THE FINALS 2 Flashcards
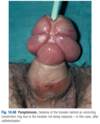
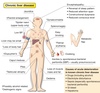
Hemiplegic gait
circumduction of the leg, with the foot dropping (hence the circumduction).
associated hypertonic flexion of the ipsilateral arm.
which extraoccular muscle attaches nasally?
Inferior Oblique
What is Hyosine used for?
(and MOA)
Motion sickness and vesibulocochlear dysfunction.
Targets the vomiting centre and vestibulocochlear nuclei.
MI and the elderly/ diabetes mellitus. What do I need to remember?
30% of patients have NO pain
What endocrine problem can cause hypertension in risk group women 30-50 years?
Conn’s
- primary >>> aldosterone
66% cases due to enlarged adrenal glands.
tx. surgery, spironolactone
What’s the difference between arterial thrombi and venous thrombi?
arterial thrombi (white); more platelet aggrevation driven
venous thrombi (red); more coagulation driven
If the JVP is not elevated but the patient has oedema, what does this mean?
origin is NOT cardiogenic
Moderate LVF management (acute)
- Larger dose of furosemide and given via IV (50mg) - can be increased with renal impairment px
- BP > 140 start GTN (25mg with 25 saline @ 0.5mg-10mg/hr)
Titrate; keep BP above 100mmHg
- hypoxic? CPAP. careful of resp failure II
- Morphine presided by Metoclopramide
MOA of Heparin
binds to body’s own anticoagulant (antithrombin III)
This complex inhibits factor Xa (and other factors)
Definition of crescendo angina
>> frequency with << reason
but not at rest
What is hypopyon?
inflammatory cells in the anterior chamber of the eye.
It is a leukocytic exudate, usually accompanied by redness of the conjunctiva
Aspirin; clinical usages and action as an antiplatelet drug
Acute coronary syndrome
Thrombic strokes; acute and prophylaxis
shown to prevent MI with angina.
Artificial heart valves, percutaneous coronary angioplasty.
ACTION: inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid.
Safe drinking limits
14 units (both men and women)
+ at least two drink-free days each week.
What is the skin like with LVF?
grey, clammy, cold skin
(assess peripheral perfusion)
Psychosis defined
Mental health problem that causes people to perceive or interpret things differently from those around them. This might involve hallucinations or delusions.
The two main symptoms of psychosis are:
hallucinations – where a person hears, sees and, in some cases, feels, smells or tastes things that aren’t there; a common hallucination is hearing voices
delusions – where a person believes things that, when examined rationally, are obviously untrue – for example, thinking your next door neighbour is planning to kill you
Moderate LVF management (acute)
- Larger dose of furosemide and given via IV (50mg) - can be increased with renal impairment px
- BP > 140 start GTN (25mg with 25 saline @ 0.5mg-10mg/hr)
Titrate; keep BP above 100mmHg
- hypoxic? CPAP. careful of resp failure II
- Morphine presided by Metoclopramide
non-vertiginous dizziness types
- presyncope
- light headedness (eg. postural hypotension)
- disequilibrum (altered gait/ balance without head symptoms)
ranitidine
H2 histamine receptor antagonist
blocks histamine and thus decreasing the amount of acid released by cells of the stomach.
Common side effects of olanzapine
Weight gain, and increased appetite + oedema
hyperglycaemia, dyslipidaemia
Drowsiness or dizziness
Constipation, dry mouth
Reduced interest in sex, erectile dysfunction
Strange muscle movements (more typical anti-psychotics)
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Assessing standing.
Why ask px to stand without pushing up with arms?
Difficulty indicates proximal muscle weakness.
(other signs; difficulty getting out of chairs, climbing stairs)
Severe LVF management
- Furosemide 50mg IV (increase if patient has renal impairment)
- CPAP
- Treat arrhythmias
- lots of discussion with senior staff
- dobutamine as inotrope in cardiogenic shock - consultant
Wernicke’s encephalopathy
- acute brain reaction to severe lack of thiamine.
Wernicke’s encephalopathy;
confusion, loss of coordination [ataxia], eye paralysis [ophthalmoplegia], nystagmus, memory disturbance, hypothermia, hypotension, and coma f
Parenteral thiamine.
Thiamine helps brain cells produce energy from sugar.
Baseline drugs for heart failure
- titrate ACE inhibitor and monitor Kidney function with increments.
- Beta blockers. titrate and assess HR, BP
- diuretics; titrate
Adverse reactions with aspirin?
GI irritation, bleeding,
hypersensitivity reactions,
tinnitus

Dacryoadenitis
- Swelling of the outer portion of the upper lid, with possible redness and tenderness
- Pain in the area of swelling
- Excess tearing or discharge
- Swelling of lymph nodes in front of the ear
Common causes include mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, staphylococcus, and gonococcus.
What group of people (ECG) is at risk of Torsades de Pointes - type of ventricular fibrillation.
People who have long QT syndrome are at
increased risk for torsades
(also - imbalanced amounts of
potassium, calcium, or magnesium in the
bloodstream can cause this condition)
Risk factors for testicular cancer
men aged 20-34 years
bilateral undescended testes x 10 risk
SAH versus thunderslap migraine
maybe clinically indistinguishable from SAH.
Thunderslap migraine usually in younger patient with history of migraine, and unilateral with previous episodes.
Acute LVF Management - What would you include in D - disability?
access consious level
blood sugar levels
Predisposing factors for aortic dissection?
Marfan’s syndrome
severe hypertension
trauma
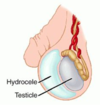
How to differentiation between hydrocele and epididymis cysts
if the testis are palpable separate from the swelling then it is a cyst.
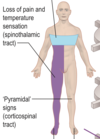
Differences between upper and lower motor neurone lesions

optic disc completely yellow or white indicates?
optic nerve atrophy
What’s this?

