Topic 10 Ear, hearing and balance Flashcards
What two membranes make up the roof and the floor of the scala media?
Roof - Vestibular/Reissner’s membrane
Floor - Basilar membrane

Describe how the vibrations from the stapes against the oval window are transferred to the spiral organ of Corti.
- The vibrations from the stapes against the oval window causes displacement of the perilymph in the Scala vestibuli (ascending part of cochlea)
- This causes the Vestibular/Reissner’s membrane to vibrate
- The vibrations then travel through the endolymph of the Scala media and down to the basilar membrane
- Movement of the basilar membrane displaces hair cells in the spiral organ of Corti.

What is the name of the structure labelled 4 in the diagram?

Cochclea
How is dynamic movement of the head communicated to the brain?
- The semicircular canals also contain hair cells that are embedded in a gel-like membrane (cupula) which is surrounded by endolymph.
- Movement of the endolymph in the canal pushes on the cupula, bending the hairs of the hair cells.
- Depending on the plane of movement, the hair cells in the relevant canal will bend (no otoliths as no relative to graviity)
- The mechanical action activates an electrical potential that is transferred to the dendritic nerve endings.
- They then transmit the signal a short distance to the cell bodies in the Vestibular ganglion.
- The impulse then travels along their axons, forming the Vestibular nerve.
- The Vestibular nerve combines with the Cochlear nerve carrying hearing information, to form the vestibulocochlear nerve (CNVIII).

Describe how vibration of the basilar membrane is turned into an electrical potential in the hair cells of the spiral organ of Corti.
- movement of the basilar membrane displaces hair cells in spiral organ of Corti
- Vibration of the hairs on the hair cells causes them to bend (becuase they are attached to the tectorial membrane)
- This mechanical action causes ions to flow from the endolymph into the cell body of the hair cell - causing an electrical potential

Idenitfy the structure labelled A

epitympanic recess
What is the round window? What is its function?
- The round window is small opening to the inner ear, inferior to the oval window.
- it is covered by a flexible membrane (secondary tympatic membrane)
- Allows for perilymph displacement in the inner ear so that the stapes can transfer vibrations.
- Relieves pressure induced by sound waves in the inner ear.
What are the names and functions of the two muscles in the ear?
- Tensor tympani
- Stapedius
- muscles contract when a sudden loud sound occurs
- stiffens the ossicles and reduces the vibration transfer from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear (called sound attenuation reflex)
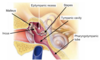
What is the bony labyrinth of the inner ear? What are its three main parts?
- The bony labyrinth is a series of tunnels and chambers in the petrous part of the temporal lobe (filled with fluid called perilymph)
- It consists of 3 parts:
- semicircular canals
- vestibule
- cochlea

What is the difference between the function of the utricle and the saccule?
- the utricle detects forward and backwards movement in relation to gravity (driving a car)
- the saccule detects up and down movement in relation to gravity (going up and down in an elevator)
Where is the Scala media (cochlear duct) located?
Between the Scala tympani and the Scala vestibuli in the Cochlea.

What are the middle ear ossicles, and where are they located?
The 3 ossicles are:
- Malleus
- Incus
- Stapes
- Located in the tympatic cavity of the middle ear
What is the spiral organ of Corti, and where is it located?
The spiral organ of Corti is a region on the floor of the Scala media comprised of hair cells that rest on the surface of the basilar membrane.

What are the two systems in the in the inner ear that regulate balance?
-
Static system (utricle and saccule)
* detects movement when head is stationary in relation to gravity (e.g. elevator, driving a car) -
Dynamic balance (3 semicircular canals)
* detects movement of head in all 3 planes
Describe how sound waves initially reach the tympanic membrane.
- Sound waves are funnelled into the external ear by the auricle
- They pass down the External Auditory Meatus (ear canal) of the temporal bone.
- Reaching the end of the ear canal, the sound waves cause vibration of the tympanic membrane.
How do the utricle and saccule communicate static movement to the brain?
- the utricle and saccule also contain hair cells.
- When static position changes, there is movement of the gelatinous matrix, which sits on top of the hair cells, aided by the otoliths (crystal like structures that move in responce to gravity).
- This causes bending of the hair on the hair cells in relation to the cell body.
- The mechanical action activates an electrical potential that is transferred to the dendritic nerve endings.
- They then transmit the signal a short distance to the cell bodies in the Vestibular ganglion.
- The impulse then travels along their axons, forming the Vestibular nerve.
- The Vestibular nerve combines with the Cochlear nerve carrying hearing information, to form the Vestibulocochlear nerve (CNVIII) before exiting the temporal bone through the Internal Auditory Meatus.

