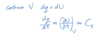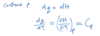Thermodynamics Flashcards
(31 cards)
Ideal gas law
pV=nRT
ideal gas law units
p
v
n
r
t
P= Nm-2
V= m3
n= mol
R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1
T= K (+273)
when does the ideal gas law work
WORKS WELL FOR GASES AT HIGH TEMPERATURE
m3 to dm3
1 m3 = 1000 dm3
partial pressures

Why is the ideal gas law not accurate
1) neglects molecular interaction
2) neglects the volume of molecules
Compressiong factor
The compressibility factor (Z) is a correction factor which describes the deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behaviour. It is simply defined as the ratio of the molar volume of a gas to the molar volume of an ideal gas at the same temperature and pressure. It is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the ideal gas law to account for the real gas behaviour.
When is the deviaion from ideal gas law is significant
In general, deviation from ideal behaviour becomes more significant the closer a gas is to a phase change, the lower the temperature or the larger the pressure.
Compression factor eqn

Real gas law and units
a and b change as molecular size increases

Internal energy U

definition and formula of enthalpy
H = U + pV
The enthalpy of a substance is a measure of the total
energy of a thermodynamic system.
It includes the internal energy (sum of kinetic and potential energies), plus an additional term, pV (which is the energy required to “make room for it” by displacing its surroudings).
Energy transferred as heat at constant pressure = enthalpy change H
energy conservation
In chemical changes, energy can be converted from one form to another but not destroyed
=> i.e. energy conservation
Changes to the internal energy of a system
1) heat transfer (q) to and from surroundings (enthaly change)
2) work done (w) (on or by system)
changes in internal energy formula
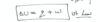
Effect of heat transfer on internal energy
1) surrounding –> system
2) system –> surrounding
1) surrounding –> system q= +ve /_\ U increase
2) system –> surrounding q= -ve /_\ U decrease
work formula

/_\ U formula

Use of differntials in chemistry
check notes pg 14

ideal gas and the First Law Constant volume change (isochoric)
dV = 0 dw = -pdV = 0
/_\U = q

ideal gas and the First Law Constant pressure change (isobaric)
dw = -pdV w = - ∆ pdV
w =-p ∆dV = -p ∆V (as p is constant)
∆U= q-p∆V ∆U =∆H - p ∆V
ideal gas and first law No heat change (adiabatic)
q =0
∆U = w
ideal gas and first law Constant temperature change (isothermal)
∆U = 0
q = -w

Heat capcity