Test 2 - vascular hemodynamics Flashcards
study of blood pressure and blood flow throughtout the circulatory system
hemodynamics
hydrostatic pressure measured within a given structure, either cardiac chamber, or a blood vessel
blood pressure
capacity to contain a varying volume of blood
distensibility
blood pressure is caused by
the recoil of the vessel walls against the blood, and its value is proportional to the stressed volume
determines what the pressure will be, relative to the stressed volume
“reflects the underlying stiffness of the blood vessels”
compliance
P - blood pressure
V - blood volume
Vo - unstressed volume
C - compliance
(V-Vo) - stressed volume

distension and recoil are ____ related in relationship with blood volume
inversely
distension: blood volume UP
recoil: blood volume DOWN
encompasses both the unstressed volume (Vo) and the compliance (C) of blood vessels
“capacity of how much blood a region of the circulation may contain”
capacitance
if you keep capacitance (Vo and C) constant:
blood pressure will then vary in _______ to changes in total blood volume
direct proportion
for a given blood volume: blood pressure will then vary ________ to a change in capacitance
inverserly
increased capacitance: compliance and/or Vo is ____
increased
the capacitance of ______ is under reflex control
distributing arteries
or
collecting venules and distal veins
collecting venules and distal veins
blood pressure is uniformly _____ throughout distributing arteries,
_______ within the collecting venules and veins
HIGH arteries
LOW venules and veins

T/F: blood pressure at the distal end of arteries is almost >95% as high as the pressure within the ascending aorta
TRUE
arterioles and capillaries present significant resistance to blood flowing through them
peripheral resistance (Rp) - reflexive control
T/F: central venous blood pressure is approximately 10% of the central arterial pressure
TRUE
vascular resistance is determined by the size of the blood vessel and by the viscosity of the blood
what law is this?
Poiseuille’s law
diameter - most important
viscosity - normally constant
length of vessel - constant

determines how high the upstream pressure (Pup) must be (relative to the pressure downstream) to cause a given rate of flow (Qout) through the distal resistance
resistance (R)
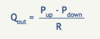
T/F:
on average Qout = Qin = Q
TRUE
however, at any given instant, Qout may not equal to Qin
if resistance is held constant:
Qout is dependent upon, and varies in _______ to, upstream pressure
direct proportion
if the upstream pressure is held constant:
Qout varies ______ to changes in the distal resistance (R)
inverse
pressure upstream from a point of resistance, dependent upon ______ and _______
reate of flow through the vascular region (Q)
and
value of resistance (R)
“ohm’s law”

(Pup-Pdown) measures the amount of pressure dissipated by flow across the ______
resistance
flow of blood through the microcirculation
perfusion
“net flow of blood from arteries into veins”
upstream arterial pressure:
Pa > ____mmHg
downstream venous pressure
Pv < _____mmHg
UPstream: >70mmHg
DOWNstream: <15mmHg
for a given Q from the L heart into system arterial circulation, the arterial blood pressure (Pa) will _____ to whatever value necessary to maintain this rate of flow through the peripheral resis. imposed by arterioles and capillaries
RISE
pressure-volume: volume needed to achieve a given upstream pressure is dependent upon the _______
vascular capacitance
(C and Vo)
pressure-flow: upstream pressure needed to achieve a given rate of outlow is dependent upon the __________
downstream vascular resistance (R)
Qin: blood from the lungs is pumped into the disributing arteries as _______
Qout: blood flows from the distributing arteries as ______ to perfuse the tissues
Qin: blood from the lungs is pumped into the disributing arteries as cardiac output (Qco)
Qout: blood flows from the distributing arteries as peripheral runoff (Qa->V) to perfuse the tissues
the collective opposition (resistance) to blood flowing through the systemic arterioles and capillaries
peripheral resistance (Rp)
“windkessel” network
FLOW IN: _____ from left ventricle
FLOW OUT: ______ through microcirculation
IN: cardiac output
OUT: peripheral runoff
if arterial blood pressure remains constant: peripheral runoff _____ rate of cardiac output
matches
if arterial blood pressure increases: peripheral runoff _____ rate of cardiac output
match
exceeds
less than
less than
if arterial blood pressure decreases: peripheral runoff _____ rate of cardiac output
matches
exceeds
less than
exceeds


