Trauma and Critical Care Flashcards
Identify the Maneuver to establish an airway

Jaw-thrust Maneuver
What are the 4 regions to scan in Focused Assessment Sonography in Trauma (FAST)
Pericardial sac
Hepatorenal fossa
Splenorenal fossa
Pelvis or pouch of Douglas
at what PaC02 level will a patient experience cerebral ischemia
Identify the BLADDER PRESSURES at the following Conditions:
Mildly elevated
Moderately elevated
Severely elevated
Normal
Normal after abdominal Surgery
Mildly elevated 10-20mmHg
Moderately elevated >20mmHg
Severely elevated >40mmHg
Normal 0mmHg
Normal after abdominal Surgery 0-15mmHg
Criteria for Brain Death
- GCS 3
- non reactive pupils
- absent brainstem reflex (oculocephalic, corneal, Doll’s eye gag)
- no spontaneous ventilatory effort on formal apnea testing
Ancillary Studies may confirm diagnosis of brain death by (3)
- EEG no activity at high gain
- ICP exceeds MAP for ≥ 1 hour
- cerebral angiography
Develops when the pressure within an osteoclastal compartment of muscle causes ischemia and subsequent necrosis
Compartment Syndrome
What is a late sign of Compartment Syndrome?
Absence of pulse
Causes of IAH and Abdominal Compartment Syndrome include:
- intraperitoneal blood
- interstitial edema from fluid resuscitation peritonitis
- ascites
- gaseous bowel distention
Implies no possibility of recovery of brain function
Brain Death
Indications for using Mannitol
- acute neurologic deterioration (1g/kg)
- dilated pupil
- hemiparesis
- LOC while being observed
Blast Injury Mechanism
Where the effects of the blast wave itself is considered
Primary Blast Mechanism
Determine the boundaries of the 3 neck zones

- Zone 1 - thoracic inlet to cricoid cartilage
- Zone 2 - cricoid cartilage to mandible
- Zone 3 - angle of mandible to base of skull
Damage Control is Indicated when?
at the Manifestation of “bloody vicious cycle”
a.k.a. Atlas fracture

Jefferson Fracture
Large defects of chest wall that remains open can result into open pneumothorax where there is a chest wound that sucks air from the environment and into the pleural space
Open Pneumothorax
what are the key phases in damage control?
Preoperative
Operative
Resuscitation
Re-operate
6 steps in Adjuncts to Primary Survey and Resuscitation
STEP 1 ABG analysis and ventilatory rate
STEP 2 CO2 monitoring
STEP 3 ECG monitoring
STEP 4 Urinary cath, gastric cath
STEP 5 Radiologic examination
STEP 6 FAST or DPL
What should be the position of the patient’s neck during airway management?
A. Hyperflexed
B. Hyperextended
C. Rotated
None of the above
What are the 2 fluids of choice when Starting Fluid resuscitation?
IV bolus of Isotonic Crystalloid
Lactated Ringer’s
What are the common ways to manage breathing of the patient?
A. Administer high-concentration oxygen
B. Mask ambubagging
C. Alleviate tension pneumothorax
D. Seal open pneumothorax
E. C02 monitoring
F. Pulse oxymeter
Identify the fracture
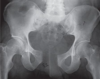
Open Book Fracture
the orientation of the longitudinal axis of the missile to its trajectory
Yaw
Ways to establish Patent Airway (4) in Step 2 (Management)
A. Chin-Lift or jaw-thrust maneuver
B. Clear airway of foreign body
C. Insert oropharyngeal airway
D. Establish definitive airway






















