The FINALS Flashcards
A good drug for gram +ve bacteria?
erythromycin
(macrolide)
because they accumulate 100 x of the drug.
What stage of labour does the placenta come away?
third
How does intussusception usually present?
Even though Intussusception presents with vomiting and abdominal distention, red currant jelly stools are often used to describe the nature of rectal bleeding. The condition is unlikely at 1 week and more common between 3-12 months.
What is achalasia?
What is a dange of this?
- Oesophageal aperistalsis
- Impaired relaxation of the lower oesophageal sphincter.
Progressive overflow of secretions and food, esp. at night and can cause aspiratory pneumonia.
What do you get atherosclerosis with CKD?
Associated with
abnormal lipid and
carbohydrate
metabolism, especially
in diabetics.
tx: Consider statins,
antiplatelets/
anticoagulants
Telangiectasia
Also known as spider veins; small dilated blood vessels near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes
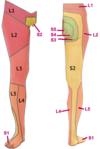
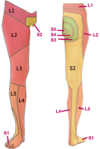
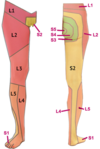
Dermatome to medial malleolus
What does raised PSA indicate?
Prostate cancer/ benign hypertrophy
other examination; PR, biopsy
Causes of hypoalbuminaemia and leukonychia
-reduced protein synthesis (cirrhosis),
increased protein excretion (nephrotic syndrome)
digestive tract; protein losing conditions (crohn’s)
What must you rule out if a joint is acutely swollen?
Septic arthritis
Common organism: Staphylococcus (this lives on the skin)

What ECG changes do you get with hyperkalaemia?
diminished P wave amplitude
increased T wave amplitude
PR prolongation
widened QRS complex
What are striae gravidarum?
Stretch marks are caused by tearing of the dermis.
(resilient middle tissue layer that helps the skin retain its shape)
Coagulation and pregnancy
Prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time remain unchanged in pregnancy, so do not reflect the profound changes that result in a hypercoagulable state
Increased factors VIII, IX and X and fibrinogen, reduced fibrinolytic activity and a decrease in antithrombin and protein S all contribute
motor speech area located on left hemisphere (dominant side)
Broca’s area
- comprehension okay, repetitive of words difficulty.
What is the Mx of a bite with suspected rabies?
And what is the potential complication?
immunoglobulin + vaccination
acute encephalitis
rem hydrophobia: water-provoking muscle spasms
hypersalivation
What is diagnosis of DKA based on?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of Type I DM.
Diagnosis based on
diabetes (blood glucose >11 mmol/L)
ketones (urine or blood)
acidosis (pH <7.30 venous blood)
Where does pain radiate with acute cholecystitis?
from right hypochondrial region to shoulder/ interscapular region.
Name some cystic lumps

- Branchial cyst
- Cystic degeneration of tumour
- Larynogocoele

Widespread purpuric rash of septicaemia
What’s the common cause of this?

cirrhosis,
the consequences of portal hypertension.
Commonly these bleed.
lower 1/3 of the oesophagus

Mean gestational age of onset is 34 weeks
More common in first pregnancy and those with multiple pregnancies
Pruritic, urticarial papules and plaques most commonly on abdomen (but sparing umbilicus) and thighs
Rapid resolution after delivery
No fetal issues
Minimal Change Disease - what’s the story

podocytes damaged, most common cause of nephrotic syndrome with children.
Proteinura and oedema of MCD can develop very rapidly- almost overnight
Pathophysiology of pleural effusion due to LVF
back up of fluids increases pulmonary pressure resulting in pulmonary oedema in the alveoli, fluid in the interstitial fluid, and finally into the pleural cavity.
80% of breast cancers are oestrogen receptor positive ( ER+ )
what pharmacological treatment is used post op?
NB. progesterone sensitive is PR+ (not common)
pre menopausal - tamoxifen (selective oestrogen receptor modulator)
post menopausal - anastrazole (aromatase inhibitor)
(aromatase enzyme is used in body fat to produce oestrogen)
Management of gestational diabetes mellitus
Diet, exercise
metformin
Fetal:
regular growth scans
monitor for pre-eclampsia
delivery at 38-39 wks
Always consider ultrasound scan for woman > 55 years if
- unexplained vaginal discharge
or visible haematuria
combined with…
thrombocytosis
(or >> glucose levels - new NICE guideline)
What is the definitive examination for a PE?
CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) computed tomography using a contrast dye to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries.
When would you take a breast cancer history from a patient? (4)
- A person has concerns about their family history of breast cancer.
- A person has breast symptoms.
- It is clinically relevant:
- In women over 35 years of age using an oral contraceptive pill.
- In women being considered for long-term HRT.
- It is clinically relevant:
foot bones 1

weight faltering implies…
conditon is transient, not serious
What’s another name for Post streptococcal GlomeruloNephritis?
acute proliferative glomerulonephritis
Name some macrolides (3)
erythromycin,, azithromycin and clarithromycin.
bacteriostatic
What is the most common type of breast cancer?
Invasive ductal carcinoma
To complicate matters further this has recently been renamed ‘No Special Type (NST)’
Heparin and LMWH can both cause what electrolyte disturbance?
hyperkalaemia
Legal requirements for termination before 24 weeks
- requires two doctors to sign -
For mothers <16 years : Fraser guidelines apply
If it reduces the risk to a woman’s life;
or
If it reduces the risk to her physical or mental health;
or
If it reduces the risk to physical or mental health of her existing children;
or
If the baby is at substantial risk of being seriously mentally or physically handicapped.
What is Ramsay-Hunt syndrome, and the symptoms?
Ramsay-Hunt syndrome is shingles affecting the facial nerve.
This results in ear pain, vesicles in the external ear canal associated with vertigo and deafness.
Which antihypertensives can be used in pregnancy?
- Methyldopa - central action
- Nifedipine - CCB
- Labetalol - α- and β- receptors
Stroke tx whilst awaiting CT scan results
Px NBM
Nasogastric tube, IV fluids
Oxygen mask, monitor cardiac rhythm (digoxin if needed)
Possibly catheter to monitor output
Aspirin 75mg
Statins (low dose) even if lipid levels normal
TED (thromboembolic disease) stockings
Risk factors for ovarian cancer?
+testing
Many ovulations; early menarche, late menopause, nulliparity.
family history of BRAC1/2 gene mutations
CA125 - done initially, then if +ve, urgent ultrasound scan
Protective factors COC (fewer ovulations), many pregnanciies.
Which drugs might need dose reduced with CKD?
- beta blockers
- digoxin
- allopurinol
- opioids
Newly presenting stress incontinence. What do you need to rule out, and what test?
a urinalysis should be performed in order to exclude diabetes or a urinary tract infection that could be the cause of, or worsening her symptoms.
What drugs would you stop with hyperkalaemia?
ACE inhibitors + others
What is acute glomerulonephritis?
– acute nephritic syndrome
Abrupt onset of glomerular haematuria (RBC casts or dysmorphic RBC),
non-nephrotic range proteinuria, oedema (periorbital, leg or sacral), hypertension and
transient renal impairment.
- OFTEN inflammation of glomeruli/ small b. vessels.
ECG changes in pregnancy include:
ECG
Findings on a ECG performed during pregnancy that are not pathological include:
Small Q waves and inverted T waves in lead III
ST depression and T wave inversion inferiorly and laterally
Left shift of the axis
What do u waves signify?
hypokalaemia
Steroids and growth.. what’s the story
Cushing’s disease is rare.
exogenous steroids (eg. asthma) is a big No No.
If steroids required, give on alternate days to minimise damage.

A gumma is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of syphilis.
Gummas are most commonly found in the liver (gumma hepatis), but can also be found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis, and other tissues.
What’s this?

itchy, papular rash most common on the palms, soles, genitalia and flexor surfaces of arms. Often polygonal in shape, ‘white-lace’ pattern on the surface
Lichen planus
Rare but significant side effect of LLETZ?
Rare but significant – as it can affect subsequent pregnancy – e.g. <strong>may require c-section</strong>,
and also
increases the risk of premature rupture of membranes, and preterm delivery.
What is the diagnosis of concussion?
Diagnosis requires less than 30 minutes of loss of consciousness, memory loss of less than 24 hours, and a GCS score of 13 to 15.
What is the role of Misoprostol?
Increases contraction of uterine smooth muscle
Causes cervical effacement
Medical termination of pregnancy
What is one of the main causes of death in pre-eclampsia women?
Cerebral haemorrhage
(signs : headaches, visual disturbances, seizures)
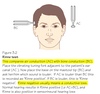
Small bony nodules (osteophytes) at the DIP and PIP joints are characteristic of what?
OA
DIP - Herberden’s nodes
PIP - Bouchard’s nodes
What are the three stages of labour?
Stage 1: from the onset of true labour to when the cervix is fully dilated
stage 2: from full dilation to delivery of the fetus
stage 3: from delivery of fetus to when the placenta and membranes have been completely delivered
What side effects are common with Typical antipsychotics?
movement disorders
Parkinsonism
Akathisia
Acute dystonic reactions: torticollis, >> muscle tone, oculogyric crisis
tardive dyskinesia
hyperprolactinaemia (including gynaecomastia and << penis/ testicle size)
What is a leiomyoma?
A leiomyoma,[fibroid] is a benign smooth muscle tumor that very rarely becomes cancer (0.1%). They can occur in any organ, but the most common forms occur in the uterus, small bowel, and the esophagus.
Polycythemia may occur due to increased erythropoietin production as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome.
What lifestyle would you give a diabetic px to reduce risk of developing ESKD?
Stop smoking, do exercise, control BP, address hyperlipidaemia.
If microalbuminuria then start ACE inhibitors or ARBs regardless of BP elevation.
What are the acquired causes of anaemia?
- Reduced RBC production: deficiencies; iron, B12, folate, marrow replacement or aplasia
- Increased RBC destruction (haemolytic anaemia)
- Systemic illness; ACD (anaemia of chronic disease), renal failure,
When?