AF
Initial treatment of LVF
- Sit up patient
- Give oxygen
- If COPD do ABG early
- Treat arrthymias (esp. tachycardia/ bradycardia)
- Ensure STEMI has been excluded (Call reg if STEMI)
- If BP >100mmHg give 0.5mg GTN S/L
Mild LVF management
Start on furosemide 40mg.
If already on furosemide then give normal dose twice per day
When is a CT scan URGENT following a stroke?
- if 3 hour window to start thrombolytics
- evidence of head injury
- severe headache at the time of onset of weakness
- GCS score deteriorating
- prior anticoagulation treatment
If the heads of the clavicles aren’t level, what does this mean?
rotation
ECG and STEMI….
persistent ST-elevation
If infective endocarditis is suspected, what is important to ask about?
recent dental work, IV drug use, skin infections (causes of bacteraemia)
(damage to peripheral vessels, eg. an infected false aneurysm of common femoral artery can be a source for infective endocarditis)
What are some symptoms of Foetal alcohol syndrome?
- decreased muscle tone
- poor coordination
- developmental delay
- heart defects
- a range of facial abnormalities
Can you give codeine for migraines?
Drugs for recurrent migraines?
No because of associated nausea and rebound headaches.
Triptans (e.g. sumatriptan)
What factors can cause an obstruction to LV flow? (3)
aortic stenosis
LV hypertropic (narrowing of lumen)
supravalvular narrowing
congenital subvalvular aortic stenosis (formation of a ridge/ diaphragm)
What is metoclopramide used for?
Given with morphine (increases GI motility)
What type of headache is common first thing in the morning?
migraine
Indications for defibrillation
Ventricular arrhythmias (VT/ VF) with no pulse.
What might to give an alcoholic patient at arrival in hospital?
- sedation - benzodiazepine
(helps to control withdrawal symptoms and prevent seizures)
- delirium tremens; lorazepam or antipsychotics eg. haloperidol or olanzapine.
- thiamine, electrolytes, fluids.
Trichomonas Vaginalis management
* Can enhance HIV transmission
TV is less common.

If T. vaginalis is suspected, a high vaginal swab can be taken from the posterior fornix but sensitivity may be low because motility reduces with transit time.
Treat both partners
metronidazole in most cases, resistant strains are on the increase.
Systemic treatments are far more effective
what happens to the T waves in hypokalaemia?
<< amplitude, flattened or inverted
also U waves can be seen.
What is 2nd degree heart block?
(Mobitz I)
Not all P-Waves followed by a QRS complex.
The baseline PR interval is prolonged, and then further prolongs with each successive beat, until a QRS complex is dropped.
crossed eyes … is a condition in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. Proper name?
Strabismus
Eye conditions not to miss
- acute-angle closure glaucoma
- peri-orbital cellulitis
- giant cell arteritis
- keratitis
- uveitis
What happens with pronator drift
and what does it indicate?
- The hand drifts so the palm turns inward and/or the hand drops
- This is a very sensitive indicator of upper motor neurone weakness, usually due to stroke
Coronary atherosclerosis isn’t the only cause of myocardial ischemia. Name two others
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
aortic stenosis
(a loud systolic murmur may point to these findings)
What drug group is used for first line tx of schizophrenia?
atypical antipsychotics
(remember clozapine - agranulocytosis risk)
clozapine
olanzapine - >> dyslipidemia and obesity
risperidone
quetiapine
aripirazole - good for raised prolactin
Premature beats don’t really need treatment unless..
- autonomic signs; pale, sweaty with heatbeats change pace.
- chest pain
- dyspnoea
- syncopic sensations
What’s the antidote for warfarin-induced bleeding
Phytonadione (vitamin K1)
Nalmefene
Is recommended for the reduction of alcohol consumption in patients with alcohol dependence who have a high drinking risk level, without physical withdrawal symptoms, and who do not require immediate detoxification
Do all patients with AF experience palpitations?
NO, especially the elderly.
Need to take case history to find cause.
Which conditions are P waves absent?
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial Flutter
Hyperkalaemia; P waves are reduced in amplitude or totally absent; associated with tall T waves and wide QRS complexes.
What are the signs and symptoms of testicular torsion?
Sudden severe pain in the scrotum
Scrotal swelling
Unusual position of testicle
pain. *blue spot on scrotum*
Typically young boys wake up with scrotal pain in the middle of the night or morning.
common between 12- years age.
MEDICAL EMERGENCY
What can cause abnormal size of pupils?
Drugs
damage to optic cranial nerve (II)
Oculomotor nerve (III)
or brain (especially trauma)
What’s the difference between nitrates and CCBs with reducing cardiac work?
Nitrates: act primarily on venous tissue, thus affect preload.
CCBs act mostly on arteriolar muscle to reduce afterload.
PACs?
PVCs?
Premature Atrial Contractions
Premature Ventricular Contractions
inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called….
Dacryoadenitis
Clinicial uses for Warfarin
Long term management of DVT, AF, and artificial heart values.
What sounds would you hear with LVF?
LUB-DUB-uh
“galloping horses”
- too much fluid
mech of action,
clinical indications,
potential adverse effects
of sucralfate,
(cytoprotective drug)
this polysaccharide adhers to ulcer craters , inhibits pepsin-catalyzed hydrolysis of mucosal proteins. Helps form a protective barrier.
Used to treat peptic ulcers, but not so effective as H2blockers or PPIs, so only indicated with patients who can’t tolerate the others.
Take 2 hours between other drugs.
What are the non-cardiogenic causes of AF?
- Hyperthyroidism
- >> alcohol
- aging
- idiopathic
Symptoms of diabetic neuropathy

symptoms of cardiogenic shock
- chest pain, palpitations, history of IHD, AF
- Cold sweaty peripherae; weak pulse, JVP raised, tachycardia
- pulmonary oedema
Varicocele cause - pathophysiology

