The Urinary System Flashcards
(14 cards)
What pathway does urine take in the body?
Urine is created in the kidneys > passes down the ureter > stored in the bladder > expelled through the urethra
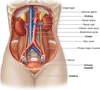
Name these features


Where are the kidneys located?
- Posterior abdominal wall
- Retroperitoneal (behind the parietal peritoneum)
- Extend from the level of the 11th or 12th thoracic vertebra to the 3rd lumbar vertebra
- Receive some protection from the lower two ribs
- Right kidney is slightly lower due to the liver pressing on it

What are these coverings?

- A & B: Renal fascia - connective tissue covering which anchors to abdominal wall
- C: Perirenal fat capsule - cushions kidney
- D: Renal capsule - encloses kidney

Name these features?


Name these features?

- A: Renal capsule
- B: Renal pyramids
- C: Renal cortex
- D: Renal medulla
- E: Renal artery
- F: Renal vein
- G: Renal column
- H: Renal papilla
- I: Major calys
- J: Renal pelvis
- K: Ureter

How does the kidney function?
- Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery.
- The nephrons then work through a two-step process. The glomerulus lets fluid and waste products pass through it. The glomerulus also prevents blood cells and large molecules, mostly proteins, from passing through.
- The filtered fluid then passes through the tubule, which sends needed minerals back to your bloodstream and removes wastes. Cleaned blood returns to the body by the renal vein.
- The final product becomes urine. This drips slowly into the renal papilla and then passes through to the calyx which is the extended opening of the ureter




Urinary bladder
What is the difference in bladder position between women and men?
In males: the bladder lies anterior to the rectum
- between pubic symphysis and rectum
- Superior to prostate gland
In females: the bladder lies just anterior to the vagina and uterus
- between pubic symphysis and uterus and vagina

What are the parts of the urinary bladder?
- Apex, base, inferolateral surfaces
- Trigone
- Ureters - oblique entry
- Urethra
- Detrusor muscle

What is the trigone?
In the inferior of the bladder, openings for both ureters and the urethra define a triangular region on the posterior wall called the trigone.
The trigone has a rich network of nerves so the bladder can sense how full it is.

What are the detrusor muscle and the urogenital diaphragm?
Muscles of the bladder
- Internal urethral sphincter: This is an involuntary sphincter of smooth muscle that keeps the urethra closed when urine is not being passed and prevents dribbling of urine between voidings
- Is more superiorly located
- External urethral sphincter: surrounds the urethra within the sheet of muscle called the urogenital diaphragm. This external sphincter is a skeletal muscle used to inhibit urination voluntarily until the proper time.
- Is more posteriorly located

What happens when the bladder fills 200ml?
When the bladder fills with 200ml of urine, stretch receptors transmit impluses to the CNSW and produce a reflex contraction of the bladder (PNS)


