TensorFlow Flashcards
(30 cards)
Explain the SoftMax function
Turns scores(integers which reflect output of neural net) into probabilities

What are logits?
Scores/Numbers. For neural nets, its result of the matmul of weights,input + bias. Logits are the inputs into a softmax function

Explain a TensorFlow Session
- an environment for running a graph
- in charge of allocating the operations to GPU(s) and/or CPU(s), including remote machines
- Sessions do not create the tensors, this is done outside the session. Instead, Session instances EVALUATE tensors and returns results
Explain tf.placeholder
- Tensor whose value changes based on different datasets and parameters. However, this tensor can’t be modified.
- Uses the feed_dict parameter in tf.session.run() to set the value of placeholder tensor
- tensor is still created outside the Session instance
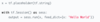
How to set multiple TF.Placeholder values
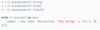
What happens if the data passed to the feed_dict doesn’t match the tensor type and can’t be cast into the tensor type
ValueError: invalid literal for
How to cast a value to another type
tf.subtract(tf.cast(tf.constant(2.0), tf.int32), tf.constant(1))
Explain Tf.Variable
- remembers its a capital V
- creates a tensor with an initial value that can be modified, much like a normal Python variable
- stores its state in the session
- assign variable to tf.global_variables_initializer(), then initialize the state of the tensor manually within a session. Or call tf.global_variables_initializer() directly in the session instance.
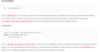
TF.normal
- The tf.truncated_normal() function returns a tensor with random values from a normal distribution whose magnitude is no more than 2 standard deviations from the mean.
- Since the weights are already helping prevent the model from getting stuck, you don’t need to randomize the bias
Softmax function call?
x = tf.nn.softmax([2.0, 1.0, 0.2])


Explain steps to one-hot encode labels
- import preprocessing from sklearn
- create an encoder
- encoder finds classes and assigns one-hot encoded vectors
- transform labels into one-hot encoded vectors

basic concept of cross entropy
calculates distances of two vectors. Usually comparing one-hote encoded vector and softmax output vector. Basic idea is to reduce distance
Describe process of calcaulting cross entropy
- take natural log of softmax outputs vector (prediction probabilities)
- Next, multiply by one hot encoded vector
- Sum together, take negative
- Since one hot-encoded vector has zeros except the true label/class, the formulat simplifies to natural log of prediction probabilities

Does the cross entropy function output a vector of values?
No, just a single value which represents distance
Quiz - Cross Entropy


how to implement mini-batching in TF
- use range to specify starting, ending and step size
- identify end of each batch
- select data and loop

Quiz - Set features, labels, weights and biases


What is a tensor
any n-dimensional collection of values
scaler = 0 dimension tensor
vector = 1 dimension tensor
matrix = 2 dimension tensor
Anything larger than 2 dimension is just called a tensor with # of ranks
Describe a 3 dimensional tensor
an image can be described by a 3 dimensional tensor. This would look like a list of matrices

TF.Constant
value never changes
Best practice to initialize weights
truncated normal takes a tuple as input

Best practice to initialize bias

What does “None” allow us to do?

None is a placeholder dimension. Allows us to use different batch sizes