What is 3rd degree heart block (complete heart block)?
Complete dissociation of P waves and QRS complexes.
Ventricular contractions only occur because of escape rhythms.
What is ‘speed’
amphetamines
- mydriasis
- tachycardia
- hyperreflexia
- euphoria, >> concentration & energy.
What are the four classes of shock?
- Distributive
- Cardiogenic
- Hypovolemic
- Obstructive
What is Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome?
A type of pre-excitation syndrome (early activation of the ventricles due to impulses bypassing the AV node via an accessory pathway.)
a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.
What does QT represent?
total duration of ventricular systole
Which type of glaucoma could be an emergency (+symptoms)?
Primary angle closure glaucoma (not common)
Can cause sudden, severe symptoms.
Symptoms can include:
intense eye pain
a red eye
a headache
tenderness around the eyes
seeing halos or “rainbow-like” rings around lights
blurred vision
feeling and being sick
Difficulty understanding speech or using correct words (receptive or expressive dysphasia) may indicate….
stroke
two big divisions of vertigo
- central
- peripheral
Acamprosate
Helps prevent relapses in people who have successfully achieved abstinence from alcohol.
Affects GABA in the brain
mech of action,
clinical indications,
potential adverse effects
of metoclopramide
others; prochlorperazine, domperidone
(acts peripherially - prokinetic drug
and acts centrally - antiemetic)
Blocks dopamine D2 receptors; this prevents the relaxation of GI smooth muscle produced by dopamine. Also increases acetylcholine from cholinergic motor neurons in the enteric nervous system.
>> tone and motility in the oesophagus and stomach. (therefore opioid induced sickness)
Also >> gastric emptying.
NB> also increases resting pressure of lower oesophageal sphincter, therefore << acid reflux.
Indications: GERD, diabetic gastroparesis, intractable hiccup, also antiemetic.
Adverse effects: CNS reactions. CONTRAINDICATED with px with seizures.
MCA occlusion; which part of the body affected?
face and arm more likely thatn the leg.
What’s the difference between angina and MI pain?
Pain is similar, but MI pain is more severe and lasts longer.
MI pain lasts 20 mins or more and is not relieved by nitrates.
If sweating, nausa and vomiting present then >> chance of MI>
What are the symptoms of a complete MCA?
(4)
facial asymmetry, arm weakness, and speech deficits
- hemiplegia (paralysis) of the (1) contralateral side, affecting the lower part of the face, arm, and hand while largely sparing the leg
- (2) contralateral sensory loss in the same areas
- (3) contralateral homonymous hemianopia—visual-field deficits affecting the same half of the visual field in both eyes.
- (4) RIGHT - neglect, poor motivation
- (4) LEFT - aphasia (inability ro comprehend and formulate language)
If px has the below ECG and chest pain, what’s the diagnosis?

(inverted U waves)
evolving M.I.
May be earliest sign of unstable angina

AF management
Rate control
Rhythm contol
Anticoagulation control
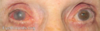
allergic conjunctivitis
bilateral, often related to hay-fever.
Chemosis (oedema of the conjunctiva) is a classic sign.
tx. antihistamines
what’s the problem with antipsychotics and the elderly?
increased stroke risk
increased VTE risk
What common virus can cause encephalitis (70% mortality rate)
herpes simplex
What investigations?
ABG
ECG
BP, etc.
CXR
chest examination. Need to rule out other causes of breathlessness
Trichomonas Vaginalis
Trichomonas vaginalis is a very common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can cause vaginitis, cervicitis and urethritis.
T. vaginalis is a flagellated protozoan
Urethral infection is present in 90% of infected women
Almost exclusively STi
Most common STi and most curable.
Can be confused with BV
Although this is usually a frothy yellowish discharge, it can vary from being thin and scanty to profuse and thick.
Other common symptoms; vulval itching, dysuria or offensive odour.
There may be signs of local inflammation with vulvitis and vaginitis.
Cervicitis may be present ; ‘strawberry cervix’.
hypomanic (Bipolar affective disorder)
less severe and without psychotic symptoms
Why don’t you treat HT immediately following a stroke?
- cerebral autoregulation of blood flow is disturbed and therefore risk of hypoperfusion.
- Watershed infarction; there can be an extension of the stroke due to reduced blood supply around area of infarction.
NB. continue with regular BP meds if taken previously.
Symptoms of Huntington’s Disease
(hereditary disorder)
- degeneration of aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurons in the striatum.
mutation in the huntingtin gene, which results in the production of a toxic form of the huntingtin protein that attacks the neurons.
- dancelike movements of the limbs (choreoathetoid movements)
- rhythmic movements of the tongue and face
- mental deterioration that leads to personality disorders
- psychosis, dementia
- Symptoms usually start in 30s
What’s a common symptom of a fractured orbit?
Diplopia
due to obstruction of rectus muscles, or suspensory ligament is not fixed.
peripheral vertigo causes
(most common cause of vertigo, not central causes)
- conflicting sensory information from ears, eyes, and joints.
- inner ear/ vesticular system disorders
- eg.
- paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Meniere’s disease
- labyrinthitis
- visual vertigo
- vestibular neuronitis
What’s best for arterial thrombosis? Anticoagulants or antiplatelets?
Antiplatelets
What clinical findings could indicate recent harmful alcohol usage?
macrocytosis without anaemia
raised y-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
Raised alanine and aspartate aminotransferase (ALT and AST), or carbohydrate deficient transferrin (CDT)
What is the cardinal symptom of serotonin syndrome?
spontaneous clonus (best found at the ankle)
Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria (HSTC)
Ocular clonus manifests as rapid and equal movements of the eyes and is best elicited by getting the patient to fix on a finger moved rapidly to the midline.
What can you get transient murmurs of mitral regurgitation with unstable angina/ MI?
Ischaemia may have affected the papillary muscle.
Acute LVF Management: What drugs for/to :
Speed up
Slow down
Irregular HR
Atropine - to speed up
Adenosine - to slow down (can be given very quickly)
Amiodarone - irregular HR (potassium channel blocker)
Used to suppress AF and flutter
Possible causes of direct swelling/ pain of the testicles (4)
hernia/ strangulated hernia
testicular torsion
epididymitis and orchitis
hydrocele/ variocele
Where does the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge?
Factor X - major rate-limiting step
What are the risk factors for generalised anxiety disorder?
Risk factors
Being aged between 35 and 54.
Being divorced or separated.
Living alone or as a lone parent.
- also remember the protective factors
These include:
Being aged between 16 and 24.
Being married or cohabiting.
what’s the Mx of an acute migraine?
oral triptan and an NSAID/ paracetamol
Acute LVF Management: What is the danger of morphine?
Resp failure II; caution with COPD, renal failure, or the elderly.
Give very slowly and reduce slowly.
* don’t give morphine orally because cannot regulate *
Fluid challenge and central venous cannula/ measurement of CVP; what’s that about?
If CVP doesn’t rise or rises transiently and then falls, then px is ‘underfilled’.
What is vasa nervorum?
blood vessels that supply the nerves
Rhythm control
NB> Used AFTER rate control if monotherapy ineffective.
Cardioversion
Can consider amiodarone for 12 months after electrical cardioversion to maintain sinus rhythm.
Torsades de pointes is an example of….. ventricular fibrillation
What can cause Torsades of pointes?
- Imbalances in Potassium, Calcium, or magnesium.
- People with long QT syndrome are at increased risk.
Some causes of aortic stenosis include;
Calcification
Congenital
Endocarditis
Rheumatic fever
Palpitations/ syncope ; are these important?
YES.
Urgent investigation. Could have malignant but treatable arrhythmia (usually bradyarrhymias)
What can cause PVC (premature ventricular contractions)?
NB. ECG; these look like broadened QRS complexes with greater amplitude.
- Hypokalaemia makes spontaneously polarization more likely.
- Hypomagnesaemia also makes poloriziation more likely.
- Existing damage to myocardium can provoke PVCs (scarring due to previous MIs, or surgery)
- Inflammation cause cause increases in cytokine levels are increase irritability of myocytes.
What is crystal meth?
methamphetamine
(related to amphetamine group)
but … more potent, longlasting and harmful.
What cardiac conditions can cause PACs?
infection
genetic defects
narrow/ blocked vessels
valve disease
What’s this?

