Topic 7 CNS Flashcards
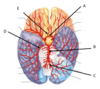
What is the name of the structure labelled E?
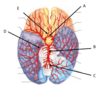
anterior cerebral artery
Describe the three sections of the brain stem.
- As spinal chord enter foramen magnum it is called the brain stem.
-
superiorly it consists of:
- medulla oblongata
- pons (latin = bridge) - links cerebellum to cerebrum
- midbrain

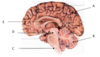
What is the name of the structure labelled D in the diagram?
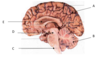
Midbrain
What is the innermost layer of the brain and spinal cord meninges called?
The pia mater (delicate mother)
Very fine transparant layer that adhers to surface of brain, contains blood vessels.
DUR-AR-PIA

What is the true spinal cord?
- true spinal cord runs from the foramen magnum to the 3rd or 4th lumbar vertebra ( at the conus medullaris)
- part of the CNS - start and finish of the PNS as senosyr and motor nerves travel to and from.

What are dural venous sinuses?
- Large dilated blood vessels (spaces) formed between the periosteal and meningeal layer of the dura mater.
- Contain venous blood that empties into the internal jugular vein
- Arachnoid granules protrude from the sub-arachnoid space into into them to transfer CSF that has already circulated the CNS

What is the ventricular system of the brain comprised of, and what is its function?
The brain’s ventricular system is comprised of a series of ventricles and ducts in the brain.

Its function is to produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and circulate it around the tissues of the CNS.
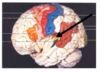
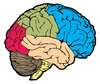
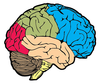
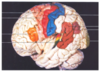
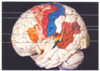
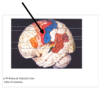
What is the name of the cerebral lobe in cream on the diagram?

Temporal lobe
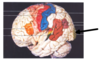
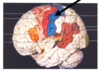
Where is the primary sensory cortex located on the diagram below? What is its function?
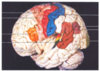
- posterior to central sulcus
- recieves sensory information from whole body
What is the name of the structure labelled M below? What does it contain?

Spinal nerve
The dorsal nerve roots (sensory) and ventral nerve roots (motor) combine to form spinal nerves.

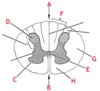
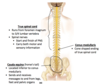
What is the name of the area of the spinal cord labelled C? What type and part of neurons does it contain?
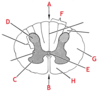
(i.e. motor/sensory, cell bodies/axons/dendrites)
Anterior horns of grey matter
Contains cell bodies of motor neurons.

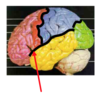
Where is the primary motor cortex of the brain located on the diagram below? What is its function?
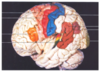
- Red area in front of central sulcus
- Sometimes called pre-central gyrus
- Controls motor function for the whole body
What is the name of the structure labelled A in the diagram?

Cerebrum
What is the diencephalon and what two important structures does it contain?
- The diencephalon is located between the mid brain and the lateral ventricle.
- It contains the thalmus (directs traffic from brain stem to correct area of cortex) and the hypothalymus (part of endocrine system that controls homeostasis)

What is the name of the structure labelled B in the diagram?

Cerebellum
What is the conus medullaris?
The cone shaped ending of the true spinal cord (around 3rd/4th lumbar vertebra)

What is the name of the area of the spinal cord labelled E? What does it contain?

Central canal
Contains CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
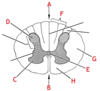
What are the two layers of the dura mater called and where are they located?
The outermost layer is called the periosteal layer
The innermost layer is called the meningeal layer

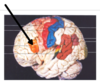
What is the name of the structure labelled C?
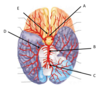
vertebral artery
What is the difference between the distribution of grey matter in the brain versus the spinal cord?
- In the brain the grey matter is located superficial to the white matter
- in the spinal cord the grey matter is located deep to the white matter (in an ‘H’ shape)

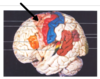
Describe the path of arterial blood supply to the posterior brain.
► L and R vertebral arteries (travel up brain stem and through foramen magnum)
► Combine to form basilar artery
► branches into:
- Left posterior cerebral artery
- Right posterior cerebral artery

What is the name of the structure labelled H below? What is it carrying?

Posterior (dorsal) root
The posterior (dorsal) root is carrying sensory fibres from the body to the cell bodies in the posterior horn of grey matter which then travel up the spine cord.

What is the ventricular system in the brain continuous with (down the spinal cord)?
Central canal of the spinal cord

What is the space between the arachnoid and pia mater meninges called. What does it contain?
Sub-arachnoid space
Contains circulating cerebralspinal fluid (CSF)

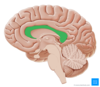
What is the name of the cerebral lobe in green on the diagram?

Parietal lobe
What is the name of the area of the spinal cord labelled D? What type and part of neurons does it contain?

(i.e. motor/sensory, cell bodies/axons/dendrites)
Posterior horns of grey matter
Contains cell bodies of sensory neurons.