UE1 Flashcards
1
Q
What does the axial skeleton contain?
A
- cranium
- spine
2
Q
What does the appendicular skeleton contain
A
- limbs
3
Q
What distinguishes the inferior and superior sides of the clavicle?
A
- superior is flat
- inferior is bumpy
4
Q
Identify

A
- red = AC joint (acromioclavicular)
- blue = GH joint (glenohumeral)
5
Q
Identify

A
- suprascapular notch
- coracoid process
- subscapular fossa
6
Q
Identify

A
- supraspinous fossa
- infraspinous fossa
- spine of the scap
- acromion
- suprascapular notch
7
Q
Identify

A
- supraglenoid tubercle
- glenoid fossa (cavity)
- infraglenoid tubercle
8
Q
Identify

A
neck of the scap
9
Q
Identify

A
- medial border
- lateral border
- superior border
10
Q
Identify

A
- superior angle
- inferior angle
- lateral angle
11
Q
Identify

A
- anatomical neck
- greater tuberocity
- surgical neck
- lesser tuberocity
12
Q
Identify

A
humeral head
13
Q
Identify

A
- bicipital groove
- lateral epicondyle
- medial epicondyle
- radial groove
14
Q
Identify

A
- radial fossa
- capitulum
- trochlea
- coronoid fossa
15
Q
Identify

A
olecranon fossa
16
Q
Identify

A
pectoralis major
17
Q
What are the two heads of the pectoralis major?
A
- clavicular
- sternocostal
18
Q
pectoralis major (origin)
A
- clavicular head = ant med 1/2 clavicle
- sternocostal head = sternum & costal cartilages
19
Q
pec major (insertion)
A
lateral lip of bicipital groove
20
Q
pec major (nerve)
A
lateral and medial pectoral n.
21
Q
pec major (action)
A
- ADD
- IR
- flexion/extension - depending on starting position and which head you are referencing
22
Q
Identify

A
pectoralis minor
23
Q
pec minor (origin)
A
ribs 3-5
24
Q
pec minor (insertion)
A
coracoid process
25
pec minor (innervation)
medial pectoral n.
26
pec minor (action)
* scap stabilizer
* depress
* protract
27
What two pathologies can be attributed to pec minor tightness?
* rounded shoulders (i.e. hockey & FH players)
* thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS)/neurovascular entrapment
28
Identify

subclavius
29
subclavius (origin)
1st rib costochondral joint
30
subclavius (insertion)
inferior surface of middle 1/3 clavicle
31
subclavius (innervation)
n. to subclavius
32
subclavius (action)
anchors/depresses clavicle
33
What is the clinical significance of subclavius?
* body's natural splint when fractured
* prevents NAV compromise
34
Identify

1. long thoracic n.
2. serratus anterior muscle
35
serratus anterior (origin)
ribs 1-8 lateral shaft
36
serratus anterior (insertion)
anterior surface of medial scap border
37
serratus anterior (innervation)
long thoracic n.
38
serratus anterior (action)
* scap protraction
* upward rotation
39
What is this pathology?

scapular winging
40
If the scapula can't rotate \_\_\_\_\_\_, then the arm cannot be \_\_\_\_\_\_.
* upwards
* abducted
41
Identify

deltopectoral triangle
42
What are the borders of the deltopectoral triangle?
* clavicle
* deltoid
* pec major
43
What does the deltopectoral triangle contain?
cephalic v.
44
Describe the cephalic v.
* superficial UE (seen over jacked biceps)
* dives deep to return to deep circulation
45
Identify

1. middle deltoid
2. posterior deltoid
3. anterior deltoid
46
deltoid (origin)
* spine of the scap
* clavicle
47
deltoid (insertion)
deltoid tuberosity on humerus
48
deltoid (action)
~ as a whole and individual sections ~
ABD
* anterior = flexion & IR
* middle = ABD
* posterior = extension & ER
49
deltoid (innervation)
axillary n.
50
Identify

teres major
51
teres major (origin)
inferior angle of scap
52
teres major (innsertion)
medial lip of bicipital groove
53
teres major (innervation)
lower subscapular n.
54
teres major (action)
* ADD
* IR
* extension
55
What muscles make up the rotator cuff?
SITS
* supraspinatus
* infraspinatus
* teres minor
* subscap
56
Identify

