Eye & Orbit Flashcards
(22 cards)
What are the major features of the eyelid?

Tarsal plates: give the eyelids their curved shape and serve as attachment sites for the eye-closing muscle orbicularis oculi
Levator palpebrae superioris (“lifter of the upper eyelid”) is the skeletal muscle that voluntarily opens the eye. Runs from the orbit to the tarsal plate

What is this feature?

Conjunctiva: is a transparent mucous membrane that covers the inner surfaces of the eyelids as the palpebral conjunctiva and folds back over the anterior surface of the eye as the bulbar conjunctiva

What are the features and function of the lacrimal apparatus?

Function: moistens eye
The lacrimal gland produces lacrimal fluid which enters the conkunctival sac through excretory ducts.
Blinking spreads the fluid across the eyeball through the lacrimal punctum which empties into a small tube the lacrimal canaliculus.
It then flows through the lacrimal sac and flows into the nasolcrimal duct which empites into the nasal cavity.

What are the extrinsic eye muscles?
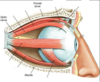
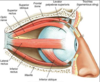
How do the muscles control eye movement?

Lateral rectus: Moves eye laterally
Medial rectus: Moves eye medially
Superior rectus: Elevates eye and turns it medially
Inferior rectus: Depresses eye and turns it medially
Inferior oblique: Elevates eye and turns it laterally
Superior oblique:Depresses eye and turns it laterally

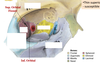

- A: Optic nerve
- B: Retina
- C: Choroid
- D: Sclera


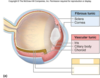
- The fibrous layer is the most external layer.
- It consists of dense connective tissue arranged into two different regions:
- Sclera
- Cornea


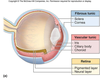
- A: Vascular Layer
- B: Iris
- Sphincter pupilae (bright light, near vision)
- Dilator pupilae (dim light, far vision)
- C: Ciliary body
- Muscular (focuses lens)
- Connects choroid with iris
- Ciliary process secretes aqueous humour
- D: Choroid
- Vascular, darkly pigmented membrane
- Brown colour - from melanocytes
- Prevents scattering of light rays


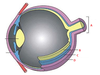
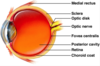
- A: lens
- B: iris
- C: cornea
- D: pupil
- E: aqueous
- F: conjunctiva
- G: sclera


- A: vitreous
- B: Retina
- C: Macula
- D: Optic nerve



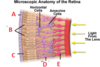
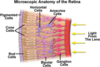
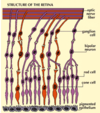
- A: Pigmented epithelial cells
- B: Cone cells
- C: Rod cells
- D: Bipolar cells
- E: Gengillion cells
What are the function of rods and cones of the retina?
- Rods
- More light sensitive
- Vision in dim light (grey and fuzzy)
- Cones
- High acuity, colour vision
- 3 types: blue, green, red

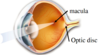
- A: Macula
- Macula lutea
- Contains mostly cones
- absorbs excess blue and UV
- Macula lutea
- Optic disc
- nasal side of fovea
- no retina
- blind spot
- ganglion cells exit retina to form optic nerve
What is this feature and what is its function?

Fovea centralis
- centre of macula
- contains only cones
- max visual acuity
- in anterior-posterior axis

- A: Macula lutea with fovea centralis at the very centre
- B: Central retinal a. (branch)
- C: Central retinal v. (branch)
- D: Optic disc

What are the fluid holding chambers of the eye?
- Anterior chamber
- between cornea and iris
- Posterior chamber
- between iris and lens
- aqeous humor
- renewed continuously
- supplies nutrients to lens and cornea
- Posterior segment
- vitreous humour
- transmits light
- supports lens
- maintains intraocular pressure
- vitreous humour
- Lens
- Thick, transparent, biconvex disc
- Held in place by its ciliary zonule


- A: Retina
- B: Optic nerve
- C: Optic chiasm (crossed and uncrossed)
- D: Lateral geniculate nucleus (thalamus)
- E: Primary visual cortex

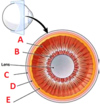
- A: Ciliary muscle
- B: Suspensory ligaments
- C: Sclera
- D: Choroid
- E: Retina



