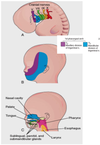
Pharengeal Apparatus Flashcards
Structurs that give rise to the head & neck develop form the pharengeal apparatus. This consists of what 4 types of structures?
Pharyngeal arches
Pharyngeal pouches
Pharyngeal grooves
Pharyngeal membranes

Pharyngeal Arches are fromed from what types of tissues?
somitomeric mesoderm and neural crest cells
Pharyngeal Arches:
the mesoderm tissues differentiates into which structures?
muscles and arteries (aortic arches)
Pharyngeal Arches:
the neural crest cells differentiate into which structures?
bone and connective tissue
Each pharengeal arch is associate with what?
a cranial nerve
By what week are 4 pharengeal arches visible externally?
Why are the 5th and 6th arches not visible?

- by week 4
- arches 5 + 6 are rudimentary; not visible externally

Pharengeal Pouches are invaginations of what type of tissue?
endoderm
(lining the foregut)

Pharengeal Grooves are invaginations of what type of tissue?
ectoderm
(located between each arch)

Pharengeal Memebranes consits of which types of tissues?
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
nerual crest cells
(located between each arch)

The 1st pharyngeal arch is also called _______?
It gives rise to what 2 prominences?
“mandibular arch”
- maxillary prominence
- mandibular prominence
The maxillary prominence (1st arch) gives rise to what structures?
- maxilla
- zygomatic bone
- a portion of the vomer

The mandibular prominence (1st arch) gives rise to what structures?

- mandible
- squamous temporal bone
The second pharyngeal arch is also called _________?
It contributes to the formation of the hyoid bone, with contributions from which other arches?
” hyoid arch”
- parts of the 3rd + 4th arches help form the hyoid bone

What is the stomodeum?
(primordial mouth)
- appears as a slight depression of the surface ectoderm

Where is the function of the oropharengeal membrance?
What types of tissue does it consist of?
- to separate the stomodeum from the cavity of the primordial pharynx
- ectoderm externally + endoderm internally
Each pharengeay arch contains what structures?
- artery
- vein
- cartilage
- muscular component
- sensory + motor nerves

where does the arteries of the pharengeal arches arise from?
Where does it carry blood to?
- arises from ** truncus arteriosus** of the primordial heart
- goes to the** aorta**
What does the cartilage of the pharyngeal arches form?
the skeleton of the arches
What does the muscular component of the pharyngeal arches become?
differentiates in to muscles fo the head + neck
What is the cartilage at the dorsal end of the 1st pharyngeal arch called?
What does it develop into?
Meckel cartilage
- develops the malleus + incus of the middle ear

The middle part of the Meckel cartilage regresses. What is fromed by its remaining perichondrium?
- anterior ligament of malleus
- sphenomandibular ligament

When does the cartilage of the 1st pharyngeal arch disappear?
What process occurs?
- disappears as the mandible develops around it
- intramembraneous ossification
What is the cartilage of the 2nd pharyngeal arch called?
What does it develop into?
Reichert cartilage
gives rise to:
- stapes of the middle ear
- styloid process of the temporal bone
- stylohyoid ligament
- lesser cornu of the hyoid bone

What does the cartilage of the 3rd pharyngeal arch develop into?

ossifies to form:
- greater cornu of the hyoid bone
- inferior part of the hyoid bone