Meniscus tear
What three acetylcholinesterase inhibitor drugs are options for managing mild/ moderate Alzheimer’s disease?
donepezil
galantamine
rivastigmine
What and where and how?

melanoma - cutaneous malignant melanoma is a cancer of the pigment cells of the skin
common backs (men), legs (women)
Usual skin type suspects. Sunbeds and sudden intense sun exposure BAD.

Most common type of breast cancer is
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)
(infiltrating ductal carcinoma)
Symptoms and management of vaginal candidiasis?
Non-offensive cottage cheese discharge.
vulvitis; dyspareunia, dysuria
itch
vulval erythema
Mx: local or oral tx.
local; clotrimazole pessary
oral itraconazole
Lower motor neurone signs
- absence of reflexes
- muscle fasciculations
- atrophy of muscles
- decrease muscular tone

Battle’s sign, also mastoid ecchymosis, is an indication of fracture of middle cranial fossa of the skull, and may suggest underlying brain trauma.
What are alternatives to labetalol in pregnancy?
methyldopa and nifedipine
Kussmaul breathing is a deep sighing pattern to decrease CO2 levels and is commonly seen with….
Diabetic ketoacidosis
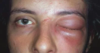
Orbital cellulitis; an emergency and requires intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
In contrast to orbital cellulitis, patients with periorbital cellulitis do not have bulging of the eye (proptosis), limited eye movement (ophthalmoplegia), pain on eye movement, or loss of vision.
What is the first line treatment of moderate 150/100 or severe hypertension 160/110 in pregnancy?
Labetalol
Gravida
Total number of confirmed pregnancies, regardless of the outcome.
What is ecchymosis?
a macular red or purple haemorrhage, > 2mm diameter in skin or mucous membrane
A woman’s hormone balance plays a part in the development of most endometrial cancers.
What is the biggest risk factor?
Hormones - a shift towards oestrogens. (Including HRT)
Obesity
Oestrogen from fat tissue has a bigger impact after menopause than it does before menopause.
- “endometrial cancer is twice as common in overweight women,*
- and more than three times as common in obese women.”*
what are the local effects of inhaled steroids?
Oral thrush
Sore mouth
Hoarse voice
Asthma affects boys or girls the most?
Asthma affects men or women the most?
BOYS
WOMEN
What’s another name for a bruise?
contusion
What three factors can influence eGFR?
eating red meat
muscle mass (amputees, body-builders)
pregnancy
Dementia with Lewy bodies; what symptoms?
Parkinsonian symptoms
visual hallucinations
fluctuations in symptoms
prone to fainting or funny turns
What is 5-HT?
5-HT is short for 5-hydroxy-tryptamine, which is serotonin.

Ludwig’s angina is a form of severe diffuse cellulitis with bilateral involvement, primarily of the submandibular space.
It presents with an acute onset and spreads very rapidly meaning early diagnosis and immediate treatment planning is key to saving lives
What type of anaemia is usually associated with Crohn’s disease?
Crohn’s disease classically causes B12 deficiency anaemia due to terminal ileal disease impairing vitamin B12 absorption.
What problems to patients commonly report with antipsychotics?
movement disorders, sedation, weight gain, sexual dysfunction
Rem: typical antipsychotics have more potent dopaminergic effects therefore extrapyramidal movement disorders more serious.
Define acute leukaemia
Clonal haematopoietic stem cell/ progenitor disorder characterized by the rapid accumulation of immature progenitor cells (blasts) and impaired normal marrow function.
Pre-eclampsia defined
Pre-eclampsia is a multisystem disorder related to inadequate placentation. The definition of the disorder is new onset hypertension and proteinuria which develop after 20 weeks of gestation.
Upper motor neurone signs
Increase in muscular tone (spasticity)
Increase in reflexes (hyperflexia)
++ Babinski sign
Huntington’s - bare facts
- inherited autosomal dominant disorder
- hyperkinetic movements. Mean age of 40.
- characterised by rapid, uncontrolled, flicking movements of the torso and limbs (chorea)
laxative - lactulose
function and indications
increase bulk by retaining water.
Takes 48 hrs to act and must be given regularly.
what can preceed a seizure?
a sensation or mood change
What’s the primary care first line tx of endometriosis?
NSAIDS and/or paracetomal for symptomatic relief
COC or progestogens can be tried.
What’s a cause of loud borborygmi?
(movement of fluid and gas)
small-bowel obstruction/ dysmotility if associated with colicky discomfort.
What nerve supplies the lateral rectus muscle?
abducens (VI)
long nerve makes it prone to injury.
Name opportunistic HIV infections
- PCP - pneumocystis jirovecii
- cytomegalovirus (CMV) in late-stage infection (CD4 <50) - main problem progressive retinitis (85%)
- toxoplasmosis - protozoa infection. Causes encephalitis (80%) in late HIV
- Kaposi’s sarcoma (herpes virus 8)
- others
What’s this? And info
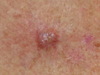
BCC is a non-melanoma skin cancer, and is the most common type (> 80%) of all skin cancer.
BCC are sometimes referred to as ‘rodent ulcers’.
Common on areas that are exposed to the sun, such as your face, head, neck and ears
How can you check for suspected csf discharge from nose or ear?
Test for glucose
What is Boerhaave syndrome?
10% of esophageal perforations which occur due to vomiting.
full-thickness tear in the esophageal wall
high morbidity and mortality and is fatal without treatment
What is petechiae ?
Similar to purpura but smaller (1-2mm diameter).
picture of macule

why do you get steatorrhoea with cystic fibrosis?
due to pancreas insufficiency of lipase enzymes; thus fat malabsorption. Maybe diabetes developing too.
What’s the management for mild, persistent asthma?
Corticosteroid inhaler - preventer
Short acting B2 agonist as and when required.
Safe Antihypertensive treatment in pregnancy
Labetalol,
nifedipine
and methyldopa
Which part of the GI tract is Crohn’s disease?
anywhere
(abdominal cramping + diarrhoea)
What are the three main manifestations of alcoholic liver disease?
- fatty change
- alcoholic hepatitis
- alcoholic cirrhosis
What is isotretinoin used for?
acne
What are the main features of Pre-renal AKI?
A decrease in blood perfusion and thus << GFR.
Both Kidneys need to be affected (why? remember?)
common causes; hypovolemia, hypotension, <
symptoms of septic shock
- warm peripherae, bounding pulse with low diastolic pressure, low JVP
- pyrexia (or hypothermia)
- history and signs of underlying infection
When should a woman stop the COC pill if having an operation?
4 weeks prior
Why to you sometimes get upper right upper side pain with pregnancy/ hypertension?
Liver distension
suspected ovarian cancer; what physical examination signs may you find?
Persistent abdominal distension (bloating)
Feeling full (early satiety)/ anorexia
pelvic/ abdominal pain
increased urinary urgency/ frequency
(Nice guidelines)

Extend the knee whilst the hip is in 90 degree flexion.
- positive if pain on extension. Sign is absent in local causes of neck stiffness.
NB> absence of this sign does not exclude meningitis.
RPGN features
focal necrosis with or without crescents and rapidly progressive renal failure over weeks.
NB> crescents are aggregations of macrophages and epithelial cells in Bowman’s space.
Symptoms of SAH?
occipital headache, thunderclap
nausea and vomiting
meningism (photophobia, neck stiffness)
coma/ seizures/ death
Which are the two SNRIs?
(Selective serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors)
Venlafaxine
Duloxetine
symptoms of Addison’s disease (adrenal insufficiency)
- aldosterone
- corticol
Thiazides
moa
side effects
Act on early segment of the distal tubule. Inhibit NaCl reabsorption.
Side effects (due to >> excretion of K+ and H+ ions)
hypokalaemia
metabolic alkalosis
Hyperuricaemia. Increase in uric acid levels may result in gout.
Glucose tolerance; thiazides are contraindicated in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
organism; bacterial tonsilitis
group A beta haemolytic streptococcus
‘Strep throat’
Post menopausal bleeding, red flag for?
Endometrial cancer
What is renal mineral bone disorder?
aka Renal Bone Disease
aka Renal Osteodystrophy
This involves softening of the bones due
to decalcification and deposition of
calcium at various sites around the body.
The mechanisms involved are complex.
Symptoms of hypovolaemic shock (this includes burns)
- symptoms of fluid loss, eg. melaena, haematemesis
- cold peripherae; weak, thready pulse, low JVP
- skin pallor, dry mucous membranes
What is Oxybutynin?
drug that decreases muscle spasms of the bladder. Can also help with kidney stone symptoms.
(therefore used for an overactive bladder)
SEs of Hydroxychloroquine
(malaria treatment)
GI effects: The most common adverse effects are a mild nausea and occasional stomach cramps with mild diarrhea.
The most serious adverse effects affect the eye.
Le Fort Fractures

Clinical manifestations of PCOS
- menstrual irregularies/ anovulation (80%)
- hirsutism (70%) ; upper lip, chin, chest, back
- Obesity (50%)
- Infertility
- Acanthosis nigricans ; dermatologic marker of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaema (at neck, groin, axillae)
What factors increase the risk of cervical ectropion?
those that increse levels of oestrogen.
eg. COC, menstruating age.
ablation if troublesome.
Diagnostic values of diabetes mellitus - fasting and non-fasting
fasting: 7 mmol/l and above
random glucose 11.1 mmol/l and above.
If patient is asymptomatic then must be tested again.
acute glomerulonephritis – acute nephritic syndrome.
Abrupt onset of glomerular haematuria (RBC casts or dysmorphic RBC),
non-nephrotic range proteinuria,
oedema,
hypertension and
transient renal impairment (temporarily oliguria and uraemia)
What’s the story?

