Unit 3.5.3 - Skeletal muscles are stimulated to contract by nerves and act as effectors Flashcards
What are the three types of muscle in the body?
Smooth, cardiac and skeletal
What is smooth muscle?
Muscle which contracts without conscious control, it is involuntary
What nervous system controls smooth muscle?
The autonomic nervous system
Where is smooth muscle found?
In the walls of internal organs
In which internal organ is smooth muscle not found?
The heart
What is cardiac muscle?
Muscle which contracts without conscious control, it is involuntary, however it is only found in the heart
What is skeletal muscle?
Muscle which contracts when you think about it, it is voluntary
What nervous system controls skeletal muscles?
Somatic nervous system
What are antagonistic muscles?
Muscles which do the opposite to each other, as one contracts one relaxes
Skeletal muscles are made up of long bundles of?
Muscle fibres
What is the cell membrane of a muscle fibre called?
Sarcolemma
What does the sarcolemma look like?
It folds inwards into the sarcoplasm
What is sarcoplasm?
A muscle cells cytoplasm
What are the It folds in the sarcolemma called?
Transerve (T) tubules
What is the function of the transverse (T) tubules?
Helps spread the electrical impulses throughout the sarcoplasm so the impulses can reach all parts of the muscle fibre
Why do muscle fibres have lots of mitochondria in them?
To provide the ATP needed for muscle contraction
What is the large vesicle inside the muscle cell called?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
To store and release calcium ions that are needed for muscle contraction
What is meant by muscle fibres are multinucleate?
They have many nuclei
What cylindrical organelle makes up muscle fibres?
Myofibrils
What are myofibrils made up of?
Bundles of thick myofilaments (myosin) and thin myofilaments (actin)
What do you see if you look at a myofibril under an electron microscope?
Alternative patterns of light and dark bands, the I band and A bands
What are the A bands made up of?
The thick myosin and some overlapping actin
What are the I bands made up of?
Only thin actin
What are the short repeating units in myofibrils called?
Sarcomeres
What is the end of each sarcomere marked with?
The Z-line
What is the middle of each sarcomere marked with?
The M-line
What is the middle of a sarcomere called where there is only myosin?
The H-zone
What theory explains muscle contraction?
The sliding filament theory
Describe the sliding filaments theory simply in two step.
1.) During contraction the sarcomere contracts and the myosin and actin filaments slide over one another 2.) Simultaneous contraction of lots of sarcomeres means the myofibrils and so muscles contract
What happens to the size of the A-band, I-band, H-zone and Z-lines during contraction?
The A-band stays the same length, but the I-band and H-zone get shorter, the Z lines get closer together
Describe what happens when an action potential arrives at a muscle cell to initiate a muscle contraction in three steps.
1.) The action potential depolarises the sarcolemma 2.) The depolarisation spreads down the T-tubules and to the sarcoplasmic reticulum 3.) This causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions into the sarcoplasm initiating the muscle contra ion
What happens when a muscle contraction is initiated in eight steps?
1.) Calcium ions bind to the troponin and changes its shape 2.) This pulls the attached tropomyosin with stand exposes the actin-myosin binding site 3.) The myosin head binds to it and forms an actin-myosin actin bridge 4.) Calcium ions also activate the enzyme ATPase which breaks down ATP into ADP and Pi releasing energy 5.) Some of this energy is used to make the myosin head kick and push the actin past the myosin 6.) After this the rest of the energy is used to break down the actin-myosin bridge and detach the myosin head from the binding site 7.) The head is re - cocked and is attached to another actin-myosin binding site further down 8.) The process is repeated shortening the sarcomere and causing the muscle contraction
What happens during muscle contraction when the muscle stops being stimulated?
1.) The calcium ions leave the binding sites on the troponin molecule and return back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum by active transport 2.) The troponin returns to its original shape 3.) Pulling the tropomyosin with it and blocking the actin-myosin binding sites 4.) The actin filaments then slide back to their original position relaxing the muscle
What are the three ATP can be generated for muscle contraction?
Aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration and ATP-phosphocreatine system
How is most of the ATP produced in aerobic respiration?
In the electron transfer chain
What is aerobic respiration good for? Any why?
Long periods of low intensity exercise because you need a constant supply of oxygen
How is most of the ATP produced in anaerobic respiration?
In glycolysis
What is the end product of glycolysis? And what happens to it?
Pyruvate, it undergoes lactate fermentation which produces lactate
Why is a build up of lactate bad?
It causes muscle fatigue
What is anaerobic respiration good for? And why?
Short periods of high intensity exercise, doesn’t require oxygen however lactate does build up so it isn’t good for too long
How is ATP made in the ATP-phosphocreaitne system?
Phosphorylating (adding a phosphate group) to ADP
What does PCr stand for?
Phosphocreaitne
Where does the phosphate group come from to add to ADP?
PCr
What is ATP-phosphcreatine system good for? And why?
Short bursts of vigorous exercise as the PCr runs out after a few seconds
What is the equation which produces ATP in the ATP-phosphocreaitne system?
ADP + PCr → ATP + Cr
What are two types of muscle fibres?
Slow twitch and fast twitch
What are slow twitch muscle fibres?
Muscle fibres that contract slowly and work for a long tie before getting tired
What are slow twitch muscle fibres good for?
Long distance running and maintaining posture
Where are high proportions of slow twitch muscles found? And why?
In the back and calves to maintain posture
How is energy released in aerobic respiration?
Through aerobic respiration
What do slow twitch muscle fibres have lots of? And why?
Lots of mitochondria and blood vessels to supply oxygen and produce ATP
Why are the mitochondria found mainly near the edge of slow twitch muscle fibres?
So theres a short diffusion pathway for oxygen from the blood vessels to the mitochondria
What colour do slow twitch muscle fibres appear? And why
Red - they have lots of a red coloured protein myoglobin which stores oxygen
What are fast twitch muscle fibres?
Muscle fibres that contract very quickly and don’t work of long before getting tired
What are fast twitch muscle fibres good for?
Short bursts of power like in sprinting and eye movement
Where are high proportions of fast twitch muscles found? And why?
In the muscles you use for fast movement like your arms and legs
What do fast twitch muscle fibres have lots of? And why?
Stores of PCr to produce energy quickly when needed
What colour do fast twitch muscle fibres appear? And why?
Whitish they don’t have many myoglobin
Draw a muscle cell, muscle fibre and microfibril.

Draw a diagram for the cross section of the A-band and H-zone.
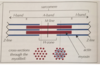
Label the different zone and bands of this sarcomere.




