taste smell part 1 Flashcards
Taste receptor cells are also located on the palate and epiglottis.
located in the epithelium not in pappilase
Taste receptor are clustered in taste buds,
which are mainly assoicated with fungiform and circumvallate/vallate papillae
tf Foliate papillae have tons of taste buds in adults.
Foliate papillae have few taste buds in adults.




epiglottis
SA from CN 10
posterior 1/3 tongue (including vallate papillae)
SA from CN-IX:
anterior 2/3 tongue, palate
SA from CN-VII:
anterior 2/3 tongue, hard and soft palate
somatic and visceral
GSA from CN 5
epiglottis
somaitc and visceral
GVA from CN 10
tf GVA from CN-IX: ant 1/3 tongue, palatine tonsils,larynx
somatic and visceral
GVA from CN-IX: posterior 1/3 tongue, palatine tonsils, pharynx
at apical end of taste receptor cell and
extend thru taste pore
microvilli
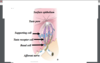
Taste receptor cells are replaced
every 7-10 days
the taste receptor cells release neurotransmitter on afferents
of CN VII, CN IX and CN X


