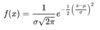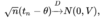Statistic Flashcards
What do we mean by the population of study?
The population is the set of sources from which data has to be collected.
What is a sample?
A Sample is a subset of the Population being studied.
What is a variable?
A Variable is any characteristics, number, or quantity that can be measured or counted. A variable may also be called a data item.
What is a statistical parameter?
Also known as a statistical model, A statistical Parameter or population parameter is a quantity that indexes a family of probability distributions. For example, the mean, median, etc of a population.
What are the two data type ?
Numerical: data expressed with digits; is measurable. It can either be discrete (finite number of values) or continuous (infinite number of values).
Categorical: qualitative data classified into categories. It can be nominal (no order) or ordinal (ordered data).
What is the mean, median and mode?
Mean: the average of a dataset.
Median: the middle of an ordered dataset; less susceptible to outliers.
Mode: the most common value in a dataset; only relevant for discrete data.
What is the range?
Range: the difference between the highest and lowest value in a dataset.
What is the variance, its properties and its formula?
Variance (σ2): measures how spread out a set of data is relative to the mean.
Var(X) = E[(X-E(X))2]
Var(aX+b) = a2Var[X]
Var[X+Y] = Var[X]+Var[Y]+2Cov[X,Y]

What is R squared?
R-Squared: a statistical measure of fit that indicates how much variation of a dependent variable is explained by the independent variable(s); only useful for simple linear regression.

What is the covariance, its properties and its formula?
Covariance: Measures the variance between two (or more) variables. If it’s positive then they tend to move in the same direction, if it’s negative then they tend to move in opposite directions, and if they’re zero, they have no relation to each other.
Cov[X,Y] = E[XY]-E[X]E[Y] (is zero if X and Y are independant)
Cov[X,Y]=E[(X-E(X))(Y-E(Y))]

What is the correlation and its formula?
Correlation: Measures the strength of a relationship between two variables and ranges from -1 to 1; the normalized version of covariance. Generally, a correlation of +/- 0.7 represents a strong relationship between two variables. On the flip side, correlations between -0.3 and 0.3 indicate that there is little to no relationship between variables.

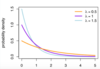
What is a probability density function (pdf)?
Probability Density Function (PDF): a function for continuous data where the value at any point can be interpreted as providing a relative likelihood that the value of the random variable would equal that sample.
What is a probability mass function (pmf)?
Probability Mass Function (PMF): a function for discrete data which gives the probability of a given value occurring.
What is a cumulative density function (CDF)?
Cumulative Density Function (CDF): a function that tells us the probability that a random variable is less than a certain value; the integral of the PDF.
What is the moment of a distribution?
Moments describe different aspects of the nature and shape of a distribution. The first moment is the mean, the second moment is the variance, the third moment is the skewness: and the fourth moment is the kurtosis.
What is the skewness of a distribution ?
Skewness is the third central moment of a distribution. It is the measure of the lopsidedness of the distribution; any symmetric distribution will have a third central moment, if defined, of zero. The normalised third central moment is called the skewness, often γ. A distribution that is skewed to the left (the tail of the distribution is longer on the left) will have a negative skewness. A distribution that is skewed to the right (the tail of the distribution is longer on the right), will have a positive skewness.
What is the kurtosis of a distribution?
Its the fourth central moment. It is a measure of the heaviness of the tail of the distribution, compared to the normal distribution of the same variance. Since it is the expectation of a fourth power, the fourth central moment, where defined, is always nonnegative; and except for a point distribution, it is always strictly positive.
What do we mean by probability?
Probability is the likelihood of an event occurring.
What do we mean by a independant event ?
Independent events are events whose outcome does not influence the probability of the outcome of another event; P(A|B) = P(A).
What do we mean by mutually exclusive event?
Mutually Exclusive events are events that cannot occur simultaneously; P(A|B) = 0.
What do we mean by conditional probability? What its formula?
Conditional Probability [P(A|B)] is the likelihood of an event occurring, based on the occurrence of a previous event.

What is bayes theorem and its formula?
Bayes’ Theorem: a mathematical formula for determining conditional probability. “The probability of A given B is equal to the probability of B given A times the probability of A over the probability of B”.

When talking about hypothesis testing, what do we means by null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, p-value, alpha and beta.
Null Hypothesis: the hypothesis that sample observations result purely from chance.
Alternative Hypothesis: the hypothesis that sample observations are influenced by some non-random cause.
P-value: the probability of obtaining the observed results of a test, assuming that the null hypothesis is correct; a smaller p-value means that there is stronger evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Alpha: the significance level; the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true — also known as Type 1 error.
Beta: type 2 error; failing to reject the null hypothesis that is false.
What are the 4 step of hypothesis testing?
Steps to Hypothesis testing:
- State the null and alternative hypothesis
- Determine the test size; is it a one or two-tailed test?
- Compute the test statistic and the probability value
- Analyze the results and either reject or do not reject the null hypothesis (if the p-value is greater than the alpha, do not reject the null!)