Zollinger–Ellison syndrome (ZES) is a disease in which tumors cause the stomach to produce too much acid, resulting in peptic ulcers.
Symptoms include abdominal pain and diarrhea.
The syndrome is caused by a neuroendocrine tumor that secretes a gastrin. The tumor causes excessive production of gastric acid.
Do you get haematuria with nephrotic syndome?
Possibly. It depends on the damage to the glomerulus.
What is Todd’s paralysis?
A focal appendage transient weakness after a seizure.
It usually subsides completely within 48 hours.
Todd’s paresis may also affect speech, eye position (gaze), or vision.
NB> important to differentiate from ischaemic stroke because seizure is an exclusion criteria for thrombolysis.
What’s the most common cause of macrolytic anaemias?
B12 or folate deficiency
xerostomia
dry mouth
possible causes; anticholinergic drugs, Sjogren’s syndrome
What two common drugs can cause hypothyroidism?
lithium
amiodarone
What investigations?
urine dip stick
MSU, FBC
EUC, LFT, Calcium levels
serum (and urine) immunoglobulins to screen for autoimmune diseases.
CXR - pleural effusion/ oedema
ultrasound, biopsy.
Which lung cells secrete surfactant?
pneumocytes type II
Odynophagia
Pain on swallowing
Possible causes; infection, oesophageal cancer, larnynx or pharynx cancer.
What specific signs are there with intussusception?
Recurrant stools
Dance’s sign - absence of bowel in the right lower quadrant.
palpable ‘sausage-shaped’ mass in the right upper quadrant.
what could be triggers for hypoglycaemia attacks?
infections; UTI, pneumonia
physiological stressors including cold, status epilepticus.
what can preceed a seizure?
a sensation or mood change
What is this?

acanthosis nigricans
Define antepartum haemorrhage
bleeding from the birth canal after the 24th week of pregnancy.
[bleeding following the birth of the baby is postpartum haemorrhage.]
Cauda Equina - signs and symptoms
- altered sensation perineal area, bowel/ urine/ sexual dysfunction
- PR - loss of tone and sensation
Where is erythropoietin produced?
peritubular complex of the kidneys (90%), and Liver
which hormones, which layer of the adrenal gland?

Which anti TB drug can cause lupus?
Isoniazid can cause drug-induced lupus
What is ACR?
albumin concentration (mg) / creatinine concentration (g)
Albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) first method of preference to detect elevated protein
What is uterine rupture?
(rare but high mortality)
A catastropic event where a full-thickness tear develops, opening the uterus directly into the abdominal cavity.
Most occur during labour; however, uterine scars following earlier caesarean may rupture during the third trimester before any contractions occur.
keloid scars in the uterine wall from c.s. causes it to ‘unzip’.
Which type of leukaemia has a peak age of onset of four years?
ALL - acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
70-80% cure rate for children.
Why do you get peripheral oedema with nephrotic syndrome?
Due to loss of protein in urine, therefore hypoalbuminemia.
What are some causes of secondary dysmenorrhoea?
fibroids, adenomyosis, endometriosis, PID, ovarian caner
Where’s the subdural space, and who’s vulnerable?
The elderly; tearing of the veins across the subdural space causing gradual seepage of blood
antibiotic for sepsis?
ceftriaxone
Prolonged or heavy menstrual bleeding is called?
Menorrhagia
What ACR level would indicate CKD?
30-300 mg/g for >3 months
(relative to young adult level)
what does the urine look like in nephrotic syndrome?
frothy
What is Asherman’s Syndrome?
(1-2% cases of 2nd amenorrhoea)
Can follow D & C, infections, endometriosis
Also referred to as intrauterine adhesions, is an acquired uterine condition that occurs when adhesions form inside the uterus and/or the cervix.
AS can be the cause of menstrual disturbances, infertility, and placental abnormalities
tx: hysteroscopy.
What is the first line treatment for pruritus due to primary biliary cirrhosis?
Cholestyramine
Cholestyramine is a bile acid sequestrant which means that it binds to bile acids in the gastrointestinal tract and prevents them from being re-absorbed. Instead the bile acids are excreted in the faeces.
What is this?

Seborrhoeic keratoses
Which receptors do typical antipsychotics affect?
(antagonists)
cholinergic
adrenergic
histaminergic


With a CVA, if the patient’s leg is more affected, which artery is occluded?
anterior cerebral artery
Immediate management of acute pulmonary oedema during pregnancy
Oxygen
diuretics
regular ECGs
Who gets neoplasms of the vagina and vulva?
mainly post menopausal and older women
What’s the medical term for irregular tear-like wounds caused by some blunt trauma
laceration
What is the most common cause of intestinal obstruction in patients aged 5 months to 3 years?
intussusception
Symptoms: paroxysmal (10-20 mins) of colicky abdominal pain
Child may appear well between paroxysms.
Early vomiting.
late sign: bloody ‘redcurrant’ stools.
non-epileptic causes of seizures
- head trauma (sub-dural haematomas)
- stroke
- brain tumours
- hypoxia
- hypoglycaemia
- fever
- chronic alcohol withdrawal
- infections (sepsis, pneumonia)
What is cor pulmonale?
Pulmonary heart disease.
Occurs in 25% of patients with COPD.
Caused by pulmonary hypertension causing enlargement of the right ventricle.
What is the criteria for possible Dementia with Lewy Bodies?
(lewy bodies; in brainstem and neocortex)
Definitely dementia
and then 2 out of 3 of the following:
- Fluctuating attention and concentration.
- Recurrent well-formed visual hallucinations.
- Spontaneous Parkinsonism.
Guillain-Barre syndrome is “an immune mediated demyelination of the peripheral nervous system often triggered by an infection.”
Which one commonly?
Campylobacter jejuni
Parity
Number of births that a woman has had after 20 weeks gestation.
Why does gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD) trigger an asthma attack?
If the stomach acid reaches into the throat or airways the
irritation and inflammation can trigger an asthma attack.
Often worse at night when lying down.
What are the two types of leukaemia?
acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) - lymphoid cell line
myeloid cell line - Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML)
Persistent fever - causes

What is pharmacokinetics?
Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug.
Absorption is part of pharmacokinetics.
IV - max bioavailability.
HELLP
H
EL
LP
The symptoms and signs of this condition overlap with those of pre-eclampsia
Hypertension and/or proteinuria are not present in 100% of cases and are often mild
Blood tests may show haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets
Tx for prolonged seizures
Intravenous Lorazepam or
Rectal Diazepam
and if no result
IV phenytoin (if not already on this drug).
BM check, regular neuro obs, GCS updated (drop of two point = serious)
Wrist drop; which nerve extends the wrist?
radial nerve
Cockcroft-Gault equation
is often used as a method of estimating GFR
from knowledge of serum creatinine, age and weight:
The calculation is unreliable if the patient has unstable renal function, is very obese, or is oedematous.
Which bone is boxer’s fracture?
5th metacaral
Tests for diabetes
Blood glucose
urine or blood test for ketones
pH (venous fine)
triple therapy for gastric ulcers
Omeprazole
amoxicillin
Clarithromycin
or
omeprazole
amoxillin
metronidazole
What could cefuroxime and clarithromycin possibly treat?
CAP
+ may need vasopressor drugs to produce peripheral vasoconstriction if px adequately filled (CVP monitoring). Renal output would be poor.
What’s the most common causal organism of a single lobar pneumonia?
Steptococcus pneumoniae
HAS-BLED score
Assess the bleeding risk of patient with AF,
to support clinical decision regarding antithrombotic therapy.
What is this?

ulcerating BCC
How does the pulse change in pregnancy?
The pulse rate increases by 10-20 beats per minute early in pregnancy. A pulse rate of up to 105 beats per minute is regarded as normal in pregnancy.
On examination the pulse may be bounding or collapsing in nature.
What does RPGN stand for?
Rapidly Progressive GlomeruloNephritis
What’s this? + info.

