URI, Pharyngitis, Tonsillitis (guest lecture) Flashcards
Some manifestations of URIs
-nose: rhinitis, rhinosinusitis -tonsils: tonsillitis -phrynx: phryngitis -often a combination of these
What percentage of URIs is viral?
90%
What are examples of viruses that cause URIs
“cold viruses” like adenovirus & rhinovirus; -influenza: uncommon, more severe sx’s
What are some bacteria that may cause a URI
strep. pnuemo> H. flu > M. cat.
transmission of cold virus
air, hand-to-face
prevention of transmission of cold virus
wash hands; avoid close contact, mask
Treatment of URIs given percentage that are viral
90% viral, so no abx
How many days do you hold off abx with URI
hold off 7 days unless strep is suspected
When do bacteria start to accumulate and become a problem with URIs?
more than 7 days- then may give abx
Main goal with treatment for URIs
treat symptoms so patient feels better
What are sx of URIs you would treat?
- runny nose: OTC antihistatmines; ipratropium spray
- congestion - decongestants
- thick secretions- guaifenesin makes more thin and runny
Most common cause of non-infectious rhinitis & characteristics
allergies -sneezing itchy, runny nose, nasal congestions -not chronic, no sudden onset, no fever
sx with pregnancy-caused non-infectious rhinitis
pregnancy (nasal congestion with or without runny nose, no fever, no purulence)
causes of non-infectious rhinitis
allergies and pregnancy
What does Waldeyer’s Ring include?
adenoids, palatine tonsils, lingual tonsils
What are tonsils also called and what type of organ are they?
tonsils=adenoiods; they are secondary lymphatic organs
What do tonsils do?
lymphatic organs; secrete topical IgA, and IgG & IgM in to blood
What are causes of stomatitis (mouth)
usually viral - aphthous ulcers, herpangina, herpes simplex -fungal - candida/thrus
What causes herpangina?
coxsackievirus A
sx of herpangina
fever, sore throat, rash/ulcers on palate –> small vesicles with erythematous base that become ulcers -pain can be severe
What type of tx for herpangina?
supportive tx - “stomatitis cocktail”
Pharyngitis causative organism
>90% viral
What body part does pharyngitis refer to?
internal throat
symptoms of viral pharyngitis
runny nose, cough, with/without conjunctivitis, with/without diarrhea
non infectious causes for pharyngitis
-snoring - red uvual -laryngeal acid reflux - chronic pharyngitis/laryngitis, nighttime cough, sensation of something in throat, absence of heartburn irrelevant
symptoms of acute tonsillitis
-Odynophagia: pain w/ swallowing -Dysphagia: difficulty swallowing, -fever -enlarged, tender lymph nodes upper neck
complications of tonsillitis
-missed work/school -dehydration -abscessess in peritonsillar or deep neck -systemic complications like strep
Acute tonsillitis exam reveals
-tonsillar enlargement, erythema, exudate -cervical adenopathy (LN’s) anterior
tonsil calculi
or tonsilloliths; chronic or recent infections
Viral causes of tonsillitis
adenovirus, rhinovirus, influenza, Mono (EBV; has exudate)
bacterial tonsillitis often has______ which is not diagnostic
exudate
types of bacteria causes bacterial tonsillitis
-Group A Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus -Other Strep species like strep. pneuma, staph. arrests, Haemophylus influenza
What are rare bacterial tonsillitis causative organisms?
N. gonorrhoeae, Clamydia, Cornebacterium diphtheria
What type of organism often causes chronic tonsillitis
Group A Stret - actinomyces
Clinical Course of Group A strep
sudden onset * fever, with or without headache, nausea, swollen LNs,
Diagnosis of Group A strep
-bacterial may have purulent exudate with tonsil involvement -rapid strep test & culture; throat swab
Treatment for Group A Strep
penixillin (amoxicillin); erythromycin if allergic -2nd line - amox/clavulanate, cephalosporins, clindamycin
Local strep complications
-peritonsillar abscess -lymphadenitis (infection within lymph nodes) -deep neck abscess
