Back Flashcards
Identify

- C7
- medial scapula border
- spine of the scap
- inferior angle of the scap
- upper trap
Identify

- costovertebral angle (CVA)
- T12
- lower trap
- lumbar paraspinal muscles
- iliac crest
- L4 (level)
- PSIS
- sacrum
What are the 4 regions of the vertebrae?
- cervical
- thoracic
- lumbar
- sacrum/coccyx
What is the function of the spine?
absorb shock
What are primary curves?
kyphotic
What are secondary curves?
lordotic
When/why do the secondary curves develop?
- cervical - hold head/sit upright
- lumbar - stand/walk
What are the motions of the spine?
- flexion
- extension
- lateral flexion
- rotation
Which are the typical vertebrae?
C3-L5
(all but 1st two)
Identify
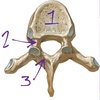
- body
- pedicle
- lamina
Identify

pedicles
Identify
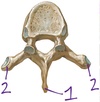
- SP (spinous process)
- TP (transverse process
Identify

- SP
- TP
What is the function of the SP & TP?
attachment and lever for spinal muscles
Identify

- superior articular process
- inferior articular process
Identify

- superior vertebral notch
- inferior vertebral notch
- intervertebral foramen
Identify

- vertebral foramen
Vertebral ______ collectively form the vertebral ______.
- foramina
- canal
Identify

- C1 (atlas)
- C2 (axis)
Helpful Hint: Atlas, the Greek god, holds up the world therefor C1 articulates with the occiput and it rotates on an axis(C2)
Identify
and
What view is this?

C1
- anterior arch
- anterior tubercle
- posterior arch
- posterior tubercl
- superior facet for articulation for occipital condyles
Superior view
Identify
and
What view is this?

C1
- posterior arch
- posterior tubercle
- anterior arch
- anterior tubercle
- inferior facet articulation for C2
Inferior view
Identify

- transverse foramen
- TP
Which are the atypical vertebrae?
- C1
- C2
Identify

dens
In _______ & ________ patients, the ______ of C2 is underdeveloped.
- RA
- down syndrome
- dens
Identify

- body
- vertebral foramen
- TP
- SP
Describe C3-C5 SP
bifid
Describe the body of a cervical vertebra
- small
- wider laterally v. AP (rectangular)
Describe the vertebral foramen of a cervical vertebra
- triangular
- large
What goes through the transverse foramen of the c-spine?
- vertebral a.
What type of vertebrae is this?

thoracic
What type of vertebrae is this?

cervical
What type of vertebrae is this?

lumbar
Describe the body of a thoracic vertebrae
- heart shaped with costal facets
Describe the body of a lumbar vertebrae
- kidney shaped
Describe the vertebral foramen of thoracic vertebra
- circular
- small vs. cervical or lumbar
Describe the TP of thoracic vertebrae
- long
- facets for rib articulations
Describe the SP of thoracic vertebrae
- long
- extend inferiorly to the segment below
Describe the vertebral foramen of lumbar vertebrae
- triangular
- larger than thoracic, smaller than cervical
Describe the SP of lumbar vertebrae
- sturdy
- hatchet shape
Identify

- accessory process
- mammilary process
How is the sacrum created?
fusion of lower vertebrae
What is sacralization?
L5 fuses to sacrum
What is lumbarization?
S1 fuses to L5
Identify

- apex
- base
Identify
(ignore #3 - my bad!)

- promontory
- ala
Identify

- median sacral crest
- sacral cornu (horns)
- sacral hiatus
Identify this space

sacral canal
Identify

coccyx
Identify the curves

- kyphotic
- lordotic
What is formed by the failure of the lamina of S5 to fuse?
sacral hiatus
What part of the individual vertebrae is the sacral cornu?
pedicles of S5
How many vertebrae make up the coccyx?
4
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5
What is the most common pathology of the coccyx and what is the etiology?
- fracture s/p fall
What is the pathology depicted on the right?

lordosis
What is the pathology depicted on the right?

kyphosis
(common in geriatrics)
What is the pathology depicted on the right?

scoliosis
*Describe scoliosis*
lateral deviation with rotary component
How do you evaluate for scoliosis?
- stand behind the patient and ask them to touch their toes
- presence of a rib hump indicates rotation
- uneven curve that straightens with flexion = muscle imbalance, not scoli
What are the treatment options for scoliosis?
- observation
- brace
- surgery
Identify

facet joint
What makes up a facet joint?
synovial joint between superiof and inferior facets of articular process
Identify

facet joint
What is the function of an intervertebral (IV) disc?
shock absorption
Where is there no disc?
- between occiput & C1
- C1-C2
Identify

- nucleus pulposus
- annulus fibrosis




















