Thyroglossal cysts
asymptomatic midline neck mass at or below the level of the hyoid bone, above the thyroid cartilage.
Most often in the midline
They may present in childhood (less than 50%) or, usually as a young adult
Move up when the tongue is protruded & with swallowing- cysts attached to the base of the tongue by the thyroglossal tract.
Most important management of diabetes
very aggressively lower blood pressure (ACE inhibitors, ARBs)
Excellent glycaemic control
stop smoking
What is the ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI)
The ratio of the blood pressure at the ankle to the blood pressure in the upper arm.
Lower blood pressure in the leg suggests blocked arteries due to peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Unreliable with calcification of arteries (e.g. diabetes)
Fleshy, protuberant, slightly pigmented vulva lesions ; what could they be, and what’s the treatment?
Genital warts
Rem types 16,18 - high risk for cervical cancer.
tx: cryotherapy, or topical podophyllum (imiquimod is second line)
CAP - antibiotic
amoxicillin
or doxycycline/ clarithromycin
intrauterine/ endometrial polyps
They often cause no symptoms, otherwise bleeding related symptoms.
Appear to be affected by hormone levels and grow in response to circulating estrogen.
Polyps can increase the risk of miscarriage in women undergoing IVF treatment.
What does the corpus luteum secrete?
progesterone
If pregnancy occurs then embryo takes over from corpus luteum by producing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Then 7-9 wks the placenta produces progesterone.
Some signs and symptoms of infective endocarditis
splinter haemorrhages
Janeway lesions
Osler’s nodes
dental hygiene
What is an inherent problem with Sulfonylurea drugs?
Since they increase insulin secretion, can lead to hypoglycaemic episode if px skips or delays meals.
Alcohol increases hypoglycaemic effect.
Symptoms and sign of infectious encephalitis
- focal or diffuse neurological signs may be present
- fever, headache
- psychiatric symptoms and seizure
- alteration in consciousness and focal neurology
What is actinic keratosis? (ak-TIN-ik ker-uh-TOE-sis)
plus treatment
An actinic keratosis (ak-TIN-ik ker-uh-TOE-sis) is a rough, scaly patch on your skin that develops from years of exposure to the sun. It’s most commonly found on your face, lips, ears, back of your hands, forearms, scalp or neck
5-fluorouracil (5-FU) cream (Efudix®)
Salicyclic acid
5% imiquimod cream (Aldara®)
cryotherapy
PDT - photodynamic therapy
curettage

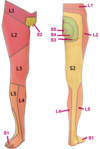
Dermatome to Toes 1-3

Name the five gynae cancers
Ovarian,
endometrial/ uterine
cervical, vaginal,
vulval
When can the foetus perceive sound and light?
sound: 24-26 weeks
light: 28 weeks
How often to women get cervical screening?
What age groups?
Offer cervical screening to all women between the ages of 25 years and 64 years.
Age 25 years: first invitation.
Age 25-49 years: screening every 3 years.
Age 50-64 years: screening every 5 years.
Women 65 years of age or older if they have not had a cervical screening test since 50 years of age or a recent cervical cytology sample is abnormal.
Definition - Primary haemorrhaging in pregnancy
Primary postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) is loss of blood estimated to be >500ml from the genital tract within 24 hours of delivery.
(this is the most common obstetric haemorrhage)
Minor PPH up to 1000ml
Major PPH over 1000ml
Relationship of aldosterone and spironolactone
Aldosterone raises BP by stimulating Na+ absorption.
Spironolactone competitively blocks the binding of aldersterone.
* weak diuretic *
SE: severe hyperkalaemia, especially in px with renal impairment.
Indications: Liver disease with ascites, severe heart failure, Conn’s syndrome
Which receptors do atypical antipsychotics affect?
(antagonists)
5HT2a
(serotonin)
What are the risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip?
Old term: congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH)
FEMALE, BREECH
firstborn children,
oligohydramnois (def of amniotic fluid)
birth weight >5kg
20% of cases bilateral
What are the symptoms of hypervolaemia? overfilling
- jugular venous distension
- S3 gallop
- dyspnoea
- ascites
- pulmonary oedema
- pleural effusions
- peripheral oedema
- hypertension
What does abnormal dopamine transmission cause?
How do antipsychotics work?
a false sense of having seen or heard something before. Leads to psychosis
blocks the dopamine D2/3 receptors, thus diminishing abnormal dopamine transmission.
What’s this?

Highly contagious, fever >40, coryzal symptoms, conjunctivitis, Kopliks spots
Rash starts on forehead/ neck goes to trunk and limbs over 3-4 days.
Mx: Self-limiting. Paracetamol and lots of fluids.
Complications; pneumonia (5%), encephalitis (1/1000)
MOA of carbimazole
Carbimazole is a pro-drug; it is converted to the active form, methimazole.
Methimazole prevents thyroid peroxidase enzyme from coupling and iodinating the tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, hence reducing the production of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 (thyroxine).
Rashes/ pruritus are common.
Serious side effect; bones marrow suppression.
What factors affect drug availability during pregnancy?
- Increased blood volume (50% increase by 34 weeks)
- Increased clearance (> GFR 50% by 24 weeks)
- Increased hepatic metabolism
- vomiting
- decreased absorption
Signs/ symptoms of fractured zygomatic arch
swelling/ bruising - periorbital
pain, numbness, diplopia, reduced eye movements
altered pupillary reflexes, facial flattening/ symmetry
- look at jaw from behind and put fingers on zygomatic arches. Compare for differences.
MOA of carbimazole
Carbimazole is a pro-drug; it is converted to the active form, methimazole.
Methimazole prevents thyroid peroxidase enzyme from coupling and iodinating the tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, hence reducing the production of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 (thyroxine).
Rashes/ pruritus are common.
Serious side effect; bone marrow suppression. AGRANULOCYTOSIS. Monitor
What’s the most common type of breast cancer?
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)
sudden foot inversion can cause….
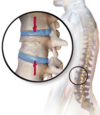
avulsion fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal.
(tightening of peroneus brevis tendon)
tx. support bandage if can weight-bear
backslab is unable to weight-bear
Tips for diagnosing CKD
- if GFR >60 ml/min/1.73m2, then not CKD unless evidence of kidney damage.
- features must be present on at least two occasions and for more than three months.
After how many weeks of gestation can you diagnosis pregnancy-induced hypertension?
20
Pregnancy related blood pressure problems (such as pregnancy-induced hypertension or pre-eclampsia) do not occur before 20 weeks.
paraparesis
partial paralysis of both legs.
(in contrast to paraplegia)
What is seroconversion?
- Period of time during which HIV antibodies develop and become detectable.
- takes place within a few weeks of initial infection.
- It is often accompanied by flu-like symptoms including fever, rash, muscle aches and swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms are not a reliable way to identify seroconversion or to diagnose HIV infection.
What is the relationship of breast cancer and HRT?
There is a very small risk of breast cancer and this is related to duration of taking HRT, and declines after stopping HRT.
After 5 years the risk is the same as a woman who has never taken HRT.
Some more facts about endometrial cancer
10% of post-menopausal bleeding is due to endometrial cancer.
Cause of intermenstrual bleeding in pre-menopausal women.
85% of cases in post-menopausal women
Risk factors; oestrogen! (therefore obesity, nulliparity, tamoxifen use, PCOS, late menopause
What is the most common cause of hypotension?
+ what drugs commonly cause hypotension
hypovolaemia
>>> diuretics
alpha/ beta blockers
Parotid tail lump - Solid
What other solid lumps are there?

- lymph node
- tumours
- vagal schwannoma


New abdo pain in pregnancy. Always consider..
Appendicitis in pregnancy should be suspected when a pregnant woman complains of new abdominal pain
Risk factors of PPCM
Multiple pregnancy
Pregnancy complicated by hypertension (pre-existing or pre-eclampsia)
Advanced maternal age
Afro-Caribbean race
Salient points of Wilson’s disease
A combination of liver and neurological disease.
Onset 10-25 typically.
neurological : basal ganglia degeneration, speech, behavioural, psychiatric problems.
Rem: Kayser-Fleischer rings and blue nails.
Can you gauge severity of attack by the wheeze?
WHY?
NO.
Severe attack… very reduced air flow (Silent chest)
Albuminuria; role in CKD diagnosis?
Persistent increased protein in the urine (two positive tests over 3 or more months) is the principal marker of kidney damage, acting as an early and sensitive marker in many types of kidney disease.

