Telencephalon and Diencephalon Flashcards
describe the folding of the neural tube
- prosencephalon (forebrain)
- mesencephalon (midbrain)
- rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
- developed from the back forward
what are the derivatives of the prosencephalon?
forebrain
- telencephalon: cerebral hemispheres, surrounds the lateral ventricles
- diencephalon: epithalamus (pineal), thalamus, hypothalamus, optic cup/nerves, surrounds the 3rd ventricle
describe the ventricles of the brain
- R and L lateral ventricles, third ventricle, fourth ventricle
- connected by foramina
- filled with CSF, contains choroid plexus (produces CSF, is located in every ventricle)
describe ventricle development and association to key brain regions

what is CSF?
- continuously produced in the ventricles
- high in sodium, low in potassium (these create chemical gradients)
- no protein (the presence of protein is usually indicative that there is a problem)
what are the 3 main purposes of CSF?
- buoyancy
- protection (positive pressure, cushion)
- chemical stability (high sodium, nutrients, etc.)
describe the volume of CSF
- total adult volume is ~100-150ml
- replaced about 4 times each day (~500ml daily)
describe the flow of CSF

what are meninges?
- a system of membranes which envelops the centeral nervous system
- 3 layers - dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
- protect organs from rubbing against bones of the skull and spine
describe the meningeal layers
dura mater - dura
leptomeninges (layers and a space):
- arachnoid - a barrier
- subarachnoid space - CSF
- pia - vessels run in this layer and penetrate the cortex
what is obstructive hydrocephalus?
- obstruction of the CSF flow that causes buildup of CSF in ventricles
- can be reversed with the use of a splint
which two main arteries supply blood to the brain?
- internal carotid artery
- vertebral arteries
name the branches of the internal carotid artery and vertebral arteries that supply the brain

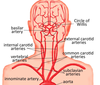
describe vertebrobasilar and carotid circulation

find the posterior cerebral a., basilar a., internal carotid a., anterior spinal a., and vertebral a.


which arteries supply each colored area of this brain?

- yellow - anterior cerebral artery
- red - middle cerebral artery
- blue - posterior cerebral artery
what is the blood brain barrier?
- composed of high-density cells connected by tight junction that restrict passage of substances from the bloodstream
- it allows diffusion of small hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones)
- cells actively transport metabolic products such as glucose across the barrier with specific proteins
describe characteristics of an epidural hematoma
- between skull and dura mater
- dura peels off skull, space fills with arterial blood
- compresses brain
- usually a result of a skull fracture and torn middle meningial artery
describe characteristics of a subdural hematoma
- occurs below the dura mater in the subdural space
- dura still attached to skull
- venous blood fills subdural space and compresses brain
- result of a torn bridging cerebral vein
what is a subarachnoid hemorrhage?
- commonly occur as a result of rupture of an a. in the circle of willis
- between arachnoid mater and pia mater; subarachnoid space
what is the telencephalon? what are its 4 main divisions?
- cerebral cortex
- frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe
what 2 structures are inside the telencephalon?
basal ganglia and limbic system
what are Brodmann’s areas?
regions of the cerebral cortex that are defined by a number
what is a commissure?
reciprocal connections






