discussed.
- OAuth: Not discussed.
- Login Method
- Login URLs
- Login Hours
- Login IP Ranges
- Trusted IP Ranges
- Computer Activation
- Security Token
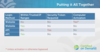
Login Methods and URLs
- Web Browser (May Require Computer Activation)
- API (Application Program Interface)
- -Data Loader
- -May require Security Token
- Single Sign On (SSO)
- OAuth (like Chatter Desktop)
URLs (whatever enviroment you are using, you must log into it)
Production (https:login.salesforce.com)
Sandbox (https:test.salesforce.com)
Login Hours & IP Ranges
(Setup>Manage Users>Profiles>edit)
Hours
- Prevent loging Exect for Specific Times
- Prevent login during non-working hours
- Prevent login during maintenance
IP Ranges
- Prevent loging Except for Specific IP Addresses
- Prevent login from home
- Prevent login without VPN connection
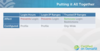
When is Computer Activation Required?
Required when Login Identity NOT confirmed
- Login from Trusted IP Range
- User Previous Login from Browser (Cookie)
- User Previous Login from Current IP Address
What is a Security Token?
(Your Name>My Settings>Reset My Security Token)
String Attached to the End of Password
Required for Login via API (excpet from Trusted Nextwork)
Describe the settings an administrator controls to conditionally allow or prevent user authentication.
- Login IP Ranges are used to prevent login except from specific IP addresses.
- Login Hours are used to prevent login during certain hours of the day.
- The permission (profile/permission set) “API Enabled” is required for a user to authenticate via the API.

How do you set company level IP Ranges?
Navitage to:
Setup>Security Controls>Network Access>New>Add new IP Addresses
** Users outside of th range are sent an activation code**