Anatomy

peri-orbital cellulitis
painful, unilateral red swollen eyelids
px often systemically unwell
Investigations for CKD
U & E, glucose
24-hr creatinine clearance; determine level of renal failure
Casts; glomerulonephritis
Red Cells; can come from anywhere
Check < Calcium, phosphates
Mx of acute asthma attack key points
Give oxygen to maintain 94-98% sats
Salbutamol, back to back if needed. Oxygen driven if needed.
Oral prednisolone 45-50mg for five days.
Combine ipratropium with salbutamol if poor response.
Consultant; magnesium/ aminophylline
Life-threatening asthma - possible signs (10), only one needed
PEFR <33% of predicted best
Sats <92%
PaO2 <8kPa, normal PaCO2 (4.6-6kPa)
Silent chest, cyanosis
arrthymia
altered mental state/ exhaustion
hypotension
Nerve involved with CTS?
median
Oedema in nephrotic syndrome also causes what problems in the thoracic region?
breathlessness
pulmonary oedema
pleural effusion
Cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
Cardiac output increases by about 40%, as a result of increased stroke volume and reduced systemic vascular resistance, in combination with an increased heart rate.
The cardiac output is greatest at 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. The heart is physiologically dilated and myocardial contractility is increased.
Which AF drug can cause thyrotoxicosis?
amiodarone
What is CHA₂DS₂-VASc Score?
Risk for stroke for AF patients
helps determine the 1 year risk of a thromboembolic event in a non-anticoagulated patient with non-valvular AF.
Causes of acute abdominal pain

Pre-eclampsia
signs and symptoms
Hypertension and proteinuria, and oedema
Can get swelling of feet, ankles, and hands
Symptoms such as headache, right upper quadrant/epigastric pain or transient visual disturbance can be reported
On examination, abnormalities such as right upper quadrant tenderness, hyper-reflexia or clonus may be present
The multi-system manifestations result from diffuse vascular endothelial dysfunction
What’s the main marker for near fatal asthma? (2)
Raised PaCO2
Requiring mechanical ventilation with increased inflation pressures.
Definition of CKD
Abnormalities of kidney function or structure present for more than 3 months.
Includes all individuals with markers of kidney damage or those with an eGFR of less than 60 ml/min/1.73m2 on at least 2 occasions 90 days apart
(with or without markers of kidney damage).
RBC and pregnancy - what happens?
Fall in haemoglobin concentration, haematocrit and red cell count (as expansion of plasma volume is greater than the increase in red cell mass)
No change in mean cell volume or mean cell haemoglobin concentration
2-3 fold increase in iron requirements
Iron deficiency anaemia is common and requires iron supplementation
ADH
made in hypothalamus
released via posterior pituitary gland
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
What is Placental abruption?
May present with vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain (usually continuous), uterine contractions, shock or fetal distress.[
Abruption is the premature separation of a normally placed placenta before delivery of the fetus, with blood collecting between the placenta and the uterus.
It is one of the two most important causes of antepartum haemorrhage (the other being placenta praevia).
What does gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) release?
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
and
luteinizing hormone (LH)
from the
anterior pituitary.
What antibiotic makes urine go orange?
Rifampicin may cause orange tears and urine
Acute asthma attack
Salbutamol nebs
add ipratropium bromide if not working well.
Give steroids (orally, IM, IV)
In the case of ischaemic stroke, what is the window for treatment?
3 hours from onset of symptoms.
(this includes getting a CT scan!)
What antihypertensives cannot be used in pregnancy?
ACE inhibitors are teratogenic and fetotoxic.
Reasons to do a lumbar puncture
- investigating bacterial meningitis
*
Acute SEVERE asthma signs (any one of)
PEFR value?
Resp rate value?
HR value?
name one observation
PEFR 33-50% predicted
Resp rate >25/min
HR >110bpm
Inability to complete sentences in one breath
How is HIV infection diagnosed?
Detection of anti-HIV antibodies by ELISA (enyme-linked immunosorbent assay).
FSH stimulates follicle develop. As Follicle grows it starts to secrete oestradiol. What does this increase in oestradiol cause?
Causes the hypothalamic-pituitary axis to secrete LH
Why is there an increased risk of aspiration with pregnant women? (esp. with general anaesthesia)
Reduced gastric motility, in combination with restriction of stomach expansion by the fetus results in gastro-oesophageal reflux, particularly in the third trimester.
Constipation common in pregnancy.
What are typical symptoms of anaemia?
SOB (mainly on exertion)
tiredness
headaches
- pallor, angina in elderly
- tachycardia

osteoma
more in males, unilateral.
often at junction of bony and cartilaginous ear canal.
what is a Keratoacanthoma?
Keratoacanthomas (KAs) are very rapidly growing squamo-proliferative lesions that look like well-differentiated squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) pathologically. KAs are characterised by rapid growth over a few weeks to months, followed by spontaneous resolution over 4-6 months in most cases.
KAs are benign epidermal growths and not a malignant variant of SCC.
They are usually solitary and begin as firm, round, skin-coloured or reddish papules that rapidly progress to dome-shaped nodules with a smooth shiny surface. A central crater of ulceration may develop, or a keratin plug that may project like a horn.
Definition of Asthma
Disease characterized by recurrent attacks of breathlessness and wheezing, which varies in frequency from person to person.
Dermatome to the thumb

Glucose and pregnancy, what’s the story?
Pregnancy is an insulin resistant state.
Hepatic glycogen stores are depleted in pregnancy, thus women can become ketotic quickly.
>> blood glucose associated with maternal age and family history of diabetes
Cellulitis - antibiotic
Flucloxacillin
- clarithromycin for penicillin allergy
What is Kussmaul breathing?
Deep and labored breathing pattern often associated with severe metabolic acidosis, particularly diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) but also kidney failure.
Cholangitis
stone obstructing the common bile duct
causing intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary obstruction.
Management of AF
cardioversion if < 48 hour onset
Rate and rhythm control
CCB - verapamil or a Beta Blocker
Rate control; amiodarone
anticoagulants to prevent thromboembolism/ stroke
surgical catheter ablation
What is Paget’s disease of the breast?
Paget’s disease of the breast is a rare type of cancer of the nipple area of the breast.
It presents as eczema affecting the nipple.
Classic monoamine group

Why can you get sepsis with nephrotic syndrome?
Loss of immunoglobulins (proteins) in the urine will compromise the immune system.
Why would you add a LABA?
If inhaled corticosteroid therapy is insufficient.
Key symptoms : endometriosis
chronic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhoea
deep dyspareunia
pelvic examination: < organ mobility and tenderness on palpation.
(rem: laparoscopy is gold standard investigation)
Definition of antepartum haemorrhage
Antepartum haemorrhage is defined as any vaginal bleeding from the 24th week of gestation until delivery.
How does type I diabetes initially present?
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- weight loss
- over a few weeks.
Dx: random blood sugar >11.1 mmol/L
or fasting blood glucose > 7mmol/L
PLUS classic symptoms
What are the first line drugs for type 2 diabetes?
metformin
sulfonylureas
meglitinides
What are the main causes of heart failure?
- CORONARY HEART DISEASE
- hypertension
- valvular disease
- cardiomyopathy
Role of LH in males?
Stimulates the Leydig cells of the testis to produce testosterone.
Where do B Lymphocytes mature?
T- lymphocytes?
mainly in the bone marrow
Thymus
T Waves
Three abnormal types
Upright in all leads except aVR and V1
- Flattened T waves (hyperkalaemia)
- Inverted T waves
- Hyperacute T waves
Common causes of acute mitral regurgitation
infective endocarditis
ruptured chordae tendineae
ischaemic papillary muscle rupture
CRB-65/ CURB-65
predicting mortality rate for pneumonia
Lab findings with Grave’s disease

aphthous ulcer
(mouth ulcer)
Management
First-line treatment is usually a topical corticosteroid
Other therapies that can be used include topical anaesthetics such as lidocaine, topical analgesic/anti-inflammatory agents such as benzydamine, and topical antimicrobial agents such as chlorhexidine gluconate oral solution, or doxycycline rinses.
What is a cervical ectropion?
The columnar epiethelium is present on the vaginal surface of the cervix (the ectocervix)
Normal physiological state for some women after puberty
There may be a red looking area around the os;
don’t confuse with cervicitis.
It can result in an excess section of mucous, as the columnar epithelium contains mucous secreting glands (normal)
It may also cause post-coital bleeding, due to the presence of delicate blood vessels in the columnar epithelium
What can cause miosis?
NB> latency of pupillary responses increases with age
Light
opiates/ opioids
anti-hypertension medication
What are the common causes of maternal death during pregnancy?
medical complications rather than obstetric and include cardiac problems, neurological disease, sepsis and thromboembolism
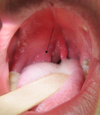
symptoms include sore throat, dysphagia, fever

Tonsillitis; a type of pharyngitis.
Usually viral (esp. under 2 years age), if bacterial then usually group A beta-haemolytic streptoccus (strep throat).
Other bacterium:
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, or Haemophilus influenzae
* can get abdominal pain due to associated adenitis in the mesenteric nodes.
Foot bones 4

Cardinal differences between syncope and epileptic fits?
syncope has no post-ictal phase
no tongue biting with syncope
Syncope has a faster recovery period
What are the tests for Coeliac disease?
Total immunoglobulin A (IgA)
IgA Tissue transglutaminase antibody (shortened to tTG)
+ eat gluten in more than one meal every day for six weeks prior to testing.
GOLD standard; duodenal biopsies with IEL ( increased number of intraepithelial lymphocytes is typical of active celiac disease)
What condition do you see this with?

