Urinary System Flashcards
(33 cards)
The urogenital system develops from what type of tissue?
During lateral folding, what ridges appear?
- intermediate mesenchyme (dorsal body wall of embryo)
- urogenital ridge (each side of dorsal aorta)
The nephrogenic cord will give rise to the …?
The gonadal ridge will give rise to the …?
nephrogenic cord = urinary system
gonadal ridge= genital system

What are the 3 sets of kidneys?
Which sets are functional and which are permenent?
pronephroi (never functional; appear@ week 4)
mesonephroi (appear@ week 4; functions briefly for 4 weeks)
metanephroi (begin developing@week 5; permanent kidney @ week 10);S1-S2

What persists after the pronephri degenerates?
What does this become?
pronepheric ducts persist
- becomes the **Wolffian duct **(mesonephric duct)
The mesonephric ducts open into what structure?
The mesonephroi degenerate at the end of the first trimester, their tubules become what adult structure?
- the cloaca (trigone of urinary bladder)
The primordia of permanent kidneys starts developing at what week?
They are functional by what week?
- week 5
- week 8 (mesonephroi)
* urine is secreted into amniotic cavity
* fatus swallows 100s mL of amniotic fluid/day
*fetal waste eliminated by maternal kidneys
By what week are the kidneys in their final abdominal position?
- what rotational change in position takes place?
week 9 (become fixed to suprarenal glands)
- 90 degrees medially; hilum faces medially
(kidneys eventually become retroperitoneal)

How does the blood supply change in the ascending kidney?
How many different positions does it have?
renal arteries:
1st: branches of common iliac arteries
2nd: distal end of the aorta
3rd: new branches from aorta
(3 positions in total)
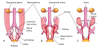
Accessory Renal Arteries
(Supernumerary renal arteries)
- about 25% of adult kidneys have two to four renal arteries
- usually arise from the aorta
- accessory renal artery to inferior pole of kidney may cross anterior to
ureter + obstruct it = hydronephrosis (distension of renal pelvis + calices with urine)
- if accessory artery is damaged/ligated kidney part supplied = ischemic

Unilateral Renal Agenesis
- left kidney is usually absent
- usually asymptomatic (other kidney = compensatory hypertrophy)

Bilateral Renal Agenesis
failure in development of the metanephric diverticula
- oligohydramnios (b/c little/no urine excreted into amniotic cavity)
- incompatible with postnatal life b/c associated pulmonary hypoplasia**
- ** new developments = potential survival with dialysis & early kidney transplant*
Characteristic facial appearance:
- eyes widely separated
- epicanthic folds (wrinkly skin)
- ears are low-set
- broad nose and flat
- limb defects (lack of space to develop)
Ectopic Kidney
One or both kidneys in abnormal position
failure to alter position during embryo growth
- in pelvis (pelvic kidney) or inferior part of the abdomen (lumbar kidney)
most common = pelvic
Horseshoe Kidney
poles of kidneys are fused; (usually inferior poles)
- lies in the hypogastrium, anterior to the inferior lumbar vertebrae
- usually asymptomatic
- normal ascent is prevented b/c they are caught by the root of inferior mesenteric artery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJ)
obstruction to urine flow from the renal pelvis to the proximal ureter
_**most common congenital obstruction of the urinary tract**_
- severe uteropelvic atresia => multicystic dysplastic kidney with severely dilated calyces
- kidney consists of grapelike, smooth-walled cysts of variable size; b/t cysts are dysplastic glomeruli + atrophic tubules

Childhood polycystic kidney disease (PCKD)
- kidneys are huge + spongy and contain cysts caused by dilatation of collecting ducts + tubules that compromise kidney function
- autosomal recessive disease (short arm of chromosome 6 (p6))
- associated clinically w cysts of the liver, pancreas, + lungs
- treatment: dialysis + kidney transplant

Wilms’ Tumor (WT)
_**most common renal malignancy of childhood**_
- large, solitary, well-circumscribed mass; (on cut) soft, homogeneous, + tan-gray
- recapitulates different stages of embryologic formation of kidney:
= 3 histologic areas: stromal, blastemal (tightly packed embryonic cells), tubular

Duplications of the Urinary Tract
Cause: division of the metanephric diverticulum
- degree of duplication depends on how extent the division was
- Complete division = double kidney with bifid ureter or separate ureters
* supranumeracy kidneys*

Ectopic Ureter
males: open into neck of bladder or into prostatic part of urethra
- above external urethral sphincter = incontinence NOT common
females: open into bladder neck, urethra, vagina or vestibule of the vagina
- below external urethral sphincter = incontinence IS common

Ureterocele
(Simple vs. Ectopic)
simple ureterocele:
- distal end of ureter has cystlike protrusion into the submucosal layer of the urinary bladder
ectopic ureterocele:
- cystlike protrusion into the submucosal layer of the urinary bladder associated with ectopic ureter + duplication
- -* ureterocele is at the end of ureter from upper renal segment & is located inferior to other ureter opening

What divides the cloaca into the urogenital sinus and rectal sinus?
How is the urogenital sinus further divided?
urorectal septum
urogenital sinus:
- cranial vesicle = bladder
- middle pelvic part = prostatic urethra (M)/ entire urethra (F)
- caudal phallic part = primordium of penis or clitoris

What are the tissue origins of the bladders layers?
What are the tissue origins of the Male & Female urethras?
BLADDER:
(M/F) epithelium = endoderm (vesicle part of urogenital sinus)
(M/F) other layers of its walls = splanchnic mesenchyme
URETHRA:
(most of M/ all of F) epithelium = endoderm (vesicle part of urogenital sinus)
(M/F) connective tissue + smooth m. = splanchnic mesenchyme

How does the allentois contribute to the development of the bladder?
- originally allentois is continuous with bladder
- allentois constricts = urachus
- urachas extendes from umbilicus –> apex of bladder
- in adult, urachus = median umbilical ligament
- (failure of urachus to constrict = urachal cyst or fistula)*
Urachal cysts

- originate from remnants of the epithelial lining of the urachus
- NO connection b/t bladder & umbilicus
Urachal Sinus
persistent inferior end of the urachus that dilates and opens into the bladder










