The Medicine Semester 1 Flashcards
What is the formula for molarity?

What is the formula for molality?

What is the formula for equivalents?
Eq= ionic valency x number of ions in solution
What shape and bond angle does an sp3 hybridised molecule have?
Tetrahedral shape with a 109 degree bond angle
What shape and bond angle does an sp2 hybridised molecule have?
Planar (trigonal) shape with a 120 degree bond angle
What shape and bond angle does an sp hybridised molecule have?
Linear shape with 180 degree bond angle
Which is more stable and why?

Staggered conformation is more stable
Less energy and reduced rotation as H atoms are as far away from eachother as possible
What is the dihedral/torsion angle?
The angle formed between two intersecting planes
In chair conformation which is preferred? Axial or equatorial?
Equatorial as it provides less steric strain
What causes E/Z isomerism and how are the isomers distinguished?
Lack of rotation around a double bond causes E/Z isomerism
If the two groups with the highest priority (largest molecular weight) are on the same side of the double bond, the Z isomer has formed.
If they are on opposite sides, it is the E isomer.
In optical isomerism how are the R/S isomers distinguished?
Group with the lowest priority (usually H should be drawn facing backwards
The three other groups should be numbered in order of priority, if the numbers read in a clockwise direction (1,2,3) it is the right handed (R) isomer
If they read in an anticlockwise direction, it is the left handed (S) isomer
What quantities are given for the differing solubilities?
(Think parts of solvent:1 part of solute)

Define solubility
The maximum amount of solid that can be dissolved
Define dissolution
The transfer of molecules from solid to liquid state
What is the common pharmaceutical name for the solvent within a drug?
The vehicle
What causes solubility to decrease?
Increased molecule size
With smaller surface area
With presence of hydrophobic regions
Presence and position of substituents
What other factors affect solubility?
Solid state (crystalline/amorphous)
Polymorph type
Salts and counter ions
Composition of aqueous media (buffer)
Ionic strength
Temperature
Define miscibility
Mutual solubilities within a liquid-liquid system
What is the dielectric constant?
It measures the ability of a substance to be able to store electrical energy within an electric field
What is the equation for Ka?

What is the equation for pH?

What is the equation for pKa?
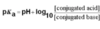
What are the equations for % ionisation of weak acids and weak bases?

What is the relationship between pH and pKa at 99%, 50% and 1% ionised?

How is the pI calculated?
The average of pKa 1 and pKa 2 is taken
What is Ksp?
The solubility product= [+ions][-ions]
How do the solubilities of charged and uncharged compounds compare?
Charged compounds are more soluble in water
Uncharged compounds are typically soluble in organic solvents and cell membranes
Define an acid
An acid donates a proton
Define a base
A base is a proton acceptor
Pharmaceutically define a strong base
Protonated at physiological pH
What is a heteroatom?
An atom other than a carbon
What is a heterocycle?
A cyclic compound where one or more of the atoms in the ring are heteroatoms
What is an alkaloid?
A natural product containing one or more nitrogen heteroatoms
What property in particular do N-heterocycles show?
They are strong bases
What is the role of a buffer?
To minimise change in pH upon the addition of a small amount of acid or base to the solution
What is the most common combination for a buffer?
A weak acid and its conjugate base
Define an isotonic cell
Concentration of solute is equal inside and out
Define a hypertonic cell
The concentration of solute is higher outside the cell
Define a hypotonic cell
The solute concentration is higher inside the cell
Define osmolarity
Concentration of a solution i.e osmoles per litre
Define an osmole
A particle dissolved in solution, regardless of charge, weight or size
What is tonicity?
A measure of osmotic pressure exerted on a membrane- specific to membrane types
What are the three known methods for adjusting tonicity?
Freezing point depression
Sodium chloride equivalent method
White-Vincent method
What is the aim when adjusting tonicity?
The freezing point of the final solution must equate the freezing point of the physiological fluid in question
What are the roles of intermolecular forces in receptors?
Stabilise receptor shape in water
Determine how receptor and small molecule react
Determine how small molecule and protein react
Insight into improvement of molecule and formulation
Which residues within a peptide chain (alpha helix) form hydrogen bonds?
The -C terminus of i and the -N terminus of i+4
What is the approximate strength of a hydrogen bond?
-5kcal/mol
What is the approximate strength of the interactions within the protein backbone?
-8kcal/mol but is dependent on partner charge
What is Wallace’s Rule and what does it mean?
Adding a G-C pair to a peptide chain will increase the melting point by 2 degrees
Adding an A-T pair to a peptide chain will increase its melting point by 4 degrees
Applies to segments up to 20 base pairs in length

What is the strength of a salt bridge interaction at short range?
Approximately 10-100kcal/mol
What particular interactions seek to minimise empty space?
Van der Waals
What is the typical strength of vdW packing between two CH2?
Approximately 0.5kcal/mol
What is pi-pi stacking?
Aromatic rings packing together
The larger the ring, the greater the interaction
What happens if covalent bonds form between drug and receptor?
Pharmacological action is prolonged or possibly even irreversible
How is a crystal formed?
Atoms or molecules closely pack together with non-covalent interactions in order to minimise potential energy, with this order repeating indefinitely
What is the unit cell of a crystal?
The smallest division of the crystal that can be made without altering any properties or its chemical composition
What are the three steps of crystal formation?
- Supersaturation- cooling or evapourating to form precipitant
- Nucelation- collision of molecules, seeding
- Crystal growth- continuous deposition of molecules on faces at a rate proportional to the difference in concentrations between bulk and crystal surface
What is the relationship between the melting point and the crystal lattice?
A relatively weak crystal lattice will have a lower melting point
What is the habit of a crystal?
The overall shape of the crystal
e.g. acicular, prismatic, lamellar
What is the form of a crystal?
The number of faces it has
What can alter the habit of a crystal?
Precipitation
pH
Impurities and excipients
Modifying the habit may affect its ability to flow as a solid
What is polymorphism?
The ability of a substance to exist in different forms
How many polymorphs will be stable?
Only one, the rest will be metastable
However, over time, they will all transform into the stable form
Define a solvate
Solvent entrapped during crystallisation
Define a hydrate
Entrapped water within a crystal when there is water in the solvent
Define an anhydrate
Crystals containing no water or solvent
What is a polymorphic solvate?
Solvent molecules that have bonded within the lattice which, when heated, recrystallise in new form
What is a pseudopolymorphic solvate?
Solvent molecules that barely occupy voids and upon heating evapourate, without changing the shape of the lattice
What is the aim of solid dispersion?
To reduce crystallinity and allow poorly aqueous soluble drugs to be held within an inert hydrophillic carrier
What does the physical state of solid dispersion depend on?
Physiochemical properties of drug and carrier
Drug-carrier interactions
Preparation method
What is the melting fusion preparation method for solid dispersion?
All components are heated above their melting point
Followed by mixing and cooling
What is the solvent method of solid dispersion?
A common solvent must be found
A solution is then made
The solvent is then evapourated
What are the benefits and disadvantages of amorphous solids?
No long range interactions between atoms or molecules
Higher molecular mobility
More readily solubilised, increasing bioavailability
Most materials can be prepared amorphously
Faster than crystallisation
Less stable, shorter half life
What is a lead candidate in drug development?
A compound demonstrating a property likely to be therapeutically useful
What is an active principle in drug development?
A compound isolated from a natural extract that is principally responsible for the pharmacological activity
Define affinity
Strength with which compounds bind to a receptor
Define efficacy
Measure of maximum biological effect resulting from binding of a compound to a receptor
Define potency
Concentration of an agonist required to produce 50% of the maximum possible effect