Grave’s disease
- inflammation
- induration
- erythema
- incidence 1-5%
Symptoms of middle cerebral artery infact
Contralateral hemiparesis and sensory loss, upper extremity > lower
Contralateral homonymous hemianopia
Aphasia
What is the most common type of Lung cancer with smokers?
Small cell lung carcinomas are more likely than alveolar cell carcinomas of the lung in smokers
Weber’s test - where is the fork placed?
middle of forehead
Examination fo asthma (things to look for)
- Abilty to speak
- PEFR is vital to assess severity of attack. Work out % of predicted peak flow.
- Rountine obs
- ABCDE approach; A - airway. Can the patient talk?
B - breathing - inspection
C - circulation HR, BP, pulsus paradoxus
E - any rash/ hives to suggest allergic reaction. Exhaustion
What are the two most common causes of acute pancreatitis?
+ main symptoms
alcohol or gallstones
- vomiting
- severe epigastric pain that may radiate to the back
- Cullen’s sign (possibly) - periumbilical discolouration
What lumps move with swallowing?
SOLID:
Goitre
lymph node
CYSTIC:
Thyroid cyst
What is Glomerulopathy?
immunologically mediated disorders with involvement of:
cellular immunity
humoral immunity
inflammatory mediators
Is glycosuria is diagnostic of diabetes mellitus in pregnancy?
No. Glucose loss during pregnancy is normal
tetanus
Anaerobic organism Clostridium tetani.
In soil, enters wounds.
Neurotoxin causes progressive painful muscle spasms.
It’s not just histamine that creates an inflammatory response in the airways; what else?
Prostaglandins
Adenosine
Bradykinin
Major basic protein
Leukotrienes
Prostaglandins
Loop diuretic
moa, indications, side effects
Inhibits NaCl reabsorption in the thick ascending loop of Henle
Indications; oedema with heart failure.
effective in patients with << GFR
High doses; endolymph disturbances and deafness.
Adverse : 4 hypos; hypokalaemia (little), hyponatraemia, hypotension, hypovolaemia.
IMP. >>> CALCIUM and >>> MAGNESIUM excretion
What is the age group for AML (acute myeloid leukaemia)?
more common with increasing age, with peak age onset of 70 years.
non-epileptic causes of seizures
- head trauma
- stroke
- brain tumours
- hypoxia
- hypoglycaemia
- fever
- chronic alcohol withdrawal
Some possible red flags for neck lumps
Dark colour suggestive of malignant melanoma,
ulceration,
skin fixation,
bleeding, or
hard texture
Is there a screening programme for ovarian cancer?
NO because there is no test that reliably picks up ovarian cancer at an early stage.
Name six neurotransmitters that I need to learn
GABA
Dopamine
Acetylcholine
Serotonin
Glutamate
Noradrenaline
Name for rectal bleeding
haematochezia
Mx tests
BMI and waist circumference
ECG
FBC, U & E, Lipids, LFT, glucose, HBA1c, prolactin
What is a common cause of asthma in childen under 10?
respiratory infection (viral or bacterial)
What does a collapsing pulse indicate?
severe aortic regurgitation
What is pseudomembranous colitis?
Also called antibiotic-associated colitis or C. difficile colitis, is inflammation of the colon associated with an overgrowth Clostridium difficile.
This overgrowth of C. difficile is most often related to recent antibiotic use.
Management of Ascending cholangitis?
intravenous antibiotics
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) after 24-48 hours to relieve any obstruction
Eye conditions not to miss
- acute-angle closure glaucoma
- peri-orbital cellulitis
- giant cell arteritis
- keratitis
- uveitis
What hormone connected to the reproductive system does the hypothalamus make?
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Common causes of pleuritic exudate (>30g/L) protein
most common ; infective; pneumonia
TB, subphrenic abscess
connective tissue disease: RhA, SLE,
Cancer
Pancreatitis, pulmoney embolism
Otitis media bugs
haemophilus influenzae
streptococcus pneumoniae
moraxella catarrhalis
if viral then short-lived and self-limiting.
What is cataplexy?
Cataplexy describes the sudden and transient loss of muscular tone caused by strong emotion (e.g. laughter, being frightened).
RIFLE
International consensus classification for AKI.
What vitamins help prevent neural tube defects?
Which drug to avoid?
Folic acid and Vit B12
Methotrexate - folate antimetabolite
What is the consequene of an increase in RENIN production with nephrotic syndrome?
In response to low renal BP, Renin is released.
Renin-Angiotensin-aldersterone causes Na2+ to be retained and thus increase in BP.
This will result in more oedema because of the hypoalbuminuria.
Function of FSH?
- Stimulates growth of follicles
- Indirectly causes an increase in oestradiol because as the follicle matures it starts to secrete oestradiol.
What type of cancer is cervical cancer?
85% squamous cell
the rest are adrenocarcinoma
What drugs impair kidney autoregulation?
ACE inhibitors
NSAIDs
Cervical screening frequency
Age 24.5 - First invitation to ensure screening before age 25
Age 25-49 - every 3 years
Age 50-64 - every 5 years
Age 65 + : only if abnormal results, or not had screen since age 50.
Can’t screen if: menstruating, infection, 12 week after pregnancy/ miscarriage/ less 12 weeks post natal, pregnancy.
What is the Schilling test?
Determine how well the patient is able to absorb vitamin B12 from their intestinal tract.
Lichenification
Chronic thickening of skin

Jones fracture is a break between the base and middle part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot.
tx. cast, 6 weeks rest.
Why avoid amoxicilin with tonsillitis?
in case causative organism is Epstein-Barr virus (glandular fever); rash
Which patients are at risk of developing HCC (hepatocellular carcinoma)?
Carriers of HBV and HCV
cirrhosis patients
Partial (focal) seizure.
Two types.
originates in one cerebral hemisphere.
Patient DOESN’T loss consciousness.
(a) Simple partial seizure; conscious not altered.
(b) complex partial seizure - altered consciousness and px exhibits repetitive behaviours.
What is Todd’s paralysis?
A focal appendage transient weakness after a seizure.
It usually subsides completely within 48 hours.
Todd’s paresis may also affect speech, eye position (gaze), or vision.
NB> important to differentiate from ischaemic stroke because seizure is an exclusion criteria for thrombolysis.
What is Wernicke Korsakoff syndrome and the treatment?
develops in alcoholics with thiamine deficiency.
Unexplained asssociated symptoms; the triad ataxia, acute confusional state, ophthalmoplegia
others; nystagmus, polyneuropathy
tx: parenteral thiamine
What is the management of CAP?
low-severity - amoxicillin (or macrolide/ tetracycline if allergic) - 5 day course
moderate-high severity - dual antibiotic tx. Amoxicillin (or co-amoxiclav) and a macrolide.
7-10 day course
What is a glioblastoma?
most aggressive form of brain cancer

Slapped Cheek syndrome
5th disease
parvovirus B19
erythema infectiosum
Upper motor neurone lesion, upper….
face sparing.
What are pseudo seizures?
NEAD - Non-epileptic attack disorder
NES - Non-epileptic seizures
paroxysmal events that mimic epilepsy, but are not due to an epileptic disorder.
Can be physiological or psychogenic.
Psychogenic is most common; dissociative seizures are involuntary and happen unconsciously.
NB> can cause injury and incontinence.
Can addison’s disease cause hypoglycaemia?
YES
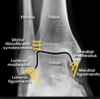
Foot bones 3
When is MMR given?
This currently occurs at 12-15 months and 3-4 years as part of the routine immunisation schedule
What is a Holter monitor?
A Holter monitor is a battery-operated portable device that measures and records your heart’s activity (ECG) continuously for 24 to 48 hours or longer .

Vertical shearing
Whis is Hirschsprung’s disease usually noticed?
Hirschsprung’s is usually noticed in the first 24-48 hours when meconium fails to pass
Two main types of conjunctiva based anatomically
- palpebral conjunctiva lines the lids
- bulbar conjunctiva is over the eyeball
When is the best time to measure troponin levels?
12 hours after event - most severe pain (peak time)
What are Charcot-Bouchard aneurysms?
Aneurysms in the small penetrating blood vessels of the brain.
They are associated with hypertension.
The common artery involved is the lenticulostriate branch of the middle cerebral artery.
Why is it important to treat asymptomatic UTI during pregnancy?
Mx: nitrites on urinalysis.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria should be treated as this can lead to symptomatic urinary tract infection or pyelonephritis.
This can be associated with low birth weight babies and preterm delivery.
Name the two meglitinides drugs that are short-acting and are useful for patients whose meal schedules vary.
Repaglinide
Nateglinide
How do MOAIs work?
Inhibit the breakdown of serotonin at the synapse by inhibition of MAO-A
What is PPCM?
Peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM) ; dilated cardiomyopathy
“deterioration in cardiac function presenting typically between the last month of pregnancy and up to six months postpartum. “
Decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) with associated congestive heart failure and an increased risk of arrhythmias, thromboembolism.
Flat feet
normal up to age six. Arches are present when non-weight bearing.
What’s the incidence of diabetes in children?
1:500
What is the danger if type I diabetes is not identified in children?
DKA
presenting with ABDOMINAL PAIN and VOMITING and COMA.
NB. The mechanism of abdominal pain in DKA is poorly understood but gastric distension, hypovolaemia and electrolyte disturbance may contribute.
Causes of anaemia; inherited
- defects of haemoglobin; sickle cell , thalassaemia
- defects of red cell metabolism; pyruvate kinase deficiency
- defects of red cell membrane; hereditary spherocytosis
- red cell aplasia/ aplastic anaemia
What’s the first line rate control for AF?
Digoxin is no longer first-line for rate control in atrial fibrillation.
Beta-blockers - Bisoprolol
What diuretics can you use in severe CKD?
Loops
(Thiazides only effective to GFR 20-25 ml/min)
+ remember can be used with Kidney stones
tonic
stiffening of all the muscles. back aches. person loses conscious and falls to the floor.
Signs and symptoms of chronic intracranial hypertension
+ causes of chronic IH
(possible causes of acutre IH; head injury, stroke, brain abscess )
- constant throbbing headache
- blurred vision/ diplopia
- nausea and vomiting
subdural haematoma, brain tumour, brain injection (meningitis/ encephalitis), hydrocephalus, venous sinus thrombosis
Many cases; idiopathic. no known cause. More common with women 20s-30s
What are koilonychia, atrophic glossitis, and angular stomatitis signs of?
iron deficient anaemia
What is macrosomia?
The term “fetal macrosomia” is used to describe a newborn who’s significantly larger than average
The transformation zone

