Surgery - Anal & Peri-anal Symptoms Flashcards
Anal and perianal symptoms

Anal Bleeding
Anal pain and discomfort
- Haemorrhoids
- Sentinal pile
- Intersphincteric abscess
- Perianal haematoma
- Proctalgia fugax - shooting pains
Perianal itching/Irritation
Perianal Discharge

Anal and perianal symptoms
Approach to investigation of anal and perianal symptoms

Inspection of the anal area, careful digital rectal examination (DRE) and proctoscopy are mandatory
Anal and perianal symptoms
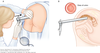
Digital rectal examination

Purpose
- Inspection of the anal and perianal area for skin changes and lesions
- Palpation of the anal canal and lower rectum and surrounding tissues.
- Normally the firm walls of the anal sphincter are felt over the first 5 cm or so. Above that level, the rectal walls are soft
Inspection
- Sentinel pile; excoriation; ulceration, perianal haematoma; fistulous opening; scars; abscess; prolapsed mucosa or haemorrhoids; skin tags
Palpation
- In lumen: faeces/blood/foreign body
- Crohn’s/anal carcinoma/lack of normal softness
- Prostatic enlargement/frozen pelvis
- Mass in pouch of douglas

Anal and perianal symptoms
Digital rectal examination
Proctoscopy

Direct visualisation of mucosa of anal canal
Findings:
Inflammation/Ulceration/Haemorrhoids/bleeding/prolapse
Anal Carcinoma/Rectal Ulcer/Pus/Fistiula/Fibrous Polyps
Melanoma
Anal and perianal symptoms
Digital rectal examination
Rigid Sigmoidoscopy

As for proctoscopy for 10 cm or so. Obturator removed and proximal end closed with lens.
Gentle inflation whilst inspecting lumen, manipulating and advancing ’scope with least discomfort to patient
Faecal loading may prevent visualisation; pain may limit examination to lower rectum only