structural geology Flashcards
for geological purposes we use gps to calculate the movement of plates. what needs to be done to the reciever to use it for this purpose?
it is important that the reciever is fitted securely to bed rock so that it is stationary.

generally how much do plates move each year?
plates generally move tens of mm a year
whats the formulas for stress, strain and strain rate?
stress = F/A
strain = X/L
strain rate = strain/time
high strain rates are associated with what?
high strain rates are associated with the edge of plates - whether in extension or comporession.
what do the arrows on a gps vector map show?
arrows point in direction of movement
size gives magnitude of movement
describe the tectonics of california.
predominantly transverse
western part of california is moving rapidly past the rest of the USA
what are satellite measurement (INSAR) used for and how do they work?
are used to view changes in depth e.g. at a normal fault.
works on a phase difference

plates generally form ____________ which predominantly deform at ___________
plates generally form rigid blocks that predominantly deform at their edges
small yearly displacement X large amount of time =
a potentially large amount of deformation
what does deformation encompass?
deformation encompasses:
folding
faulting
shearing
compressing
extension
of rock by tectonic or gavitational forces
deformation at the earth surface is mainly caused by
deformation at the earth surface is mainly caused by the horizontal movements of the lithospheric plates relative to one another
tectonic forces that deform rocks at plate boundaries are often horizontally directed and depend on the rate of plate motion
these forces can be:
compressive
shear
tensional
we use what we see at the surface to have a best guess of…
the underground
define structral geology
structral geology
the study of all deformational features in rocks from the small scale to the big scale.
it particularly addresses the geometry, distribution and formation of rock structures such as folds and faults and their links to tectonics.
what is tectonics concerned with?
tectonics is concerned with the regional processes that generate a characteristic set of geological structures in an area.
what is the role of structral geology?
reconstructing histroy of deformation on earth
earthquakes and other geohazards
vital for petroleum exploration and mining
fluid flow through rocks
understanding the growth and destruction of mountain belts.
set the boundary conditions for surface processes and sedimentation
what is the difference between the compositional and rheological classification of the earth?
compositional - based on silica content
rheological - based on strength of rock type

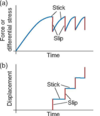
which is permentent elastic or plastic deformation?
plastic deformation is permanent
deformation style depends on?
type of material (or rock)
whether it is being extended or compressed
temperature
pressure
what to these four samples show you?

1) inital, undeformed marble cylinder
2) sample compressed under condition representative of the shallow crust. it has fractured thus brittle deformation
3) sample compressed under condition representative of mid crustal levels. there is evidnce of both bittle and ductile deformation
4) sample compressed under conditions of deep crust. it has deformed and bulged smoothly in a ductile way

what is normal faulting caused by?
normal faulting is caused by tensional forces that stretch a rock and tend to pull it apart.
what causes reverse and thrust faulting?
caused by compressive forces that squeeze and shorten the rock.
what is the difference between reverse and thrust faulting?
reverse = steep dipping fault plane
thrust = shallow dipping fault plane
how do seismic surveys work?
waves are reflected depending on acoustic impedance between layers