Test 1 Sex Hormones Flashcards
Functions of Endocrine System
Main Functions of the endocrine system are
- Homeostasis (balance)
- Reproduction
Endocrine vs Exocrine
Endocrine: secretes hormones into circulation directly (no ducts)
- Hormones act on target organs
- Broadcast signal – travels throughout the body
- Specificity is in receptor localization – only acts on where receptor is located
Types of Hormones
Steroids
Amines
Peptides
Steroid Hormones
- Lipid-soluble
- Produced in the adrenal cortex, testes, ovary, placenta
Amine Hormones
- Based on tyrosine
- Produced in the thyroid and adrenal medulla (catecholamines – not on test)
Peptide Hormones
(majority)
• Synthesized as prohormones (require cleavage)
Hormone Receptor Types
Lipid-Soluble/ Intracellular Receptors
Cell Surface Receptors/ Extracellular
Lipid Soluble/Intracellular Receptors
Ususally have a binding globulin in the blood to prevent degradation.
- Steroids-lipid soluble intracellular hormone
- Thyroid-intracellular hormone (not lipid soluble) hormone must cross into the cell via transporter to act on its receptor
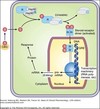
Intracellular receptors:
- Cytoplasmic receptors (nuclear receptors)
- Ligand-receptor complex translocates to nucleus
- Binds to DNA
- Increases or decreases gene transcription (specific to each hormone)
Cell Surface Receptors
Receptors located on Cell Membrane
Utilized by:
- Amine Hormones (except thyroid)
- Peptide Hormones
Receptor types:
-
G-protein coupled receptors
- increase cAMP
- Protein Tyrosine Kinases
- Another type of cell membrane receptor
- Best example is insulin receptor

Feedback regulation
- Negative feedback (most common)
- example: cortisol
- Positive feedback (less common)
- example: LH stimulates estrogen (important because it causes ovulation)

Endocrine Physiology
-
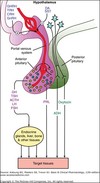
Anterior Pituitary (Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal/HPA axis) – most important
- Releasing hormones from hypothalamus
- Causes release of trophic hormones
- Portal venous delivery
- Receives input via venous blood supply
- Releasing hormones from hypothalamus
- Posterior Pituitary
- Nerve endings from brain
- Oxytocin & ADH
Endocrine Organs
- Brain, pineal gland, pituitary
- Thyroid
- Parathyroid
- Thymus
- Adrenal glands & Kidneys
- Pancreas
- Ovaries/Testes
Patterns of Hormone Secretion
- Pattern may be essential to physiological role - the body is supposed to release hormones at the appropriate time
- Insulin
- GnRH
- FSH/LH
- Basal release – may follow circadian rhythm or twice daily pattern
- Stimulated release
- Cortisol peaks when you eat, under times of stress (along with basal release)
- Measure hormone levels at the appropriate time

Interpretation of lab results:
· TSH was high and thyroid levels were low
o Negative feedback to hypothalamus and thyroid is impaired
Interpretation of lab results:
TSH was high and thyroid levels were high
o Not a pituitary malfunction
Interpretation of lab results:
· TSH was low and thyroid levels were high
o The thyroid may have a tumor, or other cells may be producing thyroid hormones (ectopic production)
Interpretation of lab results:
· TSH was low and thyroid levels were low
The problem is at the level of the pituitary, negative feedback is not responding
Which of the following are true regarding steroid receptors?
a. They are found on cell membranes
b. They are found in the cytoplasm
c. They are G-protein coupled receptors
d. They affect transcription of DNA
b. They are found in the cytoplasm
d. They affect transcription of DNA
Q: This type of hormone is lipid soluble:
a. Steroids
b. Amines (Catecholamines)
c. Peptides
d. Thyroid (T3)
a. Steroids
Q: This type of hormone is usually produced as a prohormone
a. Steroid
b. Amine (Catecholamines)
c. Peptide
c. Peptide
Q: When rising levels of a hormone released by an endocrine organ has the result of decreasing hypothalamic and pituitary release of releasing factors and trophic hormones this is referred to as:
a. Negative feedback
b. Positive feedback
c. Pulsitive
a. Negative feedback