Atrial Flutter
Severe LVF management
- Furosemide 50mg IV (increase if patient has renal impairment)
- CPAP
- Treat arrhythmias
- lots of discussion with senior staff
- dobutamine as inotrope in cardiogenic shock - consultant
What does unsteadiness with eyes open imply?
cerebellar disorders
Is alcohol a risk factor in self harming?
Studies have shown that 25% of patients who self-harm are regarded as having a problem with alcohol
Lithium

Avoid any medicines that can impair renal function or induce hyponatraemia
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
Diuretics (particularly thiazides).
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) - sometimes co-prescribed.
Aspirin, stroke, no CT scan results. What’s the story?
No evidence that starting aspirin before CT findings are known adversely affects prognosis.
High BP two weeks after stroke. Which meds?
ACE inhibitors (perindopril - take at bedtime because can become dizzy)
thiazide diuretics
POUND mneumonic
- Pulsatile
- 4-72 hOurs duration
- Unilateral
- Nausea or vomiting
- Disabling intensity
proptosis/ exophthalmos

Bilateral - Grave’s disease (abnormal connective tissue deposition).
Unilateral - possibly orbital tumour, trauma, swelling of surrounding tissue.
Corneal dryness and damage can occur if eyelids cannot close properly.
What is lithium used for?
Has slow rate of action; 7-14 days
Secreted by Kidneys; check ACR and eGFR
NB. plasma lithium levels increase with drugs that deplete sodium (competitive reabsorption at the renal level)
Mood stabilizer
Management of acute manic/ hypomanic episodes
Prophylaxis of bipolar illness. Highly effective at reducing relapes of manic episodes and suicide rates.
Can be used to augment the effect of antidepressants when co-prescribed with antidepressants in acute depressive illness.
What is Dipyridamole?
Dipyridamole is an antiplatelet medication that also has vasodilating properties that can make it unsuitable for use in those with severe coronary artery disease, unstable angina, recent myocardial infarction.
Can be combined with aspirin as an option to prevent occlusive vascular events in patients who have had a TIA, or ischaemic stroke.
What drug can be used to treat subarachnoid haemorrhage headaches?
Nimodipine
- calcium antagonist which has shown to improve outcome following SAH, probably as a result of reduced cerebral vasospasm
Thrush (vaginal and vulval candidiasis)
Candida albicans
Risk Factors; diabetes (definite risk factor)
Presents; itching (puritis vulvae), soreness
white, cheesy discharge NON-OFFENSIVE
mild dyspareunia
dysuria
NB. Thrush can give symptoms of UTI
Signs: vulval erthema (and possible oedema), satellite lesions, excoriation.
Stroke tx whilst awaiting CT scan results
Px NBM
Nasogastric tube, IV fluids
Oxygen mask, monitor cardiac rhythm (digoxin if needed)
Possibly catheter to monitor output
Aspirin 75mg
Statins (low dose) even if lipid levels normal
TED (thromboembolic disease) stockings
LVF Bundle
- ABCDE, then oxygen
- perform ECG, bloods, CXR, and ABG
- treat arrhythmias >150 or <40
- Call cardiologist reg BP <100, or STEMI
- GTN 0.5mg if BP>100
- Furosemide
When are the representative drugs steptokinase, alteplase indicated?
intravenously to degrade thrombi in px with
MI, thromvotic stroke, PE
Primary means of restoring coronary blood flow if angioplasty facilities not available.
Dysarthria isn’t just due to stroke. What are other causes?
multiple sclerosis
cerebellar disease
motor neuone disease
Characteristics of migraines
- often unilateral. Recurrent
- usually pulsatile
- builds up over minutes to hours
- occurs with or with aura
- associations include; nausea & vomiting, photophobia, sound sensitivity, family history
- exacerbation with physical activity
- triggers; cheese, chocolate, etc.
NB. neurological exam should be negative
What is Sotalol?
Drug used for serious abnormal heart rhythms.
Can cause prolongation of the QT interval along with a small risk of life-threatening polymorphic ventricular tachycardia known as torsade de pointes.
Non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker that also exhibits class III antiarrhythmic properties.
Characteristic of anterior cerebral artery occlusion
patient’s leg will be more affected than face or arm.
Where should the nasogastric tube go?
into the gastric bubble
What are the characteristics of myopathies?
Tone is affected
Reflexes are affected
* it doesn’t affect sensation *
* no fasciculations *
muscle weakness is usually proximal and symmetrical
What activates the extrinsic pathway in the coagulation cascade?
a complex tissue factor called thromboplastin.
Can PE cause syncope?
YES
and frequently overlooked reason!!
PE can obstruct outflow from the right ventricle.
Secondary headaches
- vascular
- infectious
- neo-plastic
- drug induced cause
- traumas
What pulse values might signify arrhythmias?
bradycardic <40
tachy cardic >140
or irregular
Investigation to confirm pertussis?
per nasal swap
caused by Bordetella pertussis bacterium
What is neglect?
Inability of a person to process and perceive stimuli on one side of the body or environment
It is most common after damage to the right hemisphere (therefore left hemispatial neglect). Right hemisphere of the brain is specialized for spatial perception and memory, whereas the left hemisphere is specialized for language.
ECG - normal, then what?
What findings?
strongly consider an alternative diagnosis
ST elevation/ depression
What drugs could elicit serotonin syndrome?
Drugs include SSRIs, other antidepressants, opioid analgesics, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, serotonin-releasing agents (e.g., amfetamines), lithium, and tryptophan.
Absence of exposure excludes serotonin toxicity.
Treatment of Huntington’s Disease
symptoms are consistent with excessive dopaminergic activity,
therefore drugs that block dopamine receptors (eg. haloperidol)
Diazepam potentiates GABA and thus help to reduce movements. Efficacy of benzodiazepines declines with disease progression.
What is Torsades des Pointes?
- ‘twisting of points’
- focus of VT moves around the myocardium. Appears as a sine wave.
TX: cardioversion + Magnesium
What kind of heart failure can develop with chronic lung disease?
Right sided heart failure
Personality Disorders
personality should be personal and flexible and stable and enable attachments.
Personalities are flexible and responsible.
Inflexibility; pathological. Maladaption to social and personal situations.
Change with time.
Comprises of ; genetic traits and environmental encounters.
The self : psychological interaction with the world.
Social relationships with others. Our own narrative.
Empathy and reflective.
Disorders: Impaired social functioning. Can’t find appropriate distance between others. Oscillate between people who can help them.
Maybe deviant social behaviour, or social withdrawal.
Personalities disorders
A: Asocial
B: Antisocial : violent to self, self-harming, also violence to others. Rule-breakers.
C: socially phobia: Most common
A & C groups often don’t seek help.
B: seek help but don’t use effectively.
Co-morbidities very common; psychosis, substance abuse, self-harming, etc. Poor social functioning.
Aetiology: genetics and repeated stressful environment; neglect/ abuse/ emotional trauma. Repeated hostile encounters. Insecure attachments to others has a big impact.
Presents late childhood/ early adolesence.
Can remit/ relapse in life.
Can Heparin be given orally?
No because heparin and related anticoagulants are not absorbed from the gut (large molecules) and so much be administered by IV.
What is crack?
a purified, very addictive form of cocaine. Crack ‘high’ is extremely short and on withdrawal, persecutory delusions are common.
What underlying CARDIAC conditions predispose to AF. What are these?
- HTN
- CAD
- RHD
- Also inflammation plays a role.
Management of stable angina (generally)
- Treat the underlying cause (eg. anaemia)
- management of coexisting problems (diabetes, hypertension)
- Evaluation of risk factors
What are some ‘negative’ symptoms of psychosis?
- Underactivity - which also affects speech.
- Low motivation.
- Social withdrawal.
- Emotional flattening.
- Self-neglect.
Can you see the borders of the heart with pleural effusion?
Can you see through consolidation?
NO
YES
What common things can bring on palpitations?
>> caffeine
Nicotine from smoking
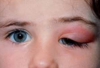
Dacryoadenitis
- Swelling of the outer portion of the upper lid, with possible redness and tenderness
- Pain in the area of swelling
- Excess tearing or discharge
- Swelling of lymph nodes in front of the ear
Common causes include mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, staphylococcus, and gonococcus.
Psychosis defined
A severe mental disorder in which there is extreme impairment to think cleary, respond with appropriate emotion, communicate effectively, understand reality and behave appropriately
Bones of skull

