Urogynaecology Flashcards
1
Q
Maintaining continence
A

2
Q
Types of urinary incontinence
A

3
Q
Urge incontinence and overactive bladder
A
- Overactive bladder (OAB)
- Symptoms of urgency with or without urge incontinence, usually with frequency and nocturia
- Urge incontinence (UUI)
- Leakage of urine in response to an involuntary contraction of the detrusor muscle
- 25% of women with incontinence have sole diagnosis of UUI
4
Q
Stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
A
- Most common cause of UI in adult women
- 40% of women with incontinence
- Leakage occurs with rise in intra-abdominal pressure without a detrusor contraction (coughing, laughing, running, walking)
5
Q
SUI definitions
A
- Stress urinary incontinence
- Sign or a symptom of urinary leakage with increased abdominal pressure
- Urodynamic stress incontinence (USI)
- Urodynamic proven leakage of urine with increased intra-abdominal pressure (old term - genuine stress incontinence)
6
Q
Aetiology of OAB
A

7
Q
Aetiology of SUI
A
- Loss of suburethral support causing increased urethral mobility (urethral hypermobility) leads to movement of proximal urethral sphincter out of the abdominal space, so increased intraabdominal pressure not spread evenly throughout bladder
- Intrinsic deficiency/primary urethral weakness
- Suburethral support may be sufficient
- Defective function of the striated and smooth urethral muscle and mucosal and submucosal cushions
8
Q
Risk factors for UI
A

9
Q
Implications of UI
A
- Empoyment
- Sleep
- Exercise and sport
- Emotions
- Relationships and socialising
- Self worth
- Travel and holidays
10
Q
Presentation of UI
A
- Stress incontinence
- Frequency
- Urgency
- Urge incontinence
- Nocturia
- Enuresis
- Haematuria
- Dysuria
- Voiding problems
- Pain
- Prolapse problems
11
Q
Diagnosis of UI
A
- Hx
- Abdominal/bimanual examination
- Pelvic masses
- Palpable bladder
- Impression of pelvic floor tone
- Vaginal examination
- Bivalve examination
- Sims speculum, left lateral position
- Identify cervix or vaginal vault
- Check walls in turn for prolapse, atrophy, fistulae and ulceration
- Ask to cough - urine leakage?
- Urine dip +/- culture (in every women)
- Leucocytes and nitrites for UTI
- Haematuria
- Glucose
- Bladder diary
- Minimum 3 days
- Input/output/times of leaking
- Cystoscopy and renal tract imaging
- Haematuria
- Recurrent UTIs
- Urodynamic testing
- Expensive and time consuming
12
Q
Urodynamics
A
- Dynamic study of bladder function
- Uroflowmetry (measuring flow)
- Filling and voiding cystometry (measuring pressures in bladder and abdomen and calculating detrusor pressure)
- In which patients?
- Failed conservative management
- Prior to surgery
- Previous failed surgery
- Treatment complications
- Suspected voiding problem
13
Q
Management
A
- Conservative
- Continence advice and lifestyle changes
- Physiotherapy
- Bladder retraining
- Medical
- Antibiotics
- Anticholinergics
- B3 agonists
- Duloxetine
- Surgical
14
Q
Continence advice and lifestyle advice
A
- Education - how the bladder works
- Good habits - starting bladder retraining
- Fluids - normalise intake (1.5l a day, avoid caffiene, alcohol and carbonated drinks)
- Lifestyle - diet, weight loss, smoking cessation, treat chronic cough and chronic constipation
15
Q
Physiotherapy
A
- First line for SUI but also role in OAB
- Pelvic floow (Kegel) exercises with regular voluntary contraction and relaxation of pelvic floor muscles
- Use of weighted cones as adjunct
16
Q
Bladder retraining
A
- Probably best treatment of OAB
- Minimum 6 weeks
- Relearning higher cortica control of detrusor muscle
- Patient empties bladder to strict time schedule (usually hourly) with time between voids increasing gradually
- Techniques to aid training
- Distraction
- Sitting on hard seat
- Pelvic floor squeezes
17
Q
Conservative management
A
- Suitable for all except:
- Haematuriam, infections, pain or voiding difficulty
- Previously tried and failed
- Patient does not want it or unable to engage with therapy
- No facilities
18
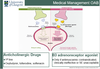
Q
Medical management
A
- Anticholinergics effective in 50% of women
- Use limited by side effects (dry mouth, dry eyes, constipation)
- 4-6 week trial to assess response
- Can try multiple kinds
- Vaginal oestrogen if post menopausal
- Duloxetine
- SNRI
- Stimulated pudendal motor neurones - increasing contractcion or urethral striated muscle of sphincter and so increases urrethral closure pressure
- Lots of side effects (GI disturbance, dry mouth, headache, suicidal ideology, SSRI withdrawal effect)
19
Q
Surgical management
A
- Botox injections
- Lasts 3-13 months
- Need to be able to self-catheterise
- Percutaneous sacral nerve stimulation
- Augmentation cystoplasty
- Urinary diversion


