Telescopes Flashcards
(42 cards)
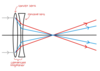
What is a Convex / Convering Lens
A lens that focuses incident light
Describe a real image being formed from a Convex Lens
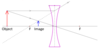
What is a Concave / Diverging Lens
A lens that spreads out incident light
Describe a diagram of light on a concave lens
What is the Principal Axis
The line passing through the centre of the lens at 90º to its surface
What is the Principal Focus
- In a converging lens - the point where incident beams passing parallel to the principal axis will converge
- In a diverging lens - the point from which the light rays appear to come from (This is the same distance either side of the lens)
What is the Focal Length
The distance between the centre of a lens and the principal focus

What is a Real Image and a Virtual Image
- Real image - formed when light rays cross after passing through the lens, can be formed on a screen
- Virtual image - formed on the same side of the lens. The light rays do not cross, so a virtual image cannot be formed on a screen
What is the Lens Formula
- 1 / u + 1 / v = 1 / f
- u is the distance of the object from the centre of the lens
- v is the distance of the image from the centre of the lens
- f is the focal length of the lens
What are the words used to describe an image that is formed
- Real or Virtual
- Magnified or Diminished
- Upright or Inverted
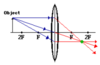
Describe the ray diagram for an object that is beyond 2F and describe the image’s apperance
Real, Inverted and Diminshed

Describe the ray diagram of an image that is very close to the lens and describe the image’s apperance
Virtual, Upright and Magnified

Describe the ray diagram of an image that is fairly close to the lens (between 2F and F) and describe the image’s apperence
Real, Inverted and Magnified

Describe the ray diagram of an image that is exactly 2F from the lens and describe the image’s apperence
Real, Inverted and same size

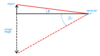
What is the Equation for Angular Magnification in Normal Adjustment
M = Angle subtended by the eye to the image/ Angle subtended by the eye to the object
What is the Equation for Angular Magnification in terms of the focal length
M = f0 / fe
Only used if both angles in other equation are below 10º
Describe the ray diagram for a refracting telescope in normal adjustment
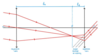
How does a Cassegrain telescope work
- There is a concave primary mirror and a small convex secondary mirror in the centre
- The light is collected by the primary mirror and focused onto the secondary mirror
- This is then reflected onto an eyepiece lens
Describe the Cassegrain Reflecting Telescope Ray Diagram
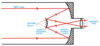
How do you minimise distortions in an image in the Cassegrain Telescope
- The mirrors in a reflecting telescope are a very thin coating of atoms
- This allows the mirrors to be as smooth as possible and minimises distortions in the image
What are the two types of aberration that can happen in a telescope
- Chromatic Aberration
- Spherical Aberration
What is Chromatic Aberration
- When a lens refracts different colours of light by different amounts as they have different wavelengths
- This causes the image for each colour to form in a slightly different position, causing coloured fringes around the image
- Since chromatic aberration is caused by refraction, it has very little effect on reflecting telescopes as it only occurs in the eyepiece lens.
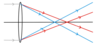
What is Spherical Aberration
- The curvature of a lens or mirror can cause rays of light at the edge to be focused in a different position to those near the centre, leading to image blurring and distortion
- This effect is most pronounced in lenses with a large diameter, and can be avoided completely by using parabolic objective mirrors in reflecting telescopes
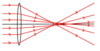
What is an Achromatic doublet
- An achromatic doublet consists of a convex lens and a concave lens cemented together in order to bring all rays of light into focus in the same position
- It minimises spherical and chromatic aberration