Naltrexone
Prevent a relapse or limit the amount of alcohol consumed.
Blocks opioid receptors
What sounds would you hear with LVF?
LUB-DUB-uh
“galloping horses”
- too much fluid
What would you find on ascultation?
bilateral crackles; widespread.
‘Fine’ crackles
3rd heart sound or gallop
What’s the two major risks of AF?
- embolic stroke
- heart failure
What is schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is the most common form of psychosis. It is a lifelong condition, which can take on either a chronic form or a form with relapsing and remitting episodes of acute illness
Harmful effects of MDMA - Ectasy
- dehydration
- hyponatraemia from excess water consumption
mech of action,
clinical indications,
potential adverse effects
of cimetidine, famotidine, ranitidine
(histamine H2-receptor antagonists)
drugs compete with histamine for binding to H2 receptors on gastric parietal cells.
Reduce volume and conc of gastric acid. This also proportionally decreases pepsin. (Gastric acid is the pepsinogen-pepsin catalyst)
cimetidine - weak antiandrogenic activity; can cause gynecomastia in elderly men.
cimetidine - WELL-KNOWN - inhibits P450 enzymes, therefore care with polypharmacy.
Physiologically, what are the two categories that can cause coronary heary disease?
- Mechanical obstructions
- atheroma
- thrombosis
- spasm
- coronary arteritis (eg. in SLE)
- decrease in flow of oxygenated blood to myocardium
- Anaemia
- hypotension (causing decrease coronary perfusion pressure)
What is ophthalmoplegia?
paralysis (-plegia) of one or more extraocular muscles which are responsible for eye movements.
It is a physical finding in certain neurologic, ophthalmologic, and endocrine disease.
How long does it take for myocardial necrosis after coronary artery occlusion?
15-30 mins
General managment of cardiomyopathy
Can’t be cured.
Beta blockers to control HR
Anti-coagulants
diruretics
ICD (implantable cardioverter defibrillators)
Heart transplant
paroxysmal noctural dyspnoea could be asthma or heart failure, so what could be differentiating symptom?
asthma; wheeze
heart failure; also have frothy, bloodstained sputum
Schizophrenia - facts
type of psychosis; person can’t distinguish their own thoughts and ideas from reality.
“a mental disorder characterised by abnormal social behaviour and failure to understand reality.”
symptoms:
hallucinations
delusions (unusual beliefs not based on reality),
false beliefs, hearing voices
Cause: genetic/ environmental
Risk factors: FH, cannabis during adolescence, being raised in a city, older father, problems during pregnancy
Treatment: anti-psychotics and CBT
<< life expectancy due to >> suicide, heart and lifestyle disease.
Gastrin and acetylcholine also stimulates the release of ……. from paracrine cells
Histamine
Diagram of heart blood supply

