Unit 2 - Carbohydrates Flashcards
Specification reference 2.1.2
A single sugar unit is known as a…
Monosaccharide (a monomer of sugar)
What is the chemical composition of a carbohydrate?
Carbon, oxygen, & hydrogen
When two or more monosaccharides are linked they form…
A polymer called a polysaccharide.
Glucose is a monosacharride composed of six carbons and is therefore a…
Hexose monosaccaride

Name the two structural variation of the glucose molecule
- Alpha (α) glucose
- Beta (β) glucose

How does alpha glucose differ from beta glucose?
The hydroxyl group (OH) on carbon 1 is in opposite positions
This affects the structure and properties of the polysaccarides when it bonds

How is a disaccharide formed?
- A condensation reaction
- 2 monosaccharides join together in a condensation reaction.
- The two hydroxyl groups interact - bonds are broken in the OH group and a new glycosidic bond is formed
- Water is released

Name this dissacharide…

Glucose + galactose = Lactose
Name this dissacharide…

Glucose + glucose = Maltose
Name this dissacharide…

Glucose + fructose = Sucrose
What is a pentose sugar?
Sugars that contain five carbon atoms

Which two pentose sugars are important components of biological molecules?
Ribose (sugar found in RNA) and Dexoyribose (sugar found in DNA)

What are the properties of starch?
- Compact
- Chemical energy store
- Easily digestible
- Made of amylose (mainly, 1-4 glycosidic bonds) and amylopectin (1-4 and some 1-6 glycosidic bonds)
- Insoluble does not create a water potential gradient (doesn’t cause water to enter cells by osmosis which would make them swell up)
Describe the properties and structure of amylose.
- Long chains of alpha glucose (unbranched)
- Joined by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
- Insoluble (does not create water potential gradient)
- Metabolically inactive
- Long chain of glucose that twists into a helix (compact for storage)
- Helix held together by hydrogen bonds
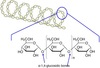
Describe the properties and structure of amylopectin.
- Long, branched chains of alpha glucose
- Joined by 1-4 glycosidic bonds (chains) and 1-6 glycosidic bonds (branches)
- 1-6 branching points occur approximately one in every 25 glucose subunits.
- Compact and idealy for storage
- Insoluable (do not affect water potential)
- Branches gives ‘free ends’ so glucose can be added or released quickly

Describe the properties and structure of glycogen
- Short, branched chains of alpha glucose
- Joined by 1-4 glycosidic bonds (chains) and 1-6 glycosidic bonds (branches)
- Compact and insoluble so good for storage
- Branching means many ‘free ends so glucose can be released (or stored) quickly

What is the function of glycogen?
- Main energy store in animals
- Stores soluble glucose that affects water potential as insoluble polysaccharide until needed

Describe the structure and properties of cellulose.
- Long, unbranched chain of beta (β) glucose
- Contains 1-4 glcyosidic bonds
- Beta (β) glucose molecules bond forming straight cellulose chains
- Every other glucose molecule is orientated at 180 degrees - e.g alternate beta (β) glucose are turned upside down.
- Chains are linked by hydrogen bonds forming strong fibres called microfibrils (compact)
- Microfibrils join to make macrofibrils, which combine to make fibres

Describe the function of cellulose?
- Cellulose is an important part of our diet as it is very hard to breakdown so if the fibre necessary for a healthy digestive system
- Cellulose provides structural support for cells
How is a disaccharide broken down?
- Hydolysis reaction
- Addition of water to hydrolyse the disaccharide into (useable) monomers
- Reactions are catalysed by enzymes
- These are the opposite of condensation reactions that form glycosidic bonds.



