SS - Structures of solid elements Flashcards
Describe isotropic interactions
Ones which are the same in all directions
Describe optimal packing for atoms or molecules with isotropic interactions
Optimal packing results in minimal volume and maximal density.
Laves proposed that symmetry and connectivity (ie coordination number) be maximised
Draw out the first two layers of a structure that optimally packed
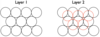
Draw the third layer of a structure that has a HCP structure (hexagonal close packed)
By coding each layer, this structure is ABAB as the third layer maps onto the first.
Importantly, the packing efficiency and coordination number of HCP and CCP structures are identical
This structure has hexagonal symmetry

Draw the third layer of a structure that has a CCP structure (cubic close packed)
By coding each layer, this structure is ABCABC.
Importantly, the packing efficiency and coordination number of HCP and CCP structures are identical
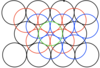
State the coordination number for both HCP and CCP structures
12
Describe the difference between HCP and CCP structures
HCP has a mirror plane, while CCP has an inversion centre
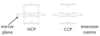
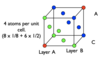
Describe the HCP structure
Describe CCP structure
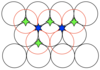
State how many neighbours a tetrahedral hole has
4 (shown in green)
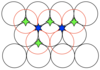
State how many neighbours an octahedral hole has
6 (shown in blue)
State how many tetrahedral and octahedral holes there will be for a structure with N atoms
2N tetrahedral holes and N octahedral holes
State the size of a tetrahedral hole
0.225r where r is the radius of one of the structure’s atoms
State the size of an octahedral hole
0.414r where r is the radius of one of the structure’s atoms.
Give the fractional coordinates of octahedral holes in a CCP structure
(0,0,0.5)
Give the fractional coordinates of tetrahedral holes in a CCP structure
(0.25,0.25,0.25)