Are px with carotid artery stenosis at risk of embolic stroke?
+ exclusions?
Yes, especially if stenosis 70-99% (very high risk). Also: is px well enough to receive tx?
Carotid stenosis diagnosis; doppler
Exclusions?
haemorrhagic strokes - TACI or POCI
What are some serious withdrawal symptoms of alcohol?
Intoxication :hypoglycaemia (acute intoxication), cerebellum symptoms
Withdrawal: autonomic hyperactivity, insomnia, hallucinations, tremor, (could be ‘delirium tremens), nausea
- seizures possible
what eye condition is associated with MS?
important
optic neuritis
Usually heart sits on diaphragm but with COPD….
maybe air under the heart as diaphragm is flattened.
if there is consolidation and CAN see the heart outline then…
more likely lower lobe.
Emotionally unstable personality disorder
(previously known as borderline personality disorder)
Types (2)
Impulsive: emotional instability and lack of impulse control. Outbursts of violence or threatening behaviour are common, particularly in response to criticism by others.
Borderline: Several of the characteristics of emotional instability are present; in addition, the patient’s own self-image often is disturbed. There are usually chronic feelings of emptiness. Intense and unstable relationships may cause repeated emotional crises and may be associated with excessive efforts to avoid abandonment and a series of suicidal threats or acts of self-harm
Sudden onset headache could be:
meningitis
subarachnoid haemorrhage
migraine
Akathisia
Akathisia is a movement disorder characterized by a feeling of inner restlessness and inability to stay still.
Usually the legs are most prominently affected.
People may fidget, rock back and forth, or pace.
The first generation antipsychotics, are a leading cause.
Around half of people on antipsychotics develop the condition.
ICD-10 Personality Disorder definition
A severe disturbance in the characterological condition and behavioural tendencies of the individual, usually involving several areas of the personality and nearly always associated with considerable personal and social disruption.
‘Personality disorders are a long-standing and maladaptive pattern of perceiving and responding to other people and to stressful circumstances.’
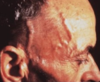
Giant cell arteritis
painless visual loss, px usually >60.
Scalp tenderness, jaw claudication, headache.
Blindness if not prompt treatment.
refer.
What is coronary artherosclerosis?
an inflammatory process characterized by accumulation of lipid, macrophages and smooth muscle cells in the intima endothelium of large/ medium coronary arteries.
What is included in acute coronary syndromes?
- ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
- Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)
- Unstable angina (UA)
Which is the most common valvular heart disease?
Mitral regurgitation
- abnormal leaking of blood from the LV to the LA during systole.

What are the symptoms of aortic stenosis?
Symptoms only develop when stenosis is moderately severe (reduced to 1/4 of original size)
- angina (CHD isn’t only cause of angina!)
- dyspnoea
- exercise induced syncope (and pre-syncope)
Poor prognosis when patient develops these symptoms. NB> At auscultation elderly px, murmour more at apex (misinterpreted as mitral regurgitation)
paranoia defined
Paranoia is thinking and feeling as if you are under threat even though there is no (or very little) evidence that you are.
Paranoid thoughts can also be described as delusions.
Paranoid thoughts could also be exaggerated suspicions. For example, someone made a nasty comment about you once, and you believe that they are directing a hate campaign against you.
Tell me about HIT 2
less common, more serious.
Immunoglobulin mediated platelet inactivation.
High risk of thrombotic complications and mortality.
In addition to severe chest pain, what else do you get with MI?
autonomic symptoms; pale and clammy patient, marked sweating. thready pulse, significant hypotension. Bradycardia or tachycardia.
What are positive and negative symptoms in mental health?
Positive: symptoms that most people don’t experience, e.g. delusions, hallucinations, disordered thoughts
Negative: deficits of normal emotional response, or other throught processes.
Name three important opiates
Heroin
Morphine
Methadone
Management of serotonin syndrome

Recent ingestion: activated charcoal
IV fluids, benzodiazepines to control agitation
Check half-life of ingested drug
What is Dipyridamole?
What is it indicated for?
Dipyridamole a coronary vasodilator and a relatively weak antiplatelet drug.
Dipyridamole is used in COMBO with aspirin to prevent ischaemic stroke in px with history of thrombotic stroke, and persons experiencing TIAs.
Which is the pulse of choice during cardiac arrest?
Carotid pulse
Acute-angle closure glaucoma
acutely painful red eye.
Px usually > 60, other symptoms; headache, nausea, blurred vision and haloes around lights.
mech of action,
clinical indications,
potential adverse effects
of promethazine
(antihistamine)
H1 Antihistamine
treats nausea and vomiting induced by medications, anesthetics, and a wide range of other stimuli.
Rectal suppository or injection.
Bipolar affective disorder (previously called manic depression)
definition
recurrent episodes of altered mood and activity, involving both upswings and downswings.
ICD 10: at least two episodes, including one hypomanic or manic episode.
What three factors combined often lead to thrombic changes?
- sluggish blood flow
- inflammation
- abnormalities in vascular endothelium
dopamine hypothesis and schizophrenia
abnormalities in dopamine neurotransmission in mesolimbic and mesocortical neuronal pathways.
Knights move
and
Flight of idea
KM: a thought disorder denoting a lack of connection between ideas. Found in schizophenia.
FOI: Accelerated thinking seen in mania and hypomanic illness. There is always a link in thought processes.
How Warfarin monitored?
Prothrombin Time (PT)
Which drugs (including recreational) can precipitate or exacerbate angina?
Starting thyroxine
cocaine & amphetamines - can cause MI, arrhythmias
Also NSAIDS
What organisms can cause Dacryoadenitis?
Common causes include mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, staphylococcus, and gonococcus.
Management of psychosis
Try and recognise early. Reduce time between appearance of symptoms and initiating therapy (i.e. duration of untreated psychosis).
Accelerate remission and prevent relapse.
Are there external factors? drugs? alcohol?
Family intervention
Maximise the patient’s ability to get back to normal life.
What’s the difference between UA and NSTEMI?
NSTEMI;
occluding thrombus - myocardial necrosis - rise in serum troponins
Diagram of vomiting pathways