1. supraspinatus
2. infraspinatus
3. teres minor
4. subscap
57
Identify

1. teres major
2. teres minor
58
Identify

subscapularis
59
subscapularis (origin)
subscapular fossa
60
subscapularis (insertion)
lesser tuberosity
61
subscapularis (action)
IR
62
subscapularis (innervation)
lower subscapular n.
63
supraspinatus (origin)
supraspinous fossa
64
supraspinatus (insertion)
greater tuberosity
65
supraspinatus (action)
ABD
66
supraspinatus (innervation)
suprascapular n.
67
infraspinatus (origin)
infraspinous fossa
68
infraspinatus (insertion)
greater tuberosity
69
infraspinatus (action)
ER
70
infraspinatus (innervation)
suprascapular n.
71
teres minor (origin)
infraspinous fossa
72
teres minor (insertion)
greater tuberosity
73
teres minor (action)
ER
74
teres minor (innervation)
axillary n.
75
What is the collective action of the rotator cuff?
dynamic stabilization of GHJ
76
Identify

upper triangular space
77
What are the borders of the upper triangular space?
* teres minor
* teres major
* triceps long head
78
What are the contents of the upper triangular space?
circumflex scapular vessels
79
Identify

lower triangular space
80
What are the borders of the lower triangular space?
* teres major
* triceps lateral head
* triceps long head
81
What are the contents of the lower triangular space?
* radial n.
* deep artery of arm
82
Identify

quadrangular space
83
What are the borders of the quadrangular space?
* subscap/teres minor
* teres major
* triceps long head
* humerus
84
What are the contents of the quadrangular space
* posterior circumflex humeral a.
* axillary n.
85
Identify

triangle of auscultation
86
What are the borders of the triangular of auscultation?
* lats
* medial border of scap
* traps
87
What are the branches off the subclavian?
Vit C & D
* Vertebral
* Interal thoracic
* Thyrocervical
* Costocervical
* Dorsal scapular
88
Identify

1. axillary a.
2. brachial a.
3. radial a.
4. ulnar a.
5. deep a. of arm
89
Identify

1. brachial a.
2. radial a.
3. deep arch
4. superficial arch
5. ulnar a.
90
Identify

1. suprascapular a.
2. circumflex a.
3. subscapular a.
4. transverse cervical a.
5. dorsal scap a.
91
Identify

1. dorsal scap a.
2. circumflex scap a.
3. suprascapular a.
92
Identify

1. anterior circumflex humeral a.
2. posterior circumflex humeran a.
93
Identify

1. deep a. of arm
2. radial collateral
3. radial recurrent
4. ulna recurrent
5. ulna collateral
6. brachial a.
94
What forms the medial wall of the axilla?
* serratus anterior
* throacic wall
95
What forms the lateral wall of the axilla?
bicipital/intertubercular groove
96
What forms the anterior wall of the axilla?
pec major & minor
97
What forms the posterior wall of the axilla?
* scap
* subscap m.
* lats
* teres major
98
What forms the base of the axilla?
concave skin, subq tissue, & axillary fascia
99
What forms the apex of the axilla?
* 1st rib
* clavicle
* superior end of subscap
aka: cervicoaxillary canal
100
What are the sections of the brachial plexus?
Real (Athletic) Trainers Drink Cold Beer
* Roots
* Trunk
* Divisions
* Cords
* Branches
101
Which levels of nerves are NOT involved in the brachial plexus?
* C2
* T2
102
What are the nerves that emerge from the roots of the brachial plexus?
* long thoracic n.
* dorsal scap n.
103
Identify

1. dorsal scap n.
2. long thoracic n.
104
What are the three trunks of the brachial plexus?
* superior
* middle
* inferior
105
What are the nerves that emerge from the trunk of the brachial plexus?
* suprascapular n.
* n. to subclavius
106
Identify

1. superior trunk
2. suprascapular n.
3. n. to subclavius
4. inferior trunk
5. middle trunk
107
What are the divisions of the brachial plexus?
* anterior
* posterior
108
Identify

green = anterior
blue = posterior
109
What are the cords of the brachial plexus?
* lateral
* medial
* posterior
110
What merge to form the lateral cord?
anterior divisions from the superior and middle trunks
111
What merge to form the posterior cord?
posterior divisions from all 3 trunks
112
What merges to form the medial cord?
just a continuation of the anterior division of the inferior trunk
113
Identify

1. lateral cord
2. lateral pectoral n.
3. posterior cord
4. lower subscapular n.
5. thoracodordsal n.
6. upper scapular n.
7. medial cord
8. medial antebrachial cutaneous n.
9. medial brachial cutaneous n.
10. medial pectoral n.
114
Identify

