Unit 2: Ch 3, 5 Flashcards
(125 cards)
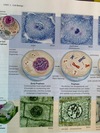
Anaphase
- 3rd phase of mitosis
- Sister chromatids are cleaved apart by microtubules and become daughter chromosomes
- Daughter chromosomes begin moving to opposite sides of the cell

Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Are the daughter cells formed at the end of Telophase II diploid or haploid?
Haploid
Are the two daughter cells formed at the end of Telophase I diploid or haploid?
Haploid
Blastopore
- Opening into the primitive gut formed at gastrulation
- Becomes the anus
What happens during blastula embryonic formation?
- Cells of the morula rearrange to form a hollow ball of cells
- Creates 2 different areas:
- Inner cell mass
- Trophoblast
- Creates 2 different areas:
- Blastula migrates into the uterus, where it burrows into the endometrial lining and latches on (implementation)
Blastula embryonic stage
- 3rd embryonic development stage
- Occurs ~ 5 days after fertilization
- Occurs in oviduct, but ends in uterus
- Creates hollow, fluid-filled ball of cells
Phases of the Cell Cycle
- Interphase
- G1
- S
- G2
- Mitosis
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
Cell development requirements
-
Cellular differentiation
- When cells become specialized in structure and function
-
Morphogenesis
- Produces the shape in tissues, organs, or the entire embryo during development
- Process of pattern formation, which directs how tissues and organs are arranged in the body
Cell Division
-
Mitosis
- Nuclear division
- Parent nucleus produces two daughter nuclei, each having the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
-
Cytokinesis
- Division of the cytoplasm
Cell Theory
- All organisms are made up of cells
- Cells are capable of self-reproduction
- Cells come only from preexisting cells
Types of Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells (non-membranous):
- Bacteria & Archaea domains
- Eukaryotic Cells (membranous):
- Eukarya domain
- Protists
- Animals
- Fungi
- Plants
- Eukarya domain
Cellular Respiration
- Occurs in both plant and animals
- It is the process by which cells convert ADP into ATP
Cellular Respiration Formula
carbohydrate + oxygen →
carbon dioxide + water + energy
Centrioles
- Occurs in the centrosome
- Help organize a miotic spindle for chromosome movement during animal cell division
Centromere
- The center of a chromosome
- Where sister chromatids of a chromosome are held together
Cervix
- Opening to uterus where sperm is deposited
Chloroplasts
- Double-walled
- Membrane-bound organelle in algae and plants with chlorophyll-containing membranous thylakoids
- Where photosynthesis takes place
Chromatin
- Contains DNA and proteins (histones)
- Description
- Loose, tangled, unorganized mass
- Too small to be seen with the light microscope, need an electron microscope to view
Chromosome
- Contains DNA and proteins (histones)
- Description
- Forms when the chromatin condenses into compact structures
- Compact rod-like structure
- Easily seen with a light microscope
Why do the cells at the end of Meiosis (I) not have the correct chromosome configuration?
- The two haploid daughter cells have the incorrect chromosome configuration
- Each chromosome should be made of only one chromatid
Cilia & Flagella
- Composition
- Function
- Microtubules
- Movement of cell
- 9 + 2 pattern of microtubules
Cleavage stage of embryonic development
- First stage of embryonic development
- Occurs immediately after fertilization
- Occurs in the oviduct
- A series of rapid mitosis without an increase in the size of the cells
- Increases the number of cells in the zygote
- Cell division without cytoplasmic addition or enlargement