Spot diagnoses/ Signs Flashcards
Name lesion
Seen in?
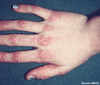
Gottron’s Papules
Seen in dematomyositis. Pathognomic!
Name sign/lesion
Seen in
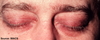
Heliotrope rash
Dermatomyositis
Name lesion/sign
Seen in?

Gottron’s papules
Seen in dermatomyositis. Pathognomic!
Name lesion/sign
Seen in

Shawl sign
Dermatomyositis
Name lesion/sign
Seen in?
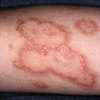
Discoid rash
Discoid eczema, discoid lupus
Name lesion/sign
Seen in?

Malar rash
SLE
Name sign?
Seen in?

Saddle nose deformity
Nasal trauma, congenital syphilis, relapsing polychondritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, cocaine abuse, and leprosy. Most important for exams is granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener’s)
Name sign
Seen in?

Heberden’s and Bouchards nodes
OA
Name sign
Seen in?

Bamboo spine and dagger sign
Ankylosing spondylitis
Name sign
Seen in?

Pencil in cup deformity
Psoriatic arthritis
Name sign
Seen in?

Lupus pernio
Pathognomic for sarcoidosis
Name the sign
Seen in?

Angular stomatitis/cheilitis
Iron deficiency anaemia
Name the sign
Seen in?

Glossitis
B12 deficiency
Name sign
Seen in?
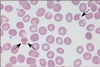
Bite cells
G6PD deficiency
Name sign
Seen in?

Heinz (inclusion) bodies
G6PD deficiency
Name the abnormal cell/sign
Seen in?

Reed-Sternberg
Hodgkins lymphoma
Name the abnormal cell
Seen in?

Hypersegmented neutrophil
Megaloblastic anaemia (B12 deficiency)
Name the abnormal cell type
Seen in?

Tear drop poikilocytes
Myelofibrosis
Name sign
Seen in?

Periorbital purpura
Amyloidosis (AL)
Name the abnormality

Barton Fracture
Name the condition

Kaposi sarcoma
…caused by HHV-8 (human herpes virus 8)
- presents as purple papules or plaques on the skin or mucosa (e.g. gastrointestinal and respiratory tract)
- skin lesions may later ulcerate
- respiratory involvement may cause massive haemoptysis and pleural effusion
- radiotherapy + resection
Name the lesion and the cause

Oral hairy leukoplakia
EBV in immunocompromised individuals (e.g. HIV)
Key finding in this head CT

Extradural haematoma
What is the key finding in this X ray?

Small bowel obstruction
Key finding in this X ray

Surgical emphysema
(note outline of the pectoralis major muscle)
Key finding on the chest X ray

Cervical rib
Name the skin condition
What is the underlying disease?
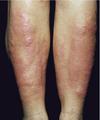
Pretibial Myxoedema
Grave’s disease
Diagnosis?

Sigmoid volvulus.
(Note the coffee bean sign)
Three dense lines converging towards the site of obstruction (Frimann Dahl’s sign) in keeping with sigmoid volvulus.


Guttate Psoriasis
…… is more common in children and adolescents. It may be precipitated by a streptococcal infection 2-4 weeks prior to the lesions appearing
Features: tear drop papules on the trunk and limbs
Prodrome: Classically preceded by a streptococcal sore throat 2-4 weeks. Many patients report recent respiratory tract infections but this is not common in questions
Appearance: ‘Tear drop’, scaly papules on the trunk and limbs. Herald patch followed 1-2 weeks later by multiple erythematous, slightly raised oval lesions with a fine scale confined to the outer aspects of the lesions.
May follow a characteristic distribution with the longitudinal diameters of the oval lesions running parallel to the line of Langer. This may produce a ‘fir-tree’ appearance
Treatment / natural history: Most cases resolve spontaneously within 2-3 months. Topical agents as per psoriasis. UVB phototherapy. Self-limiting, resolves after around 6 weeks
Name the rash
Cause?

Erythema ab igne
Excessive exposure to IR light
Note: if cause not treated patient can go on to develop squamous cell skin cancer