The transformation zone can be identified by visual inspection as there is a change in colour and texture from the pale, pink, shiny, smooth surface of the ectocervix to a reddish, granular appearance of the columnar cells that line the endocervical canal.
What’s the common cause of esophageal varices?
cirrhosis and consequences of portal hypertension
Which anti-psychotic drug is associated with agranulocytosis?
clozapine is associated with agranulocytosis
remember: important symptoms of DKA
Triggers: poor compliance/ infections
thirst, polyuria
VOMITING and ABDOMINAL PAIN
KUSSMAUL acidotic breathing
Acetone on breath
Hypovolaemic shock
Monitoring; HbA1c test (% of glycosylated haemoglobin)
List the DDs of pulmonary oedema in pregnancy
Cardiogenic (3)
Non Cardiogenic (2)
Cardiogenic
- Undiagnosed congenital heart disease
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Cardiac ischaemia
- Non cardiogenic
- Pre-eclampsia
- Iatrogenic – medications such as corticosteroids, tocolytics, non-steroidal analgesia
Gestational pemphigoid

Can occur any time in pregnancy, but usually in third trimester
Often occurs on abdomen (involving umbilicus), spreading to limbs, palms and soles
Associated with low birthweight, preterm delivery and stillbirth
Neonate can be affected by same eruption, which is mild and transient
Mx and symptoms of otitis externa?
otitis externa
Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) or fungal
ear pain, itch, discharge
otoscopy: red, swollen, or eczematous canal
Mx:
topical antibiotic or a combined topical antibiotic with steroid
if there is canal debris then consider removal
Malignant otitis externa is more common in elderly diabetics.
What cardiac problem is associated with both typical and atypical antipsychotics?
Prolonged QT interval
arrythmias
Management of Benign prostatic hypertrophy
alpha-adrenergic blockers; prazosin
alpha adrenoceptor antagonists; tamsulosin
or finasteride (inhibitor of testosterone, reduces prostatic hypertrophy)
TURP: TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate.
Examples of 2nd generation sulfonylurea drugs (3)
glimepiride
glipizide
glyburide
ACNE - antibiotic
doxycycline - tetracyclines
if not responding; erythromycin
Why is asthma worse at night?
- Impaired mucoclilary clearance during sleep.
- Possible increase exposure to allergens (house dust mite in bedding).
- Diurnal fluatuations in corticosteroids, catecholamines.
What;s the story with (during pregnancy):
Nitrofurantoin
Co-amoxiclav
Trimethoprim
Nitrofurantoin: Haemolytic anaemia in the neonate
Co-amoxiclav: Avoid in women at r_isk of preterm labour (20-36/40)_ - including risk of necrotising enterocolitis in neonate
Trimethoprim: Avoid in first trimester (folate antagonist)
infectious esophagitis.
Common cause?
Candida albicans
HIV/ cancer patients
What does Pyelonephritis increase the chances of ?
pre-term labour.
Some characteristics of CTS
- more common in women
- tingling in hand
- symptoms often occur at night
- px may hand hand and arm out of bed for relief
- associated with…. (3)
- thenar muscle wasting
what are common causes of hypocalcaemia?
hypoparathyroidism (frequently following surgery)
vitamin D deficiency or abnormal metabolism, chronic kidney disease and hypomagnesaemia
What could cause recurrent abdominal pain?
Idiopathic
constipation
inflammatory bowel disease
urine infections
sickle cell disease
which antithyroid drugs can cause aplastic anaemia or agranulocytosis?
Carbimazole
propylthiouracil
Hoes hyperthyroidism increase or decrease menstral bleeding?
oligomenorrhoea
amenorrhoea
HYPOthyroidism causes heavy bleeding
How does airflow inflammation seen in asthma lead to airflow obstruction?
mast cell degranulation releases histamine, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes.
This causes; vasodilatation and increased vascular permability causing mucosal oedema.
Increase in bronchial secretions.
Smooth muscle contraction, causing bronchospasm.
what drug would you give for acute renal colic?
Diclofenac IM (recommended by NICE)
What is a common cause of melaena.
NB> melaena is due to an upper GI bleed
peptic ulceration
What could CTS be associated with?
pregnancy
diabetes
hypothyroidism
Most common type of renal stone
Calcium oxalate
What is Von Willebrand disease?
is the most common hereditary blood-clotting disorder
It arises from a deficiency of von Willebrand factor (vWF), a protein that is required for platelet adhesion.
What is Ramsay Hunt Syndrome?
Ramsay Hunt syndrome; varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox) becomes reactivated in the geniculate ganglion of the VIIth cranial nerve (facial nerve) causing facial paralysis, loss of taste, vestibulocochlear dysfunction and pain.
As a general rule, shingles is a disease of sensory nerves but Ramsay Hunt syndrome is distinctive in that there is a motor component.
How long does it typically take for CIN to progress to cervical cancer?
15 years
although could be 3-40 years.
There is usually a linear progression from CIN stages 1,2, and 3.
Why do you get lipiduria with nephrotic syndrome?
Passing of lipoproteins in the urine due to kidney damage (thus also hypoalbuminaemia)
What does the Cockcroft-Gault formula measure, and when is it used?
- Preferred method for estimating renal function or calculating drug dosages in patients with renal impairment e.g. elderly or extremes of muscle mass.
- Estimate of CrCl
(NB> use ideal weights for obese px)
What factors cause cause a hypoglycaemic attack?
Too high a dose of medication (insulin or hypo causing tablets)
Delayed meals
Exercise
Alcohol
tonic
stiffening of all the muscles. back aches. person loses conscious and falls to the floor.
Papilloedema
Optic disc swelling; increased intracranial pressure.
Usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare.
May be asymptomatic or with a headache.
What are some risks factors for UTI in pregnancy?
GDM
use of systemic corticosteroids
history of UTI
Problem: untreated can lead to symptomatic UTI or pyelonephritis
What are the features of well-controlled asthma?
minimal symptoms at day and night
minimal need for reliever medication
no exacerbations
no limitation of physical activity
normal lung function PEFR >80% predicted/ best
What in the family history could suggest maturational delay?
Late maternal menarche
What could cause wrist drop?
Radial nerve compression
What kind of seizure activities are there?
- motor
- sensory
- cognitive and psychic
- autonomic disturbances
What’s the MOA of benzodiazepines?
Enhances the effect of gamma-aminobutric acid,
GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter.
FIGO staging system

Need to know that >>> platelets (called thrombocytosis) is closely linked to endometrial cancer.

What is orthopnoea?
orthopnoea is shortness of breath (dyspnea) that occurs when lying flat, causing the person to have to sleep propped up in bed or sitting in a chair.
What is Proctitis?
Proctitis is an inflammation of the lining of the rectum.
Proctitis can cause rectal pain and the continuous sensation that you need to have a bowel movement
Acute fever - causes

What diuretic group could be used to help with reducing the incidence of renal stones?
thiazide diuretics because they cause hypercalcaemia (i.e. hypocalciuria)
Which AF drug can cause thyrotoxicosis?
amiodarone
Dermatome to little finger?

Why don’t you treat HT immediately following a stroke?
- cerebral autoregulation of blood flow is disturbed and therefore risk of hypoperfusion.
- Watershed infarction; there can be an extension of the stroke due to reduced blood supply around area of infarction.
NB. continue with regular BP meds if taken previously.
How does an acoustic neuroma present?
should always be considered in patients with unilateral sensorineural deafness or tinnitus.
NB. otosclerosis causes a conductive deafness, and symptoms are bilateral.
Loss of proteins with nephrotic syndrome predisposes patient to what?
Thromboembolisms (due to loss of clotting proteins)
Sepsis/ infections (due to loss of immunoglobulins)
Lipid abnormalities - can accelerate atheromas
Anaemia (loss of transferrin)
Oedema (lower limbs, sacrum) + can be periorbital & hands
Syphilis - antibiotic
Benzylpenicillin
or
Doxycycline
Hamstring injury management
crutches and refer to fracture clinic
What is this?

nodular malignant melanoma
Some key points of motor neuron disease; what’s the worse type and what’s the most common?
Progressive bulbar palsy - worse. Affects tongue, muscles of mastication, facial muscles, brainstem motor nuclei. Nasty one.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ; 50% of patients. Mixture of LMN and UMN signs in legs.
protozoan parasite that causes malaria
Plasmodium falciparum
Breast cancer risk factors (5)
Female sex (75 male deaths from breast cancer in 2004)
Increasing age (80% of breast cancers in post menopausal women)
Family history of breast cancer-BRCA1 and BRCA2
Obesity (post menopausal women only)
High alcohol consumption
Name some potentially damaging Kidney drug groups
- ACEIs, ARBs,
- PPIs
- diuretics
- antibiotics
- NSAIDs
- Lithium
What’s the story with rubella (german measles) and pregnancy?
NO WOMAN should try to conceive unless the have had rubella, or been immunised.
Most dangerous in 1st trimester.
Can cause blindess, deafness, cardiac abnormalities, mental retardation.