What fluid contains a specialised ion concentration to aid nerve potential activation?
Endolymph
What happens to excess sound waves so that they don’t damage the cochlea?
The travel back down the perilymph of the Scala tympani to the round window where they are absorbed.

Identify the structure labelled C

tympanic cavity
What is the name of the structure labelled 10 in the diagram?

Incus (anvil)
What is a macula?
What is the difference between the utricular macula and the saccular macula?
- A macula is a specielised patch of cells containing hair cells, supporting cells and a gelatinous matrix.
- The utricular macula’s hair cells are positioned at right angles to the base of the skull (vertical) so only move with forward/backward motion
- The saccula macula’s hair cells are positioned parallel to the base of the skull (horizontal) so only move with up/down motion.
What is the name of the structure labelled 2 in the diagram?

Auditory tube/
Pharyngotympanic tube/
Eustachian tube
Identify the structure labelled D

pharygotympanic/auditory tube
What is the name of the structure labelled 17 in the diagram?

Semicircular canals
What is the name of the structure labelled 18 in the diagram?

Stapes (stirrup)
What are the 3 parts of the ear, and what are there general functions?
- Outer ear - captures sound waves
- Middle ear - delivers sound vibrates to the inner ear
- Inner ear - converts vibrations into neural impulses
What is the name of the structure labelled 6 in the diagram?

External acoustic meatus (ear canal)
What are the two chambers of the bony labyrinth?
- Scala vestibuli - assending part
- Scala tympani - descending part
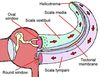
Identify the structure labelled B

Incus
What is the pharygotympanic tube, and what is its function?
- canal between the middle ear and the nasopharynx
- allows air pressure in the middle ear to be equilised (with atmospheric pressure) by allowing air to enter and leave the tympanic cavity.
- this important to allow the tympanic membrane to move freely (no suction)
Describe how vibrations of the tympanic membrane are transferred to the inner ear.
- The three Auditory Ossicles in the middle ear transfer the vibrations from the Malleus (connected to umbo (cone) of tympanic membrane)-> Incus -> footplate of the Stapes
- The footplate of the stapes vibrates againsts the oval window, causing displacement of the perilymph in the Scala vestibuli (ascending part of cochlear)

What is the name of the structure labelled 22 in the diagram?

Tympanic membrane (ear drum)
What is the name of the structure labelled 8 in the diagram?

Ganglia of the vestibular nerve (one for vestibule, one for semicircular canals)
Describe how the electrical potential occuring in the hair cell of the spiral organ of Corti reaches the brain.
- The electrical signal created in the hair cell is transferred directly to dendritic nerve endings that are attached to its base.
- The signal travels a short distance to the cell bodies in the Cochlear (spiral) ganglion.
- The axons from these nerves combine to form the Cochlear nerve.
- The Cochlear nerve combines with the Vestibular nerve to form the Vestibulocochlear nerve (CNXIII) which then travels through the internal auditory meatus to the brain stem.
- A second neuron directs the signal to the thalamus, and a third neuron to the primary auditory cortex in the temporal lobe.

What is the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear? What are its three sections and their general function?
The membranous labyrinth is a series of fluid filled sacs and ducts suspended within the bony labyrinth (filled with endolymph)
It has 3 sections:
- utricle and saccule of the Vestibule - static balance (gravity)
- three semicircular ducts - dynamic balance (head)
- cochlear duct (scala media) - hearing

What is the name of the structure labelled 13 in the diagram?

Lobule/lobe (of the auricle - outer ear)
Which three muscles are used to equilise air pressure in the middle ear?
- tensor veli palatini
- levator veli palatini
- salpingopharyngeus
All connected to pharyngotympatic/Eustachian tube
Connected to palate -> swallowing and yawning facilitates equilisation
What is the name of the structure labelled 14 in the diagram?

Malleus (hammer)