foramen and fissures of the orbit

What is Serotonin Syndrome? - triad
(serotonin toxicity)
- adverse reaction to serotonergic agents
often underdiagnosed due to heterogeneity of presentation.
- autonomic hyperactivity
- neuromuscular abnormality
- mental status changes
(not all present in all cases)
Diagnosis based on history taking, symptoms usually start within six hours of provoking drug.
Can progress from restlessness, diaphoresis, neuromuscular dysfunction to confusion, convulsions and death.
What is formication associated with?
Cocaine; visual/ tactile hallucinations of insects.
In the case of ischaemic stroke, what is the window for treatment?
3 hours from onset of symptoms.
(this includes getting a CT scan!)
What are the four main cardiovascular causes of syncope?
- postural hypotension
- neurocardiogenic syncope (eg. standing for long time in warm place)
- arrhymias (esp. AF)
- mechanical obstruction to cardiac output - hypertrophy or aortic stenosis, PE
What does broad QRS indicate?
bundle branch block
Freezing is Parkinson’s is called…
hypokinesia
What’s the management of acute thromboembolic disorders?
LMWH (Low molecular weight heparin) plus warfarin, and then withdraw LMWH when warfarin is effective.
What does hypokalaemia do to myocardiocytes?
Makes them more likely to depolarise spontaneously.
- Also hypomagnesaemia
(Also hypercalcaemia although clinically less significant)
How do antipsychotics work?
block (antagonists) to dopamine D2 receptors
How would you assess conscious level?
AVPU
Alert,
Voice,
Pain,
Unresponsive
What’s the most important diagnostic aid for valvular disorders?
Echocardiography
cyclothymic disorder
10-20% have rapid cycling - defined as four or more cycles of depression and mania a year, with no intervening asymptomatic episodes.
In cyclothymic disorder, moods swing between short periods of mild depression and hypomania, an elevated mood. The low and high mood swings never reach the severity or duration of major depressive or full mania episodes.
What’s the most important prostaglandin affecting platelet aggregation?
prostacyclin and TXA2
(prostaglandin I2 (PGI2)
Aspirin irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase; enzyme that catalyzes TXA2 synthesis.
Three characteristics of PD
- resting tremor
- rigidity (inability to initiate movements)
- bradykinesia (slowness of movement)
mech of action,
clinical indications,
potential adverse effects
of psyllium
(bulk forming laxative)
Indigestible hydrophilic drug
absorbs water and increases mass of stool. This stimulates mech peristalsis.
Also used to treat diarrhoea
What can cause orthopnoea?
- Fluid accumulating in the lungs due to congestive heart failure
- Asthma (maybe trigggered by oesophageal reflex)
Does Warfarin act immediately?
No because pool of circulating clotting factors needs to be depleted first.
Synthesis of new factors is then inhibited.
(takes 3-5 days to reach maximal effect)
Bipolar affective disorder : important fact about depression screening
Adults presenting with depression should be asked about previous periods of overactivity or disinhibited behaviour.
If the overactivity or disinhibited behaviour lasted for four days or more: referral
What’s the medical name for lazy eye?
Amblyopia
- the eye and brain not working well together.
Rapid recognition of atrial flutter….
narrow QRS complexes at 150 bpm
Turn ECG upside down and look at leads II, III + aVF
Examination; clinical features of pericardial effusion…
heart sounds soft and distant
apex beat commonly obsured
frictional rub (only at early stages, quieter as fluid accumulates)
Raised JVP
Friedreich’s sign
Kussmaul’s sign
Pulsus paradoxus
< CO
Two major groups that are stimulants
Cocaine
Amphetamines
What organism can cause a dendritic ulcer on the retina?
Herpes simplex
What is Korsakoff psychosis?
(example of an amnesic disorder)
Korsakoff psychosis is a late complication of persistent Wernicke encephalopathy and results in memory deficits, confusion, and behavioral changes.
Korsakoff psychosis occurs in 80% of untreated patients with Wernicke encephalopathy
Tx of bacterial vaginosis
metronidazole or clindamycin
avoid vaginal douching
avoid detergents (vagina is self-cleaning)
associated with SMALL risk of preterm birth.
Some common uses of Warfarin
Long-term treatment of DVT
Patients with AF
Patients with artificial heart valves.
what may preceed a prodomal aura?
Premonition; hunger, energy surges, irritability.
Which physical examinations for dizziness?
cardiovascular - vascular disease, AF
neurological - cranial nerve palsy, cerebellar signs, abnormal gait, limb weakness/ hemiparesis
ear examination
Can you see glass on CXR?
nope
Headache; red flags
- new onset or changes in headache in px over 50 years old
- thunderclap
- focal neurological symptoms
- abnormal neurological examination
- headache that changes with posture
- wakes up px during night
- worse for valsalva manoeuvre
- thrombosis risks
- jaw claudication
- neck stiffness with fever
- new onset with cancer/ HIV px
Area for receptive aphasia

Wernicke korsakoff
(thiamine deficiency)
-associated with alcholics
triad of symptoms
- acute confusion
- ataxia
- opthalmoplegia
tx. IV thiamine hydrochloride
untreated 20% mortality
What is Myasthenia Gravis caused by?
an antibody against AChR
(acetylcholine receptor)
autoimmune disease; antibodies that block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the junction between the nerve and muscle.
This prevents nerve impulses from triggering muscle contractions
Schizophrenia is a common type of psychosis.
The presence of only one of the following symptoms is strongly predictive of the diagnosis:
- Lack of insight.
- Auditory hallucinations, especially the echoing of thoughts, or a third person ‘commentary’ on one’s actions - eg, ‘Now he’s putting on his coat.’
- Thought insertion, removal or interruption - delusions about external control of thought.
- Thought broadcasting - the delusion that others can hear one’s thoughts.
- Delusional perceptions (ie abnormal significance for a normal event) - eg, ‘The rainbow came out and I realised I was the son of God.’
- External control of emotions.
- Somatic passivity - thoughts, sensations and actions are under external control.
What is a hemiplegic gait and what does it imply?
Unilateral upper motor neurone lesion.
circumduction of leg on affected side with foot plantar flexed.
Upper limb will be flexed.
Symptoms of meningitis
- high temperature of 38C or more
- headache
- blotchy rash that doesn’t fade when a glass is rolled over - septicaemia (
- often not present)
- stiff neck
- photophobia, drowsiness, seizures, confusion,
- aching muscles & joints,
- cold hands & feet, tachypnoea
Acute LVF Management: What is morpine used for?
+ dose
Reduces sympathetic activity
reduces anxiety and work of breathing
“Titrate to good and bad symptoms”
Dose IV 1-4mg IV over 5-10 mins (preceeded by 10mg of metoclopramide)
Angina pain (that isn’t stable), if MI hasn’t been diagnosed, what is it termed?
Acute coronary syndrome
How effective is prophylaxic treatment of AF with warfarin in preventing strokes?
yearly risk of cerebral embolism reduced from 3% to 1%.
Types of Bipolar affective disorder
- Bipolar I - the full monty
- Bipolar II - does not have full criteria of mania - it’s hypomania. NO psychotic symptoms.
- cyclothymic disorder
what could air under the diaphragm be?
perforated intestine
(rem. gastric bubble on the left)
central vertigo causes
stroke
MS
infection
trauma
acoustic neuroma
What would you include in D - disability?
access consious level
blood sugar levels
Aetiology of substance abuse - diagram