The hallux dorsiflexes, and the other toes fan out; this is Babinski’s sign;
damage to the central nervous system.
Stimulate from heel upwards.
HIV is caused by what type of virus?
blood-borne RNA retrovirus
- intercourse, drug use
- maternal-child transmission
- transfusion of blood products
Which coexisting illnesses increase risk of CKD?
Diabetes,
Hypertension
CVD,
structural renal tract disease
multisystem diseases that affect the kidneys, eg. SLE
Management of Otitis media
analgesia. 80% improve spontaneously.
>48hrs require antibiotics
amoxiciliin/ clarithromycin
Describe the respiratory tract effect of anticholinergics (eg. ipratropium, tiotropium)
Helps prevent the bronchoconstriction of smooth muscle by inhibiting acetylcholine and the activation of parasympathetic n.s.
** they block the bronchoconstricting effect of the vagus (parasympathetic) nerve stimulation.
When would you perform a ABG analysis?
When O2 sats are < 92%
How does placenta praevia present?
incidental finding on ultrasound
Painless bleeding starting after the 28th week; Typically, it is sudden and profuse but usually does not last for long and so is only rarely life-threatening.
bleeding during intercourse
What’s the difference between hemiparesis and hemiplegia?
Hemiparesis ; unilateral weakness
Hemiplegia; complete loss of power on one side
What’s the 1st line antibiotic for mastitis?
flucloxacillin for 10-14 days.
Breast feeding or expressing should continue during treatment.
What is the pathophysiology of asthma? (3)
Bronchospasm
mucosal oedema
mucus hypersecretion
- causing airway obstruction
What is Argyll Robertson (AR) pupil and what’s the most important cause (and very specific)?
bilateral small pupils that reduce in size on a near object (i.e., they accommodate), but do not constrict when exposed to bright light
Syphilis
+ diabetic neuropathy
What is Terlipressin?
a vasopressor analogue that acts as a vasoconstrictor to management low blood pressure.
If an egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum eventually decays cand stops secreting progesterone.
What does it decay into?
a mass of fibrous scar tissue; corpus albicans
What can cause sudden loss of vision?
retinal detachment
central retinal artery occlusion
vitreous detachment/ haemorrhage
+ full neurological examination for cv event
Diabetes; what is the initial sign of renal involvement?
microalbuminuria
.. progressing to >> proteinuria or even nephrotic syndrome.
*** Note: diabetic nephropathy usually suffer from diabetic retinopathy or neuropathy. Look for this! ***
What is vancomycin used for?
+ what happens if >> infusion rate?
MRSA (rem. staphlococcus) - given orally.
Adminstered parenterally to treat systemic infections.
>>> infusion rate = hypotension, erythematous rash on face/ upper body “red man syndrome”
Domperidone
D2 antagonist
Similar to metoclopramide but doesn’t cross the blood-brain barrier and rarely causes sedation or extrapyramidal effects.
What is CA-125?
Cancer Antigen 125
a protein that may be found in high amounts in the blood of patients with ovarian cancer.
Only 50% sensitive with early-stage cancer.
Atopic eruption of pregnancy
Commonest pregnancy specific dermatosis, and is associated with atopy. It mainly occurs in the second or third trimester, more commonly in multiparous women. It is characterised by patches of intensely itchy papules which become excoriated. Treatment includes emollients, antihistamines and topical steroids.
What type of headache is common first thing in the morning?
migraine
CVA; what’s a typical characteristic of middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion?
FACE or ARM is more affected than the leg.
Target BP for T2DM
<140/80
Mx of bronchiolitis?
Supportive; humidified oxygen if <92%
nasogastric if unable to drink/ feed
suction if needed.
MCQ - important facts about Metformin
MOA, adverse effects, contraindications
Mechanism of action
- increases insulin sensitivity
- decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis
- may also reduce gastrointestinal absorption of carbohydrates
Adverse effects
gastrointestinal upsets are common (nausea, anorexia, diarrhoea), intolerable in 20%
lactic acidosis* with severe liver disease or renal failure (rare but important to know for exams)
Contraindications**
chronic kidney disease: NICE recommend that the dose should be reviewed if the creatinine is > 130 µmol/l (or eGFR < 45 ml/min) and stopped if the creatinine is > 150 µmol/l (or eGFR < 30 ml/min)
metformin may cause lactic acidosis if taken during a period where there is tissue hypoxia. Examples include a recent myocardial infarction, sepsis, acute kidney injury and severe dehydration, iodine-containing x-ray contrast media: there is an increasing risk of provoking renal impairment due to contrast nephropathy; metformin should be discontinued on the day of the procedure and for 48 hours thereafter
**metformin is now sometimes used in pregnancy, for example in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome
What are the values of CRB-65?
(essential assessment of pneumonia in the community)
Confusion (abbreviated mental test scote <= 8/10)
Resp Rate >= 30/min
BP systolic <=90 and/or diastolic <=60mmHg
Aged <=65
(NB urea > 7 mmol/l)
What are sulfonylureas and meglitinides examples of?
hypoglycaemic drugs
What is an inherent problem with Sulfonylurea drugs?
Since they increase insulin secretion, can lead to hypoglycaemic episode if px skips or delays meals.
Alcohol increases hypoglycaemic effect.
Stopping antipsychotics, what’s the story.
Very gradual due to relapses.
Ideally should continue with medication for two years after relapse.
What is cervical excitation?
(chandelier sign)
Positive for PID (pelvic inflammatory disease) or ectopic pregnancy and it is useful to differentiate from appendicitis.
Put a finger each side of the cervix and push the cervix from side to side – this in turn stretches the tubes
If membranes rupture, baby needs to be delivered quickly. WHY?
Risk of infection
What is uterine atony?
Uterine atony is a loss of tone in the uterine musculature. Normally, contraction of the uterine muscles during labor compresses the blood vessels and reduces flow, thereby increasing the likelihood of coagulation and preventing hemorrhage.
Clinically, 75-80% of postpartum hemorrhages are due to uterine atony.
tx of rhabdomyolysis
Rapid IV fluid rehydration (saline)
properly perfuse the kidneys and limit damage to the kidneys due to myoglobin.
What’s the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto thyroiditis
-autoimmune disease
associated with T1DM
Can cause transient thyrotoxicosis in the acute phase.
What is myeloma
+ common symptoms

Blood cancer - most common (15%), from the plasma cells.
CRAB - Calcium, Renal, Anaemia, Bone lesions
Pain, Fractures, hypercalcaemia
Fatigue - anaemia
Recurring infection
Kidney damage
Peripheral neuropathy

AOM
How does mianserin and mirtazaline work?
block presynaptic alpha2 -receptors increases monoamine output
EM tx of hypoglycaemia
50ml of glucose 50% if IV access available.
otherwise 1 mg glucagon
(as PAs 10% glucose IV okay)
non-emergency; dextrose, then more complex carbohydrates.
What age is typical for pyloric stenosis, and what’s the cut off age?
2-8 weeks, rare above 6 months
Partial (focal) seizure.
Two types.
originates in one cerebral hemisphere.
Patient DOESN’T loss consciousness.
(a) Simple partial seizure; conscious not altered.
(b) complex partial seizure - altered consciousness and px exhibits repetitive behaviours.
Most common cause of aortic stenosis and physiological effect
senile calcification
Heart has to work harder to push blood through the stenotic valve.
>> Volume load = hypertrophy + myocardial dysfunction, arrhythmias, heart failure.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis

Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
After a few days a rash appears, which may look like a target – darker in the middle and lighter around the outside. The rash isn’t usually itchy, and spreads over a number of hours or days. Large blisters then develop on the skin, which after bursting leave painful sores.
EMERGENCY

Why give 400IU daily Vit D to pregnant women?
- Vit D is common during pregnancy and post partum causing transient osteoporosis of pregnancy.
- Vit D def causes fetal morbities; growth restriction, skeletal deformities, tooth and bone problems
Peptic ulcers location
stomach
upper part of duodenum
Risk factors for OA of the hips
+ scoring system
Female - twice as common
Obesity
Increasing age
developmental dysplasia of the hip
Oxford Hip Score
General advice for facial fractures
no nose blowing
no sneezing
knocked out teeth; keep in saline or milk. 1-4 hour window to reimplant.
Bites; Augmentin antibiotic
What benign things can increase urinary protein output?
Pyrexia
exercise
adoption of upright posture(postural proteinuria)