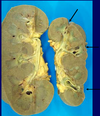
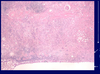
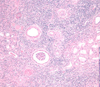
Tubulointerstitial Dz Pathology Flashcards

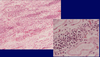
Acute TID; characterized by active inflammation; see eosinophils and lymphocytes (left) and neutrophils (right)

Normal kidney tubules and glomerulus

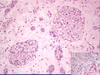
Tubular necrosis; necrotic cells slough off into the tubular lumen; seen in Acute TID

Edema; seen in interstitium as foamy/vacuoles between tubules. Characteristic of Acute TID

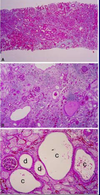
Interstitial fibrosis; seen in Chronic TID; fibrinous tissue is very pale and separates the renal tubules
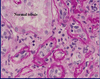
Tubular atrophy; tubules shrink in diameter, the epithelium simplifies and the basement membrane thickens; seen in Chronic TID where tubules atrophy in response to slow ischemia

Chronic inflammation; uniform small lymphocytes which are remnants of a previous active inflammation. Seen in Chronic TID.
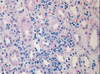
Acute TID; active inflammatory cells in interstitium: lymphocytes, neutrophils, plasma cells, macrophages

Chronic TID; fibrosis of interstitium; tubular atrophy
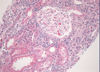
Interstitial Nephritis; inflammation localized to interstitum primarily, with minor involvement of the tubules

Acute interstitial nephritis; infiltration of plasma cells, eosinophils, lymphyocytes, macrophages; also see edema
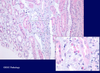
Acute interstitial nephritis; diffuse infiltration of inflammatory cells; tubules relatively unaffected.
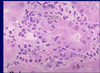
Acute allograft rejection; form of acute interstitial nephritis; where lymphyocytes actually infiltrate the tubules

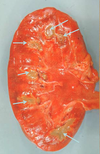
Acute Tubular Necrosis (main photo); normal photo in bottom Right corner; ATN most commonly affects the Prox. CT and can be caused by ischemia or toxins

Ischemic ATN; caused by shock, hypovolemia, and hypoxemia; usually milder than toxic ATN, the tubular epi. cells fall off individually.