1. musculocutaneous n.
2. axillary n.
3. radial n.
4. median n.
5. ulnar n.
115
What should you look for to orient yourself when identifying the brachial plexus?
Classic "M"
* musculocutaneous n.
* median n.
* ulnar n.
116
How can you distinguish the median n. from the other two n. of the classic "M"?
only one with two cords merging to form it
117
Identify

1. musculocutaneous n.
2. coracobrachialis
118
coracobrachialis (origin)
coracoid process
119
coracobrachialis (insertion)
middle humerus
120
coracobrachialis
| (innervation)
musculocutaneous n.
121
coracobrachialis
| (action)
GH flexion
122
Identify

* biceps brachii long head
* biceps brachii distal tendon
* bicipital aponeurosis
* biceps brachii short head
123
biceps brachii
| (origin)
long head: supraglenoid tubercle
short head: coracoid process
124
biceps brachii
| (insertion)
radial tuberosity
125
biceps brachii
| (action)
primarily supinates forarm; when supine, can flex elbow
126
biceps brachii
| (innervation)
musculocutaneous n.
127
Identify

biceps long head rupture
128
Identify

brachialis
129
brachialis
| (origin)
mid humerus
130
brachialis
| (insertion)
ulna
| (coronoid process)
131
brachialis
| (action)
elbow flexion
132
brachialis
| (innervation)
musculocutaneous n.
133
Identify

1. deep a. of arm
2. triceps long head
3. radial n.
4. triceps medial head
5. triceps lateral head
134
triceps
| (origin)
* long head: infraglenoid tubercle
* lateral head: posterolateral humerus
* medial head: middle posterior humerus
135
triceps
| (insertion)
olecranon process
136
triceps
| (action)
elbow extension
137
triceps
| (innervation)
radial n.
138
Identify

anconeus
139
anconeus
| (origin)
lateral epicondyle
140
anconeus
| (insertion)
lateral olecranon
141
anconeus
| (action)
elbow extension
142
anconeus
| (innervation)
radial n.
143
What geometric space does the axillary n. pass through?
quadrangula space
144
Identify

axillary n.
145
What cord does the axillary n. emerge from?
posterior
146
What does the axillary n. innervate?
* deltoid
* teres minor
147
What cord does musculocutaneous emerge from?
lateral
148
Describe the path of musculocutaneous n.
* pierces coracobracialis
* travels between biceps & brachialis
* continues to forearm
* forms lateral cutaneous n. of formarm
149
What does musculocutaneous n. innervate?
* coracobrachialis
* biceps brachii
* brachialis
150
Identify

1. corachobrachialis
2. musculocutaneous n.
3. brachialis
151
What cord does the radial n. emerge from?
posterior
152
Describe the path of the radial n.
* exits posterior inferior to teres major
* descends w/deep a. of arm in spiral groove then between med and lat heads of triceps
* wraps anteriorlyas it pierces lateral intermuscular septum
* passes anterior to elbow
153
Identify

radial n.
154
Identify

radial n.
155
Identify

median n.
156
What is the median n.'s innervation in the upper arm?
None, only innervates below the elbow
157
What cords does the median n. emerge from?
medial & lateral
158
Describe the path of the median n.
* follows brachial a.
* enters forearm via cubital fossa
159
Identify

ulnar n.
160
What cord does the ulnar n. emerge from?
medial
161
Describe the path of the ulnar n.
* follows brachial a.
* descends posterior to medial epicondyle
* enters forearm via cubital tunnel
162
Identify

1. coracoacromial ligament
2. acromioclavicular (AC) ligament
3. trapezoid
4. conoid
5. coracoclavicular ligament
163
What pathology is this?

Grade III AC Joint Sprain
164
What does, "I separated my shoulder" really mean anatomically?
AC joint injury
165
Describe a Grade I AC joint injury
AC joint sprain
166
Describe a Grade II AC joint injury
AC joint rupture
coracoclaviuclar sprain
167
Describe a grade III AC joint injury
AC and coracoclavicular rupture
168
What is different between these two XRs?
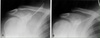
B was taken with axial distraction
169
Identify

1. coracohumeral ligament
2. transverse humeral ligament
3. slack for GH ABD
4. GH ligament (3 parts: sup, mid, inf)
170
What is the function of the transverse humeral ligament?
holds down long head of the biceps when contracted
171
Identify

1. coracoacromial ligament
2. coracoacromial arch
3. acromion
4. subacromial (SA) space
5. supraspinatus (cut)
172
What is compressed with GH ABD?
subacromial space ==\> supraspinatus
173
Mobility of the SC joint is critical for shoulder \_\_\_\_\_\_.
elevation