What is used primarily for the treatment of motion sickness?
Scopalamine - muscarinic receptor antagonist similar to atropine.
Been used by astronauts.
Skin patch slow 72 hr release.
Emotionally unstable personality disorder
(previously known as borderline personality disorder)
defined.
Emotionally unstable personality disorder is characterised by pervasive instability of interpersonal relationships, self-image and mood and impulsive behaviour. The term ‘borderline’ is misleading.
‘sometimes rapid fluctuation from periods of confidence to despair, with fear of abandonment and rejection’
‘strong tendency towards suicidal thinking and self-harm.’
’ interaction between adverse life events and genetic factors.’
Which SSRI has a long half-life?
Fluoxetine
Conjunctivitis characteristics
- red, watery eye, often bilateral.
- VA is usually normal.
- bacterial or viral
Infectious, topical treatment,
NB> check for FB, abrasion before diagnosing conjunctivitis
Overdose symptoms of opiates
(heroin, morphine, methadone)
- Miosis
- Respiratory depression
If you can’t see the right edge of the heart then…
possible middle lobe pneumonia
Lack of expression may indicate
Parkinson’s disease
Phimosis - definition
narrowing of the preputial orifice which prevents foreskin retraction.

F A S T
F - face. Has their face fallen on one side?
A - arms. Are the unable to raise one arm?
S - speech. It is affected?
T - time . Call 999 if any of the above is positive.
If pain doesn’t subside after 3 sprays (5 min interval) of GTN then….
assume myocardial infarction.
What is antithrombin?
an endogenous anticoagulant (potent inhibitor of coagulation)
When do you use the Qrisk2 calculator?
If you do not already have a diagnosis of coronary heart disease (including angina or heart attack) or stroke/transient ischaemic attack.
mech of action,
clinical indications,
potential adverse effects
of milk of magnesia
(osmotic laxative)
poorly absorbed salt that osmotically attracts water.
Administer to px to evacuate the bowel in prep for surgery.
Danger> loss of fluids and electrolytes
What are the symptoms of stable angina?
- Crushing sensation in chest or neighbouring areas
- associated with effort
- relieved by rest of nitroglyerin
When do you find a positive Extensor Plantar Response (Babinski)
Upper motor neuron lesion
Anorexia nervosa
The Facts
10 x more common in females.
often starts in teenage years
restrict consumption of food and drink.
Dangerous low weight. Deliberate weight loss; main symptom.
typically 15% or more below expected weight and BMI below 17.5
Can: vomiting after eating, use of laxatives
What could cause a pale retina?
Central retinal artery occlusion
What are the cardinal features of a MCA stroke?
- hemiplegia (paralysis) of the contralateral side, affecting the lower part of the face, arm, and hand while largely sparing the leg
- contralateral (opposite-side) sensory loss in the same areas
- contralateral homonymous hemianopia—visual-field deficits affecting the same half of the visual field in both eyes.
When do you get fibrillations and fasciculations?
Lower motor neurone lesions
What are some of the causes of mitral regurgitation?
Acute mitral regurgitation; commonly endocarditis (S. Aureus).
Also; papillary muscle rupture/ dysfunction, mitral valve prolapse
Name the four types of supraventricular arrhythmias
- AF
- Atrial flutter
- PSVT (paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia)
- WPW (wolff-Parkinson-White) syndrome
Management of Bipolar affective disorder (previously called manic depression)
Develop a good rapport and trusting relationship with patient and their carers.
Self-help groups, support groups, self-monitoring of symptoms, coping strategies, psychological therapy.
- Drugs commonly used are haloperidol, olanzapine, quetiapine and risperidone.
Titrate to max dose if needed. Change to a different drug if ineffective.
- Consider adding lithium if still ineffective. If Lithium not appropriate try valproate.
- If px taking anti-depressants with anti-psychotics, then stop the anti-depressants in the mania stage.
NB> antidepressants in bipolar disorder can INDUCE mania or hypomania or rapid cycling. Best use to combine with anti-psychotic.
- Very careful withn women of child-bearing age: Advise about contraceptive usage.
What drugs can cause hypovolemia?
diuretics
chronic use of Beta-Blockers (slows heart and << contractility). Bradycardia often produces hypotension.
chronic use of Alpha-Blockers
What is the most common symptom of peripheral vascular disease?
intermittent claudication; calf pain on walking (comes and goes).
How do you measure the size of the heart from an x-ray?
Name three LMWH
enoxaparin
dalteparin
tinzaparin
Important case history questions to ask re CVD
What degree of activity causes chest pain or breathlessness?
eg. walking up stairs?
Can they continue with their normal activities/ hobbies?
Which neural pathway do the negative psychotic symptoms affect?
Lack of activity in the mesocortical neuronal pathway
Suspected subarachnoid haemorrhage headache diagnosis
CT scan (reliability 90% only)
If CT negative, LP > 12 hours following onset of symptoms.
LP: uniform RBC in bottles suggests SAH
Presence of bilirubin suggests bleed (and not trauma)