The Integument Flashcards
(57 cards)
What does the Integument System do for the body (4 Things)
- Provides Protection (Physical/Chemical/Barrier)
- Sensation and Excretion
- Thermoregulation
- Synthesis of Vit D
What are the 2 parts of the Integument System?
What additional part is sometimes added?
Epidermis and Dermis
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Fascia)
What type of Tissue is the Epidermis?

Keratinized Stratified Squamous
What cell’s predominate the Epidermis?
and what is difference of these cell’s as they are in the outermost border?
Keratinocytes
Lack Nuclei and other Organelles (Full of Keratin)
What are the layers of Thick Skin? (From most Superficial to most Basal)
And Where is this Found?
- Stratum Corneum
- Stratum Lucidum
- Stratum Granulosum
- Stratum Spinosum
- Stratum Basale
Palms and Soles (Fingerprints)

What are the Layers of Thin Skin (Most Superficial to Most Basal)
Where is this Found?
- Stratum Corneum
- Stratum Granulosum
- Stratum Spinosum
- Stratum Basale
All over the body (With Glands and Hair Follicles)

What is this Cell Type?

Stratum Basale
Stains Dark (Melanocytes)
For Stratum Basale List:
Shapes of Cells within?
What does it do?
What is it bound by?
How many Layers?
Its Cuboidal and Low Columnar Cells
It is Mitotically Active - so it creates new cells that migrate up and replenish old ones.
it is bound on top by Desmosomes and on bottom by Hemidesmosomes to Dermis (Dense Irregular Tissue)
A Single Layer of Keratinocytes
What is this Cell Type?

Stratum Spinosum
(Several Layers Thick)
For Stratum Spinosum
How many layers?
what type of cells encompass it? and Shape?
What does it do?
Several Layers thick
Containes Polyhedral Keratinocytes that have Spiny Processes
It creates thick layers that due to pressure produce Corns and Calluses.
What is this Cell Type?
(The G)

Stratum Granulosum
Has Irregular Shape
For Stratum Granulosum
What is this layer known for?
What do the Keratinocytes here contain?
Having the thickest layer of non-keratinized cells in the epidermis - but has TONS of Granules
They have Keratohyalin Granules - stains very basophilic
What is Keratohyalin Granules a precursor of?
Filaggrin
What is this Cell Type? (Black Arrow)
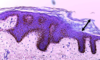
Stratum Corneum
(Most Superficial Layer)
For Stratum Corneum
What do the cells do here?
What is the Plasma Membrane coated with?
How many layers here for Thick vs Thin?
They get rid of their Nucleus and Organelles and flatten out while filling themselves with Keratin. They are also continously shed.
coated with an EC Layer of Lipids that form the water barrier of Epidermis
Thick: 15-40 Layers
Thin: 10-20 Layers
What is the Cell type inbetween Stratum Corneum and Stratum Granulosum?
what letter does this layer reside on top of (In the picture)?

Stratum Lucidum (Part of Stratum Corneum)
(Where the G is pointed)
For Stratum Lucidum
Is in what type of Skin?
How does it stain?
What do the Keratinocytes lack here?
Thick Skin
Stains poor, and is transulucent
They Lack Organelles and a Nucleus - to be full of Keratin
What do Keratinocytes undergo?

They undergo Keratinization and Desquamation (Shed over time) - they also produce ‘cornified’ cells that are full of keratin.
What changes do we see as cells go more superficial?
We see changes in Morphology
Changes in cell components
Increase in Keratin
Where do tonofibrils form?
(and what are they?)
In the Basal Layer
Bundles of Intermediate Fil. (Keratin) <– continues to happen more in more superficial layer
What are Lamellar Bodies?
Fatty Based Granules that contribute to the Water Barrier
What is happening in a Spinous Cell?
Keratin Synthesis continuation
Forming Glycolipid-Cont. Lamellar Bodies
start synthesis of Keratohyalin
Where do we Discharge Lamellar Bodies?
In Granular Cells to form Water Barrier (Stratum Granulosum)
What does Filaggrin do?
Assists with formation of Tonofibrils (Keratin Filaments) to help make Keratin
Starts to lose Nucleus/organelles as well?









