Head & Neck Cancer (Dr. Mao) Flashcards
(50 cards)
Potential Skin and Mucosal sites for head/neck cancer
-nose cavity -paranasal sinuses -oral cavity -pharynx -larynx -thyroid glands -salivary glands
essentials of H&N cancer for PAs
-early diagnosis!!! (recognizing tumors) -pt. support -post-treatment surveillance (recognize tumor recurrence) -modifying causative patient behaviors (tumor prevention)
second most common skin cancer
squamous cell carcinoma
most common skin cancer
basal cell carcinoma
how does basal cell carcinoma spread?
spreads by local invasion (gets bigger and bigger), but does not tend to metastasize to distant sites
characteristics of BCC (how it looks)
-open sores -pearly! shiny bumps -red patch/pink growth -raised
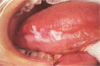
SCC presentation (how it looks)
-tend to be ulcerated -scaly -elevated growths with central depressions
Where does malignant melanoma originate?
melanocytes
Important acronym for diagnosis of malignant melanoma
Assymetric Border irregularity Color variation/multiple Diameter >6mm Enlarging, evolving
Types/names of malignant melanoma
-superficial spreading -lentigo melanoma -acral lentiginous -nodular
staging melanoma is based on
depth of invasion -clark’s levels or Breslow’s
Risk factors of skin cancer
-sun exposure -# moles -fam hx -immunocompromised (like kaposi’s sarcoma, etc) -precancerous lesions like actinic keratosis or dysplastic nevi
Presenting signs of cancer
-non-healing ulcer -enlarging mass, neck mass -pain -hoarseness, dysphagia -anosmia, nasal obstruction, serous otitis, cranial neuropathies, otalgia
risk factors of cancer
-tobacco & alcohol -viral (HPV, EBV) -immune suppression -nutritional deficiencies -occupational exposure like woodworking -gastroesophageal reflux
How much greater is risk of H&N cancer in smokers with nonsmokers
5-35x greater in smokers
___% of patients with H&N cancer smoke tobacco
85-90%
Alcohol increases risk of cancer by how much
2-15x
_________ are synergistic carcinogens
alcohol and tobacco
Potentially premalignant lesions in the head and neck
-leukoplakia -erythroplakia -actinic keratoses of skin -squamous carcinoma in situ -dysplasia -verrucous hyperplasia
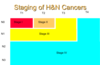
T in TNM staging system
T (0-4)
-size or characteristics of primary tumor
N in TNM staging system
N (0-3)
-size & location of cervical lymph node metastases
M in TNM staging system
M (0-1)
-distant metastases
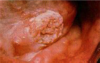
SCC of tongue

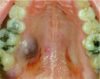
SCC of maxillary alveolar ridge