Why treat strep throat?
local complications like abscess, systemic complications, contagious nature, shorten course of illness (self limited an most resolve without antibiotics)
Symptoms/Presentations of Peritonsillar abscess
-Unilateral symptoms -tonsil, uvula medially deviated -bulging soft palate -trismus - inability to fully open jaw -dysphagia “hot potato voice”
Peritonsillar abscess treatment
abx -can aspirate or I&D if necessary -quinsy tonsillectomy
Complications of Peritonsillar Abscesses
spread-retropharyngeal or parapharyngeal abscess *airway obstruction
Systemic complications of Group A Strep
-Rhuematic Fever -scarlet fever -glomerulonephritis
Rheumatic Fever does what? What is it a complication of?
-infects heart valves (rheumatic heart disease) -complication of Group A Strep
Scarlet fever causes what? What is it a complication of?
-toxin produced -causes nausea, headache -widespread red, punctate rash -strawberry tongue -Group A Strep
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by what? What is it a complication of?
“coca-cola” urine -Group A Strep
When do you treat asymptomatic strep carriers?
-“ping-pong” infections among family -outbreaks of strep illness in class
Chronic strep may occur when? what tx would you consider
may occur after repeated abs; consider tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy
Diphtheria occurrence & problems
Rare because of immunization -grey pseudomembrane can obstruct -systemic toxins - cardiac, neurologic
Treatment for diphtheria
erythromycin or PCN, antitoxin
What causes infectious mononucleosis?
Epstein-Barr virus
Sx of infectious mononucleosis
-prolonged malaise, fatigue lasts 1-3 months or more -significant tonsil and lymph node enlargement, including posterior neck nodes -tonsil exudate common
_____% of people with mono are also infected with what other microorganism?
20-30% also infected with strep
complications of mono
-splenomegaly 50%, risk of rupture and hemorrhage -hepatomegaly - 10%, elevated LFT’s -hepatosplenomegaly 2nd to 4th week
Which complication of mono has risk of rupture and hemorrhage?
splenomegaly -no contact sports
Diagnosis of Infectious mononucleosis
-monospot (rapid)-only 60% positive 1st two weeks and 90% after 1 month -WBC: elevated lymphocytes 50% & atypical lymphocytes -mono panel; IgM elevated in acute
tx for mono
supportive, maybe steroids -abx if infected but NOT AMOXICILLIN -limit activity because of spleen complications
Tonsil & adenoid hypertrophy is the most common cause of what?
childhood obstructive sleep apnea
sx of tonsil & adenoid hypertrophy
-snoring, poor sleep, bedwetting, apneas, behavioral problems, hard to awaken -adenoids - otitis media, mouth breathing, chronic rhinorrhea, “nasal” speech
tx of tonsil & adenoid hypertrophy
tonsilectomy & adenoidectomy are curative
cause of epiglottitis
Hemophilus influenza type B (HIB)
What is epiglottis & what does it cause
Airway emergency! Causes epiglottis & supraglottic swelling (above vocal cords)
In what population(s) do you see epiglottitis
-rare in children since HIB vaccine -immunocompromised adults (alcoholics)
sx of epiglottitis
-sitting forward, drooling, cannot swallow secretions -inspiratory stridor (noise w/inhalation) means it’s above vocal cords -fever, “toxic”
Tx & special notes for epiglottitis
-Do NOT use tongue blade or scope -IV steroids, ibx, racemic epi -urgent anesthesia & ENT eval -may need intubation vs trach
Ankyloglossia
tongue-tie
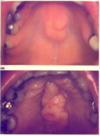
Torus Palatini

Ankyloglossia
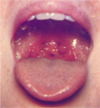
Obstructing tonsils (tonsil hypertrophy)

infectious mononucleosis
-tonsil enlargement & tonsil exudate common

Peritonsillar abscess
(local complication of strep)

Acute Tonsillitis
(tonsillar enlargement, erythema, exudate)

acute tonsillitis
(tonsillar enlargement, erythema, exudate)

viral pharyngitis/ tonsillitis

Candida (Oral Thrush)

aphthous ulcers